Chemistry: Periodic Table
advertisement

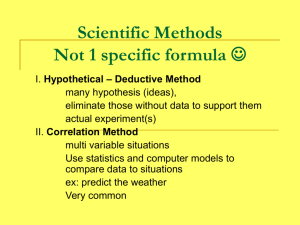
Scientific Method and Experimental Design 7th Grade Science What is the Scientific Method? • It is a simple method scientists (and non-scientists) use to conduct an investigation • It is a way to ask & answer scientific questions by asking questions & conducting experiments • You use it each day when you make simple choices Inductive vs Deductive Reasoning • When using the scientific method to explain data or develop theories, scientists can use inductive or deductive reasoning – Inductive reasoning: uses evidence and observations to make conclusions – Deductive reasoning: uses beliefs and what you know to make conclusions (may try to find a way to make their prior knowledge align with what they were seeing) Steps of Scientific Method • Question/Problem – Does (or will) _____ affect ______? • Must relate to an observation • Usually a “what”, “why”, or “how” – Must be measureable – Can lead to several types of investigations Steps of Scientific Method • Hypothesis – Statement that proposes (predicts) an answer to the question based on observation and data/research – Focus on one variable only (independent) – Rules for writing hypothesis • If _______ changes, then _______ changes. • Must be testable, measurable, and repeatable Steps of Scientific Method • Experiment – Testing your hypothesis (independent variable) – Investigating to see if your independent variable has an affect on the dependent variable • Collect data – Must have numerous re-tests or trials (at least 10) to support your results – Measurements must be recorded with units – Data can be qualitative (description based) or quantitative (numbers based) Steps of Scientific Method • Conclusion – Summary of your experiment that re-states the hypothesis and explains why hypothesis is supported or not supported – Use data from experiment to draw conclusion – Addresses possible errors – Explains why experiment is important Experimental Components • Variables – Independent • What is tested • Manipulated or changed in the experiment – Dependent • What is measured • Changes due to the IV’s manipulation (change) – Does the (IV) affect the (DV)? Experimental Components • Constants – All other variables that must remain the same – Ensures that you are only testing the independent variable • Control Group – Group that has nothing done to it (group without the IV) – May not always have a control group non-defined, true comparison Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) • 6th, 7th, and 8th – 7.1.A.a (DOK 2), 7.1.A.b (DOK 2), 7.1.A.e (DOK 2)