Part 3 DNA Replication
advertisement

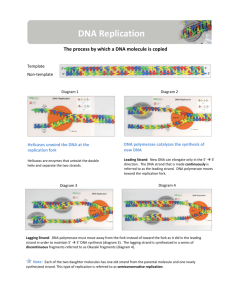
Part 3 DNA Replication 24-1 Learning Targets 5. Understand base pairing and its role in replication, transcription and translation. 6. Understand that replication is semi-conservative and occurs on a lagging and leading strand. 7. Know the role of enzymes in replication including helicase, primase, DNA polymerase and ligase. 24-2 DNA Replication • Found only in the nucleus • Origin of replication • Multiple origins on a chromosome • Occurs during S phase of the cell cycle • Semiconservative each new DNA strand has 1 new/1 old strand 24-3 DNA Replication Enzymes • DNA helicase unzips DNA unwinds it • At “replication fork” • “unzipped” bases form H bonds with “free” nucleotides • Primase assembles RNA Primer • “seats” DNA Polymerase • DNA polymerase bonds sugar to phosphate makes new strand of DNA • (DNA Ligase (see Okazaki Fragments)) 24-4 Accuracy • DNA Polymerase also “proofreads” • Very accurate (only 1 error every billion nucleotides!) • 20 repair enzymes “edit” goofs mutagens (heat, chemicals, radiation, etc.) • EXACT SEQUENCE is VERY IMPORTANT 24-5 Okazaki fragments • DNA is “anti-parallel” • Sugar/phosphate groups “point” in diff. direction • 5’3’ “leading strand” • 3’5’ “lagging strand” • DNA Polymerase only assembles new strand in 5’3’ direction • Leading strand is OK • Lagging strand forms in segments Okazaki fragments • DNA Ligase ties sugar/phosphates together 24-6