Origins of the State PP
advertisement

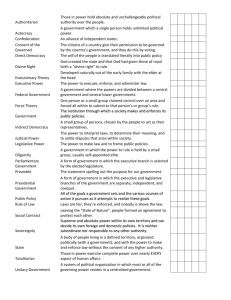
Origins of the State The State a body of people, living in a defined space, with the power to make and enforce laws without having to check with any higher authority, and with an organization to do this. Population Territory a body of people, living in a defined space, Sovereignty Government with the power to make and enforce laws without having to check with any higher authority, and with an organization to do this. That’s us! Population Definition: People who are the members or citizens of a state The size of the population doesn’t matter Population has a big influence on the type of government chosen by the state: • Is the population rural or urban? • What do people do for jobs? • Do people get along or disagree on basic issues? Territory Definition: the area in which a state’s rule applies A state must have set boundaries, but they are not always agreed on. Boundaries can change in three ways: • war – people win or lose territory • negotiation – people agree to trade territory • purchase – states can buy territory from other states Sovereignty Definition: the ability to rule absolutely within a given territory Because of sovereignty… states can set their own foreign policy and agendas. states are all equal in theory, but in reality that isn’t always the case. Government Definition: the organization that makes and enforces the laws Government has many roles that all involve making public policy, but there are four main ways their governing affects the public… • Keeping Order • Protecting the Country • Providing Services • Making Economic Decisions That’s us! Keeping Order Making and enforcing laws is all a part of keeping order in society Structures like the police force and court system are in place to enforce the laws and settle disputes Protecting the Country The government is responsible for defending the territory of the state Security organizations like the Department of Homeland Security and the Department of Defense are established to protect citizens Treaties and alliances are formed with other countries to help keep our citizens safe Providing Services The government is responsible for providing basic services… Programs for people who need help: • help buying food • welfare • medical services Programs to keep people safe: • medicine • food • buildings Making Economic Decisions The government makes decisions every day about how it spends money The government also makes decisions about how our economy is going to function Most public policy set by the government has to do with how money is spent!! 4 Theories that Explain the Origins of the State Force Theory The state was born by force. One person or group claimed control and forced all within that area to submit to that person’s rule The physically stronger person became chief of the tribe and then they fight other tribes Evolutionary Theory The state was developed naturally out of the early family Head of the house is the head of the family As the family developed networks of families became clans which became tribes and then a state was born Religion plays a huge part Divine Right Theory Started with Aztecs, Mayan, Egyptians, China Japan and then very accepted in the 15th -18th centuries by the Europeans God created the state God gave “divine right” to rule: royalty was only accountable to God because he created the state Social Contract Theory Human beings in their unpleasant conditions agreed together to create the state A contract was agreed upon and within that contract the people only gave as much power that was need to keep them safe. This power was given to a government voluntarily from free people The state only exists to sever the will of the people The people are the sole source of political power and that they are free to give or withhold power from the government This theory promotes the ideas of popular sovereignty limited gov’t and individual rights