Brain Presentation
advertisement

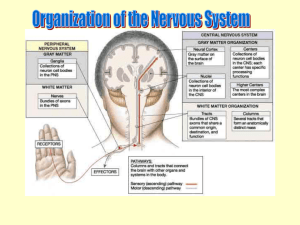
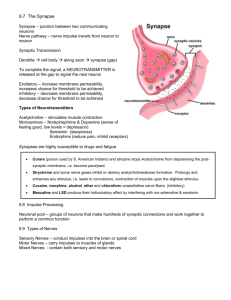
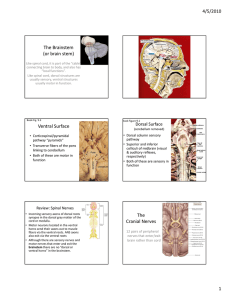
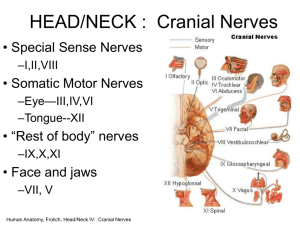
Brain Presentation Jiseung Kang, Isa Lopez, Crystal Carrillo Functions of the Brain ● ● ● ● ● ● Thinking or Cognition Perception or sensing Emotion or feeling Behaviour Physical or Somatic Signaling Development of the brain ● ● ● ● First developed after 3 weeks of conception. Fore, Mid and Hind brain for at one end of neural tube at 5 weeks Cerebrum begins to form at 13 weeks Cerebellum appears Division of the brain ● Three parts of the brain Forebrain o Midbrain o Hindbrain o Forebrain ● Also known as prosencephalon ● Nerves o Olfactory (Sensory) Smell o Optic nerve (Sensory) Vision Midbrain ● ● ● Also known as mesencephalon Midbrain connects forebrain and hindbrain Nerves o Oculomotor (Primarily motor) - Eye movement upward, downward and inward o Trochlear (Primarily motor) Movement of eyes Hindbrain ● ● ● Also known as rhomnencephalon It contains medulla oblongata, pons, cerebellum Nerves o Vestibulocochlear (Sensory) - Hearing and Equilibrium o Abducens (Primarily motor) - Eye movement o Accessory (Primarily motor) - Head movement o Hypoglossal (Primarily motor) - Tongue o Trigeminal (Mixed) - Somatosensory information from face to head o Facial (Mixed) - Taste, Face expression o Glossopharyngeal (Mixed) - Taste, Swallowing o Vagus (Mixed) - Speech, Swallowing Cerebrum ● Function- In charge of thinking and action ○ Largest part of human brain ○ Interprets Impulses ○ Initiates voluntary muscle movements ○ Stores info as memory ○ Retrieves info for reasoning Four Lobes of Cerebrum ● ● ● ● Frontal Lobe: reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, & problem solving Parietal Lobe: movement, orientation, recognition, & perception of stimuli Occipital Lobe: visual processing Temporal Lobe: perception & recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, & speech Cerebellum ● Little brain- regulation and coordination of movement, posture and balance ● Cerebral Ventricles ○ Two lateral ventricles: ■ Location- Extend anteriorly and posteriorly in cerebral hemispheres ■ Function: Protects brain from trauma ● Contains CSF Cerebral Ventricles Cont. ● ● Third Ventricle o Location- Midline of brain underneath corpus callosum o Connected to fourth ventricle via cerebral aqueduct Fourth Ventricle o Location- In brainstem just in front of cerebellum o Continuous with central canal of spinal cord o Choroid plexus o CNS o CSF Brainstem ● Brainstem: located underneath the limbic system, responsible for vital life functions like breathing, heartbeats, & blood pressure. “Simplest” part of human brain made of three part ○ Midbrain: rostral part of brain stem that includes the tectum and tegmentum. Functions include; vision, hearing, eye movement, and body movement. ○ Pons: part of the metencephalon in the hindbrain, involved in motor control and sensory analysis ○ Medulla Oblongata: biggest part of Brainstem, between pons and spinal cord in charge of breathing and heart rate Limbic System ● Limbic System “emotional brain”: buried within the cerebrum. Consists of; o Thalamus: sensory and motor functions o Hypothalamus: homeostasis, emotion, thirst, hunger, circadian rhythms, & control of autonomic nervous system and controls the pituitary. o Amygdala: memory, emotion, & fear o Hippocampus: Learning and memory, converts short term memory into permanent memory and recalling relationships. Layers of the meninges ● ● ● ● Function : Protect Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerve roots Dura Mater - composed of tough, white dense connective tissue ○ the outermost layer ○ Attached to inner surface of skull ○ Subdural hematomas Arachnoid Mater - Webbing of fibers and collage, ○ The middle layer ○ subarachnoid space ○ Lack of blood vessels ○ Cerebrospinal fluid Pia Mater ○ Innermost layer ○ Attached to surface of brain and spinal cord by astrocytes ○ Supplies blood to the brain ○ Production of cerebrospinal fluid Reflex ● ● Definition: involuntary and relatively stereotyped response to a specific sensory stimulus. Spinal reflexes are the sensory stimuli arise from receptors in muscles, joints and skin, and in which the neural circuitry responsible for the motor response is entirely contained within the spinal cord. Reflex ● ● ● Brain stem reflexes: such as gagging and vestibulo-ocular reflex knee jerk reflex: stretch reflex. Spinal reflex: the stretch reflex, simplest reflex known Works cited "12 Cranial Nerves." 12 Cranial Nerves RSS. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Apr. 2015. "Behavioral Problems of TBI." Behavioral Problems of TBI. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Apr. 2015. "Brain Function (by Lobes)." Brain Function (by Lobes). N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Apr. 2015. "Functions of the Brain." Functions of the Brain. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Apr. 2015. "Meninges and Nerves." Spinal Meninges Anatomy, Diagram & Function. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Apr. 2015. "Overview of the Cranial Nerves." - Cranial Nerve Disorders. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Apr. 2015. "Overview of the Cranial Nerves." - Cranial Nerve Disorders. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Apr. 2015.