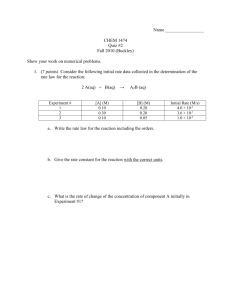
Chem 100
advertisement
Thursday February 7, 2013 (Discussion and WS – Limiting Reactant) Bell Ringer Thursday, 2-7-13 A baker has a recipe for a cake that calls for the following ingredients: •4 cups of flour •2 cups of sugar •1 tsp of baking soda •1 tsp of baking powder •1 cup of milk The baker finds she has the following supplies in her store room: •17 cups of flour •9 cups of sugar •6 tsp of baking soda •5 tsp of baking powder •3 cups of milk 3 Without going to the grocery store, how many cakes can she make? Announcements National Wave All Your Fingers At Your Neighbor's Day! Announcements I will be available after school today until 5:00. Assignment Currently Open Summative or Formative? Date Issued Date Due Date Into GradeSpeed Final Day QUIZ 16 S1 1/18 1/18 1/24 TODAY WS – Mole to Mass Stoichiometry F11 1/30 2/1 TOMORROW WS – Mass to Mole Stoichiometry F12 1/31 2/5 TOMORROW QUIZ 17 S2 2/1 2/1 WS – Mass to Mass Stoichiometry F13 2/4 2/8 TOMORROW Activity - Using Stoichiometry to Prove the Law of Conservation of Mass F14 2/5 2/5 TOMORROW 2/1 2/15 Limiting Reactant •In the laboratory, a reaction is rarely carried out with exactly the required amounts of each of the reactants. •In most cases, one or more reactants is present in excess; that is, there is more than the exact amount required to react. •Once one of the reactants is used up, no more product can be formed. Limiting Reactant • The substance that is completely used up first in a reaction is called the limiting reactant. • The limiting reactant is the reactant that limits the amounts of the other reactants that can combine and the amount of product that can form in a chemical reaction. • The substance that is not used up completely in a reaction is sometimes called the excess reactant. Limiting Reactant • Consider the reaction between carbon and oxygen to form carbon dioxide. C + O2 → CO2 • According to the equation, one mole of carbon reacts with one mole of oxygen to form one mole of carbon dioxide. • Suppose you could mix 5 mol of C with 10 mol of O2 and allow the reaction to take place. Limiting Reactant • • • The figure below shows that there is more oxygen than is needed to react with the carbon. Carbon is the limiting reactant in this situation, and limits the amount of CO2 that is formed. Oxygen is the excess reactant, and 5 mol of O 2 will be left over at the end of the reaction. Limiting Reactant Sample Problem Silicon dioxide (quartz) is usually quite unreactive, but reacts readily with hydrogen fluoride according to the following equation: SiO2 + 4HF → SiF4 + 2H2O If 2.0 mol of HF are exposed to 4.5 mol of SiO 2, which is the limiting reactant? Answer - The given amount of either reactant is used to calculate the required amount of the other reactant. The calculated amount is then compared with the amount actually available, and the limiting reactant can be identified. We will choose to calculate the moles of SiO2 required by the given amount of HF. Limiting Reactant Sample Problem SiO2 + 4HF → SiF4 + 2H2O Under ideal conditions, the 2.0 mol of HF will require 0.50 mol of SiO2 for complete reaction. Because the amount of SiO2 available (4.5 mol) is more than the amount required (0.50 mol), the limiting reactant is HF. Worksheet Limiting Reactant