Chapter 20 - missdannocksyear11biologyclass
advertisement

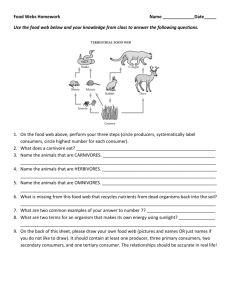
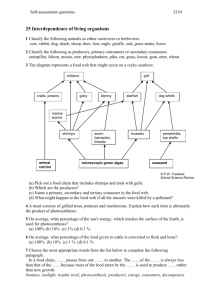
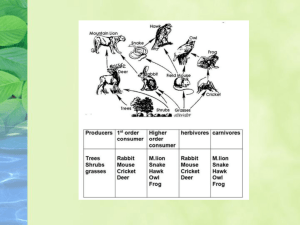
Chapter 20 Food Chains are the sequence of who eats who in an ecosystem is called a food chain. Living organisms need a constant supply of energy to maintain cellular activities and stay alive. In ecosystems the initial source of energy is light from the sun. This is used by plants during photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates. Organisms (i.e. plants) that can manufacture their own food from inorganic materials are called autotrophs. The initial source of energy in an ecosystem is light from the sun. Some of the light absorbed by plants is converted through photosynthesis into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates such as glucose. Photosynthesis is summarised as: light carbon dioxide + water REACTANTS glucose + oxygen ENERGY SOURCE PRODUCTS Some of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is broken down during the process of respiration. Respiration can be summarised as follows: Glucose + oxygen water + carbon + energy dioxide The energy produced during respiration is then used for cellular processes. Herbivores are consumers that graze directly on the producers. Herbivores include: • • • • • • • • Elephants Giraffes Pandas Koalas Deer Rhinoceros Zebras Horses Carnivores are consumers that eat other consumers (prey). Carnivores that catch live prey are called predators. The carnivore that directly feed on herbivores are known as first order carnivores. The carnivore that is the last link of the chain is known as the top carnivore. Carnivores include: • • • • • Lions Tigers Eagles Birds Snakes Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and other animals. Many omnivores will eat the eggs of other animals. Some omnivores are scavengers which means they eat dead animals. Most will eat plants that produce fruit and vegetables. They also eat the fruit and vegetables. Omnivores include: • Pigs • Grizzly bears • humans Parasites are specialised consumers that live and feed on the surface of, or inside other organisms causing them harm. Parasites include: • Tape worm • Flat worm • Nematodes Scavengers are consumers that eat dead animals . Scavengers include: • Tasmanian devil • Vultures • Hyenas Detritivores eat small particles of dead plant and animal organic matter that accumulates as detritus. They also eat waste products such as dung. Detritivores include: • Crustaceans • Worms • Snails Decomposers are consumers that breakdown dead material. Decomposers work differently to detritivores as they secrete enzymes over the dead material and then absorb the broken down products as food. Decomposers include: • Decomposing bacteria • Fungi The interrelationship between many food chains is called a food web. Producers Animals are consumers. An organism that feeds on plants is a first-order consumer. An organism that feeds on a first-order consumer is called a second-order consumer, and so on. The level occupied by a consumer in a food chain is referred to as a feeding or TROPHIC level. First-order consumers occupy the first trophic level; second-order consumers occupy the second trophic level, and so on. Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers Tertiary Consumers Competition is a relationship in which two organisms compete for a limited resource. In the short term this results in a decrease in the abundance of one of the species. In the long term it can result in extinction of the less successful species. Mutualism is a relationship between two organisms where both of them benefit. Mutualism and fungi: A Lichen consists of a fungus and an alga joined together. The fungi provides structure and the alga provides food Mutualism and animals: Rabbits and horses rely on organisms in their gut because no vertebrate can break down cellulose. Bacteria have enzymes which can break down cellulose to substances which they can use. Commensalism is where one organism benefits but the other neither benefits nor comes to any harm. An example of this are Remoras which are the fish found swimming at the sides of a shark. In this location the fish are getting a free ride and access to food scraps form the sharks meal. This is a relationship between two organisms where one benefits at the expense of the other organism Example: the pimple wasp. It lays its eggs on the leaves of the mangrove. The larvae eat through the leave when they hatch and the leaf is damaged Pollination is the transfer of pollen from one flower to another. Successful reproduction in many flowering plants is reliant on them attracting insects, birds or small mammals (all known as pollinators) that will transport pollen from one flower to another.