ecology3_2 and 3_3
advertisement

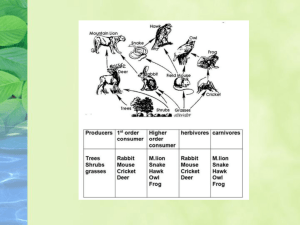
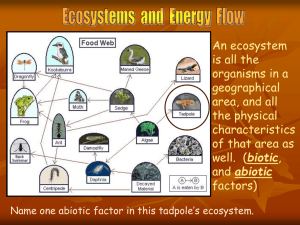
All living systems require energy No energy = no life PRIMARY PRODUCERS are AUTOTROPHS that make their own food from either SOLAR energy (most of them) or from CHEMICAL energy This energy is meant for themselves but other organisms eat their energy stores PHOTOSYNTHESIS – is the most common form of harnessing energy for living things Plants on the land Algae in the water Cyanobacteria – photosynthetic bacteria are also important How do you get energy deep in the ocean where the sun can’t shine? CHEMOSYNTHESIS HETEROTROPHS –get their energy from eating other organisms – they are called CONSUMERS Consumers are categorized by what and how they eat Carnivores Herbivores Omnivores Scavengers Detritivores Decomposers Carnivores – kill and eat other animals Lion, otter Herbivores – eat plants: leaves, seeds or fruits Macaw, zebra Omnivores – eat plants and animals Pigs, humans These organisms eat dead organisms and waste products – recycling the nutrients Scavengers – animals that consume carcasses Decomposers – bacteria and fungi break down organic matter into detritus (dead and decaying animal and plant remains) vultures mushrooms Detritivores – feed on detritus particles Earthworms, crabs Energy FLOWS through the community in a oneway direction by feeding ABCD etc. All begin with primary producer primary consumer secondary consumer tertiary consumer quaternary consumer etc. Feeding relationships are usually much more complicated and interconnected – forming FOOD WEBS Food Web site Extremely important in food webs Decomposers break down organic matter – dead or decaying plant and animal matter into DETRITUS that is eaten by detritivores Nutrients are released – these can be used by plants and other primary producers They are the biosphere’s recyclers! Without them dead stuff would just pile up So thank your cockroaches today Begins with algae or PHYTOPLANKTON These are eaten by krill or ZOOPLANKTON What happens if sea ice melt causes less krill?? Each step in a food web or chain is called a TROPHIC LEVEL Primary producers make up FIRST trophic level ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS are diagrams that illustrate the ecosystems’ relative amount of energy, mass or numbers At each trophic level Only 10% of energy goes on to the next level (10% rule) 90% is released as HEAT. Mass of living matter at each trophic level Grams per unit of area Example: g/m2 Numbers of organisms in each trophic level Not always a pyramid shape!! One tree can support hundreds of catepillars