Cost Management Slides
advertisement

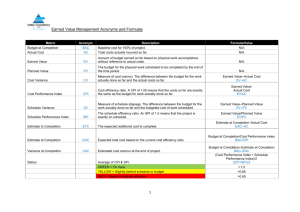
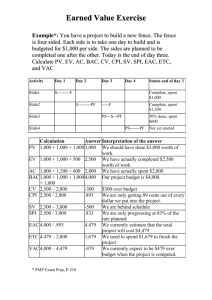
Project Cost Management Sections of this presentation were adapted from A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge 4th Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., © 2009 Project Cost Management “The processes involved in planning, estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs so that the budget can be completed within the approved budget” Why Do We Manage Cost? Part of triple constraint, can’t manage one without the others (scope, time, and quality) Plots of cost and scope against plan can help spot problems early Today Actual Costs (AC) Planned Value (PV) Cumulative Value Earned Value (EV) Time Is this project over/under budget? Is it ahead of/behind schedule? Cost Management Key Terms PV - Planned Value, estimated value of the planned work EV – Earned Value, estimated value of work done AC – Actual Cost, what you paid BAC – Budget at Completion, the budget for the total job EAC –Estimate at Completion, what is the total job expected to cost? ETC – Estimate to Complete, forecasted costs to complete job VAC – Variance at Completion, how much over/under budget do we expect to be? How Do We Manage Cost? Three processes Estimate Costs Determine Budget Control Costs Estimate Costs Determine Budget Control Costs Estimate Costs Enterprise Environmental Factors Inputs Tools & Techniques Outputs Analogous estimating Determine resource cost rates Organizational Process Assets Activity Cost Estimates Bottom up estimating Project Scope Statement Parametric estimating Activity Cost Estimates Supporting Detail Project management software Work Breakdown Structure Requested Changes Vendor bid analysis WBS Dictionary Reserve analysis Cost Management Plan Updates Cost of quality Project Management Plan •Schedule Mgmt Pln •Staffing Mgmt Pln •Risk Register Estimate Costs Determine Budget Control Costs Estimating Methods Analogous (Top Down) estimating – Managers use expert judgment or similar project costs [quick, less accurate] Bottom-Up estimating – People doing work estimate based on WBS, rolled up into project estimate [slow, most accurate] Parametric estimating – Use mathematical model (i.e. cost per sq ft). [accuracy varies] Two types: Regression analysis – based on analysis of multiple data points Learning Curve – The first unit costs more than the 100th, forecasts efficiency gains Estimating Methods Vendor Bid Analysis – Estimating using bids + allowances for gaps in bid scope [slow, accuracy depends on gaps] Reserve Analysis – Adding contingency to each activity cost estimates as zero duration item [slow, overstates cost] Determine Budget Tools & Techniques Project Scope Statement Cost aggregation Work Breakdown Structure Reserve analysis Cost Baseline Parametric estimating WBS Dictionary Activity Cost Estimates Outputs Inputs Project Funding Requirements Funding limit reconciliation Activity Cost Estimates Supporting Detail Cost Management Plan Updates Project Schedule Requested Changes Resource Calendars Contract Cost Management Plan Estimate Costs Determine Budget Control Costs Determine Budget Budgeting is allocating costs to work packages to establish a cost baseline to measure project performance Remember Contingency items are for unplanned but required changes it is not to cover things such as: Price escalation Scope & Quality Changes Funding Limit Reconciliation – Smoothing out the project spend to meet management expectations Control Costs Inputs Tools & Techniques Cost Baseline Cost change control system Project Funding Requirements Performance measurement analysis Outputs Cost Baseline Updates Performance Measurements Forecasting Performance Reports Project performance reviews Forecasted Completion Project management software Work Performance Information Requested Changes Variance management Approved Change Requests Cost Estimate Updates Recommended Corrective Actions Organizational Process Assets Updates Project Management Plan Project Management Plan Updates Estimate Costs Determine Budget Control Costs Earned Value Progress is compared against the baseline to determine whether project is ahead of or behind plan Percent complete can be difficult to measure, some managers use rules 50/50 Rule – Assumed 50% complete when task started, final 50% at completion 20/80 Rule – 20% at start 0/100 Rule – No credit until complete Planned Value (PV) – Budgeted Cost Earned Value (EV) – Actual work completed Actual Cost (AC) – Costs incurred Estimate to Complete (ETC) – What’s Left Estimate at Completion (EAC) – What final cost will be Earned Value Graph Variance at Completion (VAC) Target Cost & Schedule Planned Value (PV) Schedule Variance (Time) Earned Value (EV) Earned Value Formulas NAME FORMULA NOTES Cost Variance (CV) EV-AC Negative = Over budget Positive = Under budget Schedule Variance (SV) EV-PV Negative = Behind Schedule Positive = Ahead of Schedule Cost Performance Index (CPI) EV/AC How much are we getting for every dollar we spend? Schedule Perform Index (SPI) EV/PV Progress as % against plan Estimate to Complete (ETC) EAC-AC How much more do we have to spend? Variance at Completion (VAC) BAC-EAC At the end of the day, how close will we be to plan? Estimate at Completion (EAC) See following slide Earned Value Formulas (Cont’d) NAME Estimate at Completion (EAC) FORMULA NOTES BAC/CPI Use if no variances from BAC have occurred AC+ATC Use when original estimate was bad. Actuals + New estimate AC+BAC-EV Use when current variances are not expected to be there in the future AC+(BAC-EV)/CPI Use when current variances are expected to continue Tricks for Earned Value EV is always first Variance = EV minus something Index = EV divided by something If the formula relates to cost use AC If the formula relates to schedule use PV Interpreting results: negative is bad and positive is good Interpreting results: greater than one is good, less than one is bad Project Start PV AC Current Status BAC ETC EAC Terms to Remember Present Value Net Present Value (NPV) Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Payback Period Benefit Cost Ratio = BCR>1, Payback is greater than the cost Opportunity Cost Sunk Cost Working Capital Straight Line Depreciation Accelerated Depreciation Double Declining Balance Sum of Years Digits Value Analysis (Value Engineering) You won’t be calculating most of these numbers on the test, just remember the concepts for general questions