World War II - Miami Beach Senior High School

Mr. Ermer
U.S. History Honors
Miami Beach Senior High
Congress rejects Treaty of Versailles, League of Nations Pact
Sec. of State Charles Evans Hughes negotiates separate treaties
Contrary to claims of isolationism, U.S. plays active role in global politics throughout 1920s
Washington Naval Conference of 1921
U.S., Britain, France, Italy, Japan agree to limit naval tonnage
Nine-Power Pact to continue Open Door Policy in China
Four-Power Pact b/w U.S., Britain, France, Japan to respect Pacific lands
Kellogg-Briand Pact 0f 1928
A multilateral pact aiming to outlaw war
The Dawes Plan
The United States loans money to Germany so they can pay their reparations to former Allied Powers in return for lower payments
Fordney-McCumber Act of 1922 raises tariffs, hurts Europe
Growing Latin American indebtedness breeds resentment of
“Yankee Imperialism”
Global Great Depression triggers growing nationalism
Many leaders around the world being replaced by angry people
Roosevelt rejects many of Hoover’s foreign policies
Moves to strengthen economic ties with Europe
Reciprocal Trade Agreement Act
Most competitive non-American import goods still limited
Good Neighbor Policy
Increased imports from and exports to Latin America
Rejection of American intervention in Latin America
Inter-American Conference of 1933 held in Montevideo
1930s Americans grow increasingly isolationist
U.S. signs on to World Court, mostly symbolic
Neutrality Act of 1935
Prohibits American intervention in Italy’s invasion of Ethiopia
Followed by the neutrality acts of 1936 & 1937
Americans could travel on foreign ships only at own risk
Warring nations could only buy non-military goods from U.S. in cash and carry them away on own ships—“cash and carry” policy
Fascism: Political system run by a dictator, extremely nationalistic, intolerant, and highly ordered
Anti-Communist, pro-empire
Italy (1922): Benito Mussolini brings Fascism
Becomes “Il Duce” or “Leader” of Italy—Premier
Germany (1933): Hitler elected German Chancellor
Upset about terms of WWI’s Treaty of Versailles
Tries to start revolution in 1923, arrested
Writes book in jail: Mein Kampf (“My Struggles”)
Becomes leader of Nazi party
Blames Jews and other minorities for Germany’s problems
Wants to establish a new German empire (Third Reich)
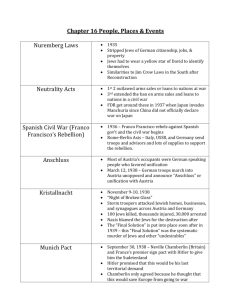
Spanish Civil War
Hitler and Mussolini support Fascist party of Francisco Franco
Britain, France, & U.S. don’t help republican side
Russia renamed Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, or
USSR, in 1922—Communist government
Joseph Stalin becomes Soviet premier in 1924
Five Year Plan to build up economy
Collectivization
Sets eyes on conquest of eastern Europe
Japan needs more natural resources to help economy
Emperor Hirohito’s power=absolute (thought a god)
Prime Minister Tojo is military dictator for emperor
Japan under military control, begins conquering empire
1935: Hitler builds new air force, military draft
European leaders, afraid of another war, want to make deal
Assumed Germany just wanted union and peace
1938: Hitler forces the “peaceful” union of Germany and
Austria (the Anschluss)
The Munich Conference
Hitler wants the Sudentenland, part of Czechoslovakia
France and Britain agree, start appeasement policy
1939: Germany attacks, splits land b/w Czechs & Slovaks
Hitler now wanted city of Danzig from Poland
Britain and France “have Poland’s back”
September 1939, Germany invades Poland
Hitler does not want a two-front war like World War I
Sends ministers to Russia to negotiate deal with Stalin
Stalin sees chance to turn capitalists against each other
August 23, 1939: Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact
After Hitler invades Poland, Britain & France declare war
One month later, Poland falls to the Nazis
British and French wait for Nazis in Belgium
Hitler surrounds Belgium, French surrender
British and French troops escape to England through
Dunkirk, French Gen. Charles de Gaulle flees to Algiers
Hitler orders his Luftwaffe (air force) to bomb London
Americans disillusioned by failure of World War I
Rise of dictators
Non-payment of debts during Great Depression
Nye Committee/Backlash against arms industry
Support of isolationism
Neutrality Act of 1935: illegal to sell arms abroad
Spanish Civil War erupts
Germany, Italy, & Japan form “Axis Powers”
Neutrality Act of 1937: All nonmilitary goods bought by warring nations on a “cash & carry” basis
FDR supports internationalism
Supplies China with weapons against Japan
Neutrality Act of 1939: weapons sales OK, cash & carry
FDR lends British old navy ships in exchange for British bases
Lend-Lease Act: lend the British arms to fight war
1941: Nazi’s invade USSR, break non-aggression pact
FDR est. Hemispheric Defense Zone
USA protects ships in “neutral” western Atlantic
August 1941: The Atlantic Charter
Agreement for after the war to pursue democratic world, free trade, economic advancement, freedom of the seas
FDR’s “shoot on sight” order for German U-boats
FDR restricts sale of strategic materials to Japan
Lend-lease to China
Japan, in need of resources, attacks British and Dutch colonies in eastern, southern Pacific
Japan attacks U.S. Philippines
December 7, 1941: Japan surprise attacks the American
Pacific naval fleet at Pearl Harbor
The United States declares war on Japan
Germany and Italy declare war on U.S.A.