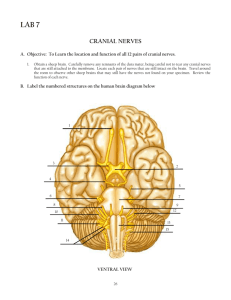
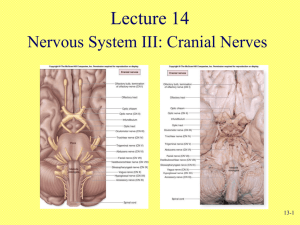
Cranial nerves
advertisement
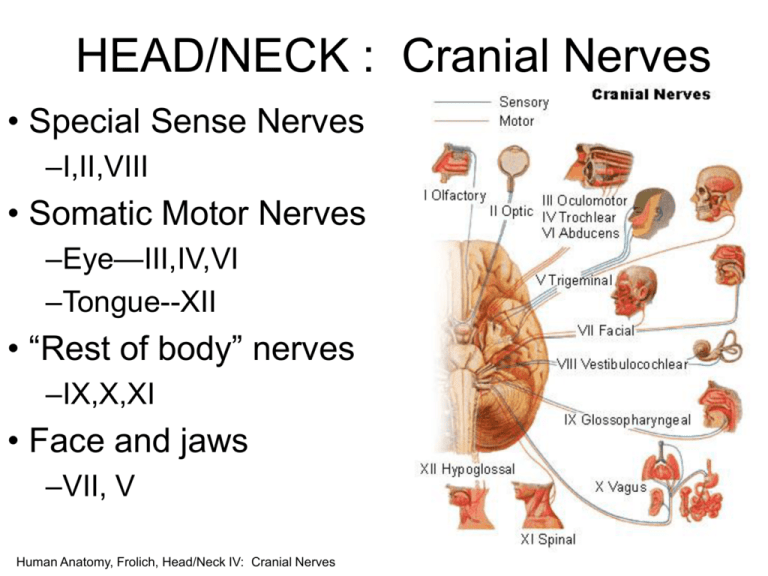
HEAD/NECK : Cranial Nerves • Special Sense Nerves –I,II,VIII • Somatic Motor Nerves –Eye—III,IV,VI –Tongue--XII • “Rest of body” nerves –IX,X,XI • Face and jaws –VII, V Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Nerve “targets” in head • SENSORY • MOTOR Special Smell Vision Hearing Muscles Glands eyes salivary extrinsic sweat intrinsic lacrimal jaws mucous facial expression larynx tongue throat ear General skin teeth eye tongue oral cavity nasal cavity middle ear throat meninges Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Base of the skull—cranial nerves out Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves • Ethmoid (olfactory) I. Olfactory • Sphenoid (optic) II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear VI. Abducens • Temporal (otic) VII. Acoustic/Auditory/ Vestibulocochlear • Face/Jaws V. Trigeminal VII. Facial • Throat (rest of body) IX Glossopharyngeal X. Vagus XI. Spinal Accessory XII. Hypoglosal Special Sense Nerves NERVE TARGET EXIT FROM CRANIAL CAVITY I. Olfactory Olfactory epithelium Cribiform plate (ethmoid) II. Optic Retina Optic canal (sphenoid) VIII. Auditory Inner ear Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Internal auditory meatus (temporal) Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Somatic Motor Nerves (eye muscles and tongue) NERVE TARGET IV. Trochlear Superior oblique m. (with trochlea) VI. Abducens Lateral rectus III. Oculomotor •Sup.,med.,inf.rectus (Also parasympathetic • Inferior Oblique to ciliary mm, constrictor •Levator palpebrae pupillae) superioris XII. Hypoglossal Intrinsic, extrinsic mm. of tongue Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves EXIT CR. CAVITY Sup. Orbital fissure (sphenoid) “ “ Hypoglossal canal (occipital) Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves “Rest of body” nerves (all exit from jugular foramen) NERVE TARGET Somatic motor to larynx/pharynx Parasympathetic to most of gut Taste to back posterior pharynx XI: (Spinal) Motor to traps, Accesory sternocleidomastoid IX: Glosso- Sensory to carotid body/sinus pharyngeal Taste to posterior tongue Sensory to ear opening/middle ear Parotid salivary gland X: Vagus Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerves • Twelve pairs: – 2 attach to forebrain (Telen- & Diencephalon) – 10 attach to brainstem (Mes-, Met- and Myelencephalon) • Names relate to appearance or function • Classification ? Olfactory Nerve (= CN or N I) 1º function? Origin? Destination? _____________(By way of cribiform plate of ethmoid) Only CN directly attached to Cerebrum Visual System • Eye • Accessory structures – Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes, tear glands – Protect eyes from sunlight and damaging particles • Optic nerve (II) – Tracts – Pathways • Eyes respond to light and initiate afferent action potentials Optic Nerve (N II) 1º fu? ori? dest? - by way of optic foramen of sphenoid to Diencephalon (optic chiasma) and to occipital lobe Oculomotor (N III) C: Motor O: Mesencephalon D: Somatic motor to superior, inferior, medial recti and inferior oblique; visceral motor to intrinsic eye muscles by way of superior orbital fissure Trochlear (N IV) C: Motor O: Mesencephalon D: superior oblique by way of superior orbital fissure Trigeminal (N V) C: Mixed three major branches 1. ophthalmic (sensory) 2. Maxillary (sensory) 3. Mandibular (mixed) O: face / nuclei of pons D: sensory nuclei in pons / muscles of mastication V: Trigeminal (3 nerves in 1!) • V1. Ophthalmic – Exits with eye muscle group (superior orbital fissure, through orbit to superior orbital notch/foramina) – Sensory to forehead, nasal cavity • V2. Maxillary – Exits foramen rotundum through wall of maxillary sinus to inferior orbital foramina) – Sensory to cheek, upper lip, teeth, nasal cavity • V3. Mandibular – – – – Exits foramen ovale to mandibular foramen to mental foramen Motor to jaw muscles--Masseter, temporalis, pterygoids, digastric Sensory to chin Sensory to tongue Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Abducens (CN VI) C: Motor O: Pons D: Runs lateral rectus eye muscle VII: Facial Nerve (exits cranial cavity with VIII--internal auditory meatus) • Facial muscles (five branches fan out over face from stylomastoid foramen) – – – – – Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Mandibular Cervical • “chorda tympani” (crosses interior ear drum to join V3 ) – Taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue – Submandibular, sublingual salivary glands • Lacrimal glands Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Facial (N VII) C: Mixed O: sensory from taste receptors of anterior 2/3 of tongue / motor from pons D: Sensory to sensory nuclei of pons / motor muscles of facial expression, visceral motor to tear gland. Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Vestibulocochlear (N VIII) C O ? D Glossopharyngeal (CN IX) C: mixed O: sensory from posterior 1/3 of tongue / motor from medulla oblongata D: medulla / muscles for swallowing, parotid gland Vagus (N X) C: Mixed O: Sensation from pharyngeal area and outer ear / motor from medulla D: Sensory to medulla / visceral motor to thoracic and abdominal cavities and their organs. Major motor pathway for ANS Accessory (N XI) and C: Motor O: Motor nuclei of medulla and spinal cord D: Swallowing, trapezius & scm muscles Hypoglossal (N XII) C: Motor O: Motor nuclei of medulla D: Tongue musculature Mnemonic Out On Our Table Top Are Fruits, Very Green Vegetables And Hamburgers Extrinsic Eye Muscles Anatomy of the Eye • Three coats or tunics – Fibrous: Consists of sclera and cornea – Vascular: Consists of choroid, ciliary body, iris – Nervous: Consists of retina Anatomy of the Eye • Fibrous tunic: Outer – Sclera: White outer layer, maintains shape, protects internal structures, provides muscle attachment point, continuous with cornea – Cornea: Avascular, transparent, allows light to enter eye and bends and refracts light • Vascular tunic: Middle – Iris: Controls light entering pupil; smooth muscle – Ciliary muscles: Control lens shape; smooth muscle • Retina: Inner – Contains neurons sensitive to light – Macula lutea or fovea centralis: Area of greatest visual acuity – Optic disc: Blind spot • Compartments – Anterior: Aqueous humor – Posterior: Vitreous humor – helps maintain ocular pressure – keeps eye inflated – largely responsible for shape of eye • Lens – Held by suspensory ligaments attached to ciliary muscles Functions of the Complete Eye • Eye functions like a camera • Iris allows light into eye • Lens, cornea, humors focus light onto retina • Light striking retina is converted into action potentials relayed to brain The Retina • Provides black backdrop for increasing visual acuity • Sensory retina and pigmented retina • Photoreceptors – Rods: Noncolor vision • Rhodopsin reduction: Light adaptation • Rhodopsin production: Dark adaptation – Cones: Color vision Sensory Receptor Cells Rods and Cones • Photoreceptors are depolarized in the dark, continuously releasing neurotransmitter. • When hyperpolarized by light-->decrease amount of neurotransmitter. • Rods- activated below starlight. Scotopic vision, no color, poor acuity. • Cones- activated with brighter light. Photopic vision. Color vision. Rods and Cones • Most of what we think of as seeing is mediated by cones. • Individual loses cone vision, legally blind. • Individual loses rod vision, experience difficulties at low levels of illumination (night blindness). • Cones are only receptors in fovea. Other visual pathways • Ganglion cells--> pretectum. Between thalamus and midbrain. Coordinates the pupillary reflex. • Suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus. Involved in day/night cycle and biological rhythms. • Superior colliculus in midbrain. Coordinates head and eye movements.