10 NTASC Standards
advertisement

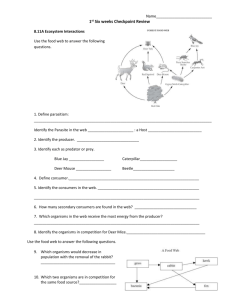
10 NTASC Standards 1. Learner Development - The teacher understands how learners grow and develop, recognizing that patterns of learning and development vary individually within and across the cognitive, linguistic, social, emotional, and physical areas, and designs and implements developmentally appropriate and challenging learning experiences. Using a pre-assessment before the start of a new unit is a great way to assess student’s prior knowledge on the material. This allows a teacher the opportunity to develop and design the unit based on the knowledge students already have. The teacher is able to design appropriate and challenging learning experiences for the students. This specific preassessment was used for the unit on Ecology. After looking over student’s scores and seeing where students excel or struggle, the teacher is able to design the unit around the needs of the students. This assures that the students are able to grow and develop properly with each new unit. Biosphere Pre-Assessment Name Match each vocabulary word with the correct definition on the right. Write the letter corresponding with the definition on the blank line. 1. Biosphere among organisms in an ecosystem A. Network of complex interactions formed by feeding relationships _____ 2. Ecology B. nonliving part of the environment, such as sunlight, heat, precipitation, humidity, wind or water currents _____ 3. Ecosystem C. Any living part of the environment in which an organism might interact _____ 4. Biome D. series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten _____ 5. Biotic Factor E. consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists _____ 6. Abiotic Factor their physical environment F. study of interactions among organisms and between _____ 7. Food Chain G. a group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms _____ 8. Food Web H. All the organisms that live in a place, together with their physical environment Multiple Choice Select the correct answer based on the choices given. Write the letter on the blank line. Use the diagram below to answer question 9. organisms and _____ 9. What is happening to water at D in Figure 3–2? a. Water is falling to the ground as precipitation. b. Water is evaporating from the ocean. c. Water is being taken up by plants through transpiration. d. Water is seeping into the ground to become groundwater. _____ 10. Carbon cycles through the biosphere in all of the following processes EXCEPT a. photosynthesis. b. transpiration. c. burning of fossil fuels. d. decomposition of plants and animals. _____ 11. Which of the following descriptions about the organization of an ecosystem is correct? a. Communities make up species, which make up populations. b. Populations make up species, which make up communities. c. Species make up communities, which make up populations. d. Species make up populations, which make up communities. _____ 12. What animals eat both producers and consumers? a. herbivores c. chemotrophs b. omnivores d. autotrophs _____ 13. Animals that get energy by eating the carcasses of other animals that have been killed by predators or have died of natural causes are called a. scavengers. c. heterotrophs. b. omnivores. d. detritivores. Modified True/False: Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the underlined word or phrase to make the statement true. Write the corrected word or phrase on the line underneath the statement. _____ 14. Producers release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere during the process of photosynthesis. _____ 15. Seawater, sand on a beach, pebbles in the sand, and broken seashells are all examples of abiotic factors at a seashore. 16. Organisms that break down organic matter and return it to the environment are called decomposers. 17. Organisms within an ecosystem are biotic factors in that ecosystem. Open Ended Questions: Answer the following questions based on the food web provided. 18. What organism is in the highest trophic level? 19. What organism is an omnivore? 20. List an autotroph in the food web 2. Learner Differences - The teacher uses understanding of individual differences and diverse cultures and communities to ensure inclusive learning environments that enable each learner to meet high standards. The following assessments are different versions of the SGO testing used to assess students on the material covered during the year. The results of the testing are part of the assessment of teachers in the Danielson evaluation. The first assessment was designed for the Standard/General level Biology classes, while the second assessment was designed for the College Prep level biology classes. The assessments are given at the beginning of the school year and then again towards the end of the school year to assess student’s progress. As you may see, the assessments were designed based on the differences between the two levels. The general biology assessment is less difficult then the college prep biology. The teachers of each of these levels use the understanding of the differences between the classes to ensure each class meets the standards set for each assessment. Instruction and methods used in the classroom have been based on the differences between the levels to make sure students meet their needs. General Biology Post-Assessment Name:__________________________ Multiple Choice: Pick the correct choice 1. A possible explanation for a set of observations is a. Data b. Hypothesis c. Theory d. Inference 2. The genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents is a. DNA b. Stimulus c. Nucleus d. Protein 3. The part of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and air/atmosphere is a. Science b. Chemical Reaction c. Biosphere d. DNA 4. Which is a substance formed by the chemical joining of 2 or more elements in definite amounts? a. Compound b. Nucleus c. Isotope d. Enzyme 5. What type of ion forms when an atom loses electrons? a. Neutral b. Negative c. Positive d. Radioactive 6. Identify the reactant(s) shown here: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 a. CO2 + H2O and H2CO3 c. H2O b. H2CO3 d. CO2 + H2O 7. Which of the following is the strongest acid? a. 4.2 b. 1.3 c. 9.2 d. 6.5 8. What part(s) of an atom are contained within the nucleus? a. Protons and Neutrons b. Protons and Electrons c. Electrons d. Neutrons 9. How are multicellular living things organized from smallest to largest? a. Cell, organ, organism, organ system, tissue c. organism, organs system, organ, tissue, cell b. Organ, organ system, cell, tissue, organism d. cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism 10. Which of the following defines a cell as eukaryotic? a. Does NOT have a nucleus b. Bacteria 11. Which summarizes the process of diffusion? c. Virus d. HAS a nucleus a. Requires energy b. Moves low to low c. Moves low to low d. Moves high to low c. Cleans the cell d. Does photosynthesis c. Lysosome d. Endoplasmic Reticulum 12. A nucleus does which of the following? a. Modifies Proteins b. Holds DNA 13. Which organelle does photosynthesis? a. Chloroplast b. Cytoskeleton 14. Which of the following is NOT a unit of the metric system? a. Gram b. Meter c. Pound d. Liter c. 1 d. 0.1 15. 10 m is equal to how many cm? a.100 b. 1,000 16. What is the term for the step of the water cycle that recycles water from the ocean to the clouds? a. Transpiration b. precipitation c. ground water d. evaporation 17. Which is a process by which a parent reproduces by itself? a. Sexual reproduction b. Photosynthesis c. Asexual reproduction d. Meiosis 18. An advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that sexual reproduction a. Takes less time b. Provides genetic diversity c. Requires more time d. Produces identical individuals 19. Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost the ability to control their a. Size b. Lysosomes c. Spindle Fibers d. Growth and Division 20. Which of the following would be considered homozygous recessive? a. rr b. R c. RR d. Rr 21. Genetics is the study of a. how traits are passed to offspring b. Cell Parts c. Chromosomes d. Organelles 22. A human sex cell should have _____________ chromosomes a.46 b. 43 c. 23 d. 24 23. Which is the following is an example of a phenotype? a. white fur b. heterozygous c. Bb d. BB 24. Could a child be born with a recessive trait if one parent is a pure dominant for that trait? a. Yes, 50% chance b. Yes, 100% chance c. No d. Yes, 75% chance 25. In penguins long wings (W) are dominant to short wings (w). A penguin that is Ww would have ______ wings. a. Long b. Medium c. Short d. Irregular 26. A breed of chickens shows incomplete dominance for feather color. 1 allele codes for black feathers and 1 for white feathers. As an incomplete dominant trait, the feathers of a heterozygous chicken would be _________. a. White b. Gray c. Black d. Black and White 27. What happens when a piece of DNA is missing? a. Genetic information is stored c. Genetic information is lost b. Genetic information is copied d. Genetic information is transmitted 28. During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a complementary strand with which of the following bases? a. TCGAAC b. AGCTTG c. GATCCA d. GAUCCA 29. The structure of DNA is known as a. Single Strand b. Double helix c. Ring d. Square 30. In a pedigree, a shaded square means which of the following a. affected male b. affected female c. unaffected male d. unaffected female 31. If a male is affected more than a female, what type of inheritance pattern would this trait follow? a. dominant b. recessive c. sex linked d. multiple allele 32. What are the correct sex chromosomes of a normal male? a. XXY b. XY c. XX d. XO 33. The giant tortoises of the Galapagos had different shells and necks due to this reason a. Mobility b. temperature c. location of food d. space 34. The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its specific environment a. Diversity b.Traits c. Fitness d. evolution 35. Based on the names Papio annubis and Papio cynocephalus, these two organisms belong to the same a. Kingdom b. Family c. Genus d. species 36. Oxygen + Glucose Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy What is required to start the aerobic cellular respiration above? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Methane d. water 37. Which of the following scientific names is written correctly for humans? a. Homo sapiens b. homo sapiens c. Homo Sapiens d. homo Sapiens 38. The use of DNA fingerprinting to identify individuals relies on the fact that a. Almost all genes are different from one person to the next b. No two people, except identical twins, have exactly the same DNA c. All genes used in identification are dominant d. Using DNA is not a reliable way to identify people 39. One reason farmers often use genetically modified (GM) crops over non-GM crops because GM crops are a. Much safer b. make more food c. less controversial d. cheap 40. Which kingdom is ONLY multicellular? a. Animalia b. eubacteria c. archaebacteria d. protista 41. Which of the following resources limits the diversity, density, and carrying capacity of living things on Earth? a. Water b. Space c. Carbon d. all of the above 42. The species of finches that Charles Darwin found on different Galapagos Islands varied in certain adapations. The most significant was a. Size of their eggs b. shape of their beaks c. color of their feathers d. location of their nests 43. Which of the following is a biotic factor? a. Dirt b. Mountain c. bridge d. dog Use the following equations to answer numbers 44 and 45 Photosynthesis: CO2 + H2O + light C6H12O6 + O2 Cellular Respiration: C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP (energy) 44. What does photosynthesis used light energy to do? a. Make carbon dioxide b. Make Water c. Make Light d. Make glucose 45. What does cellular respiration break down to produce energy for the body? a. Carbon dioxide b. glucose c. light d. water 46. How many animals have 4 limbs? a.1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 47. How many animals do not have a boney skeleton? a. 1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 48. Which organism is a producer? a. Plant b. grasshopper c. frog d. bird c. grasshopper d. bird c. frog d. bird 49. Which part of the food chain is a carnivore? a. Sun b. plant 50. Which part of the food chain is an herbivore? a. Plant b. grasshopper College Prep Biology Post-Assessment 1. Which statement is true about macrocmolecules? a. Simple sugars are made of polysaccharides b. Glycerol is made of fatty acids. c. Proteins are made of amino acids. d. Nucleotides are made of nucleic acids. 2. What stores information in a cell? a. Proteins b. Carbohydrates c. Lipids d. DNA 3. What is the purpose of homeostasis? a. Create new cells. b. Maintain relatively constant internal physical conditions. c. Pass on genetic information to offspring. d. Return a disturbed environment to the original climax community. 4. If an action in your body produces a chemical that enhances that action, it is called ______. a. Cellular respiration b. Negative feedback c. Accentuation d. Positive feedback 5. Which of the following would be an example of a negative feedback system? a. Body temperature regulation b. Blood type c. Sex determination 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. d. No reaction to a stimulus Which list represents the levels of organization in a multicellular organism from the simplest level to the most complex level? a. Cell tissue organ system organ b. Organ system organ tissue cell c. Tissue organ organ system cell d. Cell tissue organ organ system During early development, all cells in the embryo of a multicellular organism are identical. Later on in development, the cells will become specialized through a process called _________. a. Apoptosis b. Cytokinesis c. Cancerization d. Differentiation Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into_____. a. Oxygen and carbon. b. Sugar and proteins. c. ATP and oxygen. d. Oxygen and sugar. Which of the following correctly describes the process of cellular respiration? a. Oxygen + glucose carbon dioxide + water + heat b. Oxygen + glucose + sunlight carbon dioxide + water c. Carbon dioxide + water oxygen + glucose + heat d. Carbon dioxide + water + sunlight oxygen and glucose How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related? a. Photosynthesis breaks down food and cellular respiration creates food. b. Photosynthesis is positive and cellular respiration is negative. c. Photosynthesis makes food from sunlight energy and cellular respiration breaks the food to release energy. d. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are not related. Which of the following is an effect of mitosis? a. The cell’s volume increases. b. It becomes more difficult for the cell to get rid of wastes. c. The organism grows. d. It becomes more difficult for the cell to get enough oxygen and nutrients. During a normal mitosis cell division, a parent cell that has 4 chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing __________. a. 1 chromosome b. 2 chromosomes c. 4 chromosomes d. 8 chromosomes Meiosis can be a cause of genetic variation because _______. a. Fertilization occurs b. Cytokinesis occurs c. Commensalism occurs d. Crossing over occurs Which is the correct sequence of the transfer of information in most organisms? 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. a. Protein DNA RNA b. RNA DNA Protein c. DNA RNA Protein d. RNA Protein DNA Approximately how many DNA molecules are found in a single chromosome? a. 1 b. 100 c. 1,000 d. 1,000,000 Which statement is true of DNA within a species? a. All individuals in a species have the same DNA with different genes expressed b. It is common for individuals to have different numbers of chromosomes c. All genes on DNA are exactly the same between all individuals d. The environment does not have any effect on which genes are expressed Which of the following is a function of DNA? a. Code for protein b. Regulate functions in the cell c. Unknown functions d. All of the above e. None of the above Similar DNA sequences in genes between different species can be evidence of ______. a. Binomial nomenclature b. Mutations c. Different breeding habits d. Common ancestry What do all organisms have in common? a. They all use DNA to pass on genetic information. b. They are all prokaryotes c. They are all eukaryotes d. They are all genetically identical Which statement about the members of a population that live long enough to reproduce is consistent with the theory of evolution by natural selection? a. They transmit characteristics acquired by use and disuse to their offspring. b. They tend to produce fewer offspring than others in the population. c. They are the ones that are best adapted to survive in their environment & pass on their traits to their offspring. d. They will possess unfavorable characteristics. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, the individuals that tend to survive are those that have _____. a. Characteristics their parents acquired by use and disuse. b. Characteristics that plant and animal breeders value. c. The shortest sleep time. d. Genetic variations best suited to the environmental conditions What is the basic concept behind natural selection? a. Mutations do not affect evolution. b. Variations that occur are conscious decisions made during a lifetime. c. Mutations in DNA can increase the chance of survival and can be passed on to offspring . 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. d. Variations in phenotype can only decrease the chance of survival. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, individuals who survive are the ones best adapted for their environment. Their survival is due to the ______. a. Possession of adaptations developed through use. b. Possession of inherited adaptations that maximize fitness. c. Lack of competition within the species. d. Choices made by plant and animal breeders. Mistakes can occur during DNA replication, which can cause ________. a. An increase in genetic variation b. A decrease in genetic variation c. The environment to change d. The cellular respiration rate to increase Which of the following environmental factors could cause mutations in DNA, thereby increasing genetic diversity? a. X-Rays b. Tobacco Smoke c. Ultraviolet light d. All of the above e. None of the above If a mutagen alters the DNA of an organism, which statement would be accurate about the probability of that trait being expressed in that population? a. The probability of survival with or without the trait would be the same. b. If the mutated DNA offered no advantage, the organism would be likely to survive and reproduce. c. Mutagens can cause beneficial mutations in DNA that could allow the likelihood of survival to increase. d. Mutations that increase the survival rate of a species cause extinction. If a forest turns from light to dark, what is likely to happen to the moth population that depend on camouflage for protection from predatory birds? a. The light moths would increase compared to the dark moths. b. The dark moths would increase compared to the light moths. c. The proportion of both populations would remain unchanged. d. Both populations are likely to go extinct. Matter can recycle through the biosphere because ______. a. Matter does not change into new compounds. b. Matter is the same as energy. c. Biological systems do not eliminate matter, they change/transform it. d. Biological systems use only carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. How does energy enter an ecosystem? a. Animals absorb sunlight through their skin. b. Animals carry out cellular respiration. c. Plants consume other organisms. d. Plants absorb sunlight for photosynthesis. Carbon is an essential element for all living things. Carbon enters the ecosystem via ______ and is recycled through _______. a. Fixation; Meiosis b. Photosynthesis; Cellular respiration c. Mitosis; Cytokinesis 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. d. Osmosis; Facilitated Diffusion What causes changes in the biodiversity of an ecosystem? a. Speciation b. Extinction c. Both A & B d. Neither A nor B Which human activity could cause a change in the biodiversity of an ecosystem? a. Habitat destruction b. Pollution c. Climate change d. All of the above e. None of the above Why might some solutions not work when solving problems involved with preserving biodiversity? a. The solution costs too much b. It is unsafe to interfere. c. People disagree with interfering because of their social or cultural differences. d. All of the above. Which of the following could be an effect of bio hazardous materials being dumped into a river? a. Mutations caused by the chemicals could cause new species formation b. An advantageous mutation could cause an increase in number of one species c. A harmful mutation could cause a decrease number of one species d. Any of the above are possible e. None of the above are possible What would happen if a species cannot adjust to new environmental conditions? a. Evolution will not occur. b. Evolution will definitely occur. c. Natural selection. d. The environment will change back. Which of the following human activities adversely affects biodiversity? a. Overpopulation b. Climate change c. Introduction of invasive species d. All of the above e. None of the above After a wildfire sweeps through the Pinelands, what is likely the result of that disturbance? a. Primary succession creates a completely new ecosystem. b. Secondary succession creates an ecosystem similar to one that was there previously. c. Tertiary succession moves the ecosystem to a different location. d. No succession will occur because ecosystems are not resilient. What causes a population to reach its carrying capacity? a. Abundant food b. Variety of mating partners c. Lack of predators d. Limiting resources Only 10% of the energy stored in an organism can be passed onto the next trophic level. Of the remaining energy, some is used for the organism’s life processes, and the rest is ______. a. Used in reproduction b. Stored as tRNA c. Stored as carbon dioxide d. Released as heat 40. What happens as an effect of the loss of energy through the trophic levels? a. Less organisms exist at the higher trophic levels because there is less energy available b. Less organisms exist at the lower trophic levels because energy comes from the sun c. More organisms can exist in the higher trophic levels because they need less energy d. Energy does not determine the number of organisms per trophic level 3. Learning Environments - The teacher works with others to create environments that support individual and collaborative learning, and that encourage positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and selfmotivation. The following is a lab assignment that is used during the unit on plants. The lab lasts for three weeks as students plant their seeds and then observe the growth of their plants over that time. Students work in groups as they monitor and take care of their plants. The experiment is designed to encourage interaction among the groups and students as they take care of their plant. It also is a great way to have students actively engage in learning as they track the growth of their plant. It also allows them to sharpen their observations skills and learn to work on labs skills as well. Name________________________________ Pre-lab Questions 1) What materials do plants need to survive? 2) Label the Plant drawing: leaf, terminal bud, node, inter node, lateral root, stem, and branch 3) What is photosynthesis and why is it important for plants? 4) W rite the equation for photosynthesis and label what each abbreviation means Background information: Beans are warm season crops grown for their immature pods (snap beans), immature seeds (shell beans), or mature seeds (dry beans). Beans are easy to grow and provide excellent nutritional value. Beans grow best in full sun and well-drained, fertile, and friable (crumbly) soil so seedling emergence is not inhibited. Rotate crops by alternating the location of bean plantings with a different crop each year. Kidney, navy, soldier, and pinto beans are used as dry seeds and are harvested when the pod and seed are completely mature and dry. They often require a long growing season and a dry fall for good quality and so may not be the best-adapted for Indiana gardens. Procedure: Day 1- Get a petridish, and label it with a piece of tape with your groups name on it Get two kidney beans Get a paper towel, cut it to fit in the Petri dish, and moisten it (not soaking wet!) Observations: What do the beans look like? ( place these in the chart) Day 2 Make observations: measure roots and sketch a drawing ( in chart) Get a pot and soil from your teacher Put the bean plant in the pot with soil. Make sure the bean plants roots are covered Day 3-5 Make observations and measure growth with a ruler. Put data in the chart below Observations Day 1 Day2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Amount of water given Growth(mm) Pictures Post Lab Questions: 1) What emerges from the seed first, the roots, the leaves, or the stem? 2) Each leave has to perform a different function. Can you identify the primary functions of each leaf surface and the adaptations that are present and support each function? 3) What parts of the plants contain chloroplasts? What parts do not? 4) Compare your data with the other groups in the class. Graph your data and at least two other groups’ data on a sheet of graph paper. Did the amount of water have any effect on the growth? Group # Amount of Water Given Growth D2 Growth D3 Growth D4 Growth D5 4. Content Knowledge - The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and creates learning experiences that make these aspects of the discipline accessible and meaningful for learners to assure mastery of the content. This assignment was part of the chapter on Evolution and it served as reinforcement to the material covered during the unit. The activity was designed to actively engage students in the material and provide students with a way to assure mastery of the content. Students are able to see how specific adaptations allow for organisms to accomplish some tasks easier. The activity is a learning experience that makes the material much more meaningful for the learners. Name ____________________________ Period _____ Date ______________ Chapter 16: Adaptation Activity Thumbs Up, Thumbs Down Grasping the Idea of Evolution Introduction Living things have bodies that are adapted for the places they live and the things that they do. Fish have gills so they can remove oxygen from water. Birds hollow bones that allow them to be lighter for flight. Humans, too, are adapted to their environment and the things they do. Only apes and primates have hands capable of grasping objects. The grasp is made possible by the opposable thumb, so called because it moves opposite to the rest of the fingers. In humans, the thumb can move farther across the hand than in any other primate. In this experiment you will compare your performance of a series of tasks using your thumb and fingers together with your performance of the same tasks without the aid of your thumb. Procedure: Perform each task in the chart below and time how long it takes with your thumb free Try to perform all of the tasks with the equipment that is available Have a partner help tape your thumb to the palm of your hand – careful! Do not tape too tight! Perform the same tasks as before with the taped hand and record your time. If an activity takes longer than 5 minutes, then record the word “unsuccessful” for that task. 5. Complete the analysis and questions that follow. Task Thumbs Free Time Thumbs Taped Time Time Difference Write your name and address on a piece of paper Open and close a bottle 1. 2. 3. 4. Open a book to page 55 Draw a picture of a house and surrounding landscape Pick up 10 coins from a table and place them in a cup Tie a shoe Open and close a zip-lock bag Analysis 1. Was there a large time difference in any of these tasks? Explain which tasks were the most difficult and why. 2. Explain why dog and cats paws are not adapted to doing the tasks you tested 3. What are dog and cat paws adapted for? 4. Describe how your hand is adapted for doing the tasks you performed 5. You have an opposable thumb. Explain what that means. 6. Explain how this adaptation (opposable thumb), along with larger brain capacity, gives humans some unique communication abilities. 7. What are some other unique adaptations humans have? Write your address here Regular thumb Draw Picture of house here (regular thumb) Taped Thumb Draw Picture of house here (taped thumb) 5. Application of Content - The teacher understands how to connect concepts and use differing perspectives to engage learners in critical thinking, creativity, and collaborative problem solving related to authentic local and global issues. This activity was used as reinforcement to the material presented on carrying capacity and patterns on population growth and change. Students are able to look at how populations change and the effects it can have. This is something that is especially important for students to learn because it is a major deal today with how the human population continues to increase and it may be reaching the carrying capacity for earth. This is a local and global issue and something students need to be aware of. The assignment also allows students to work on their analysis and graphing skills. Name:_____________________________________ The Lesson of the Kaibab Introduction: The environment may be altered by forces within the biotic community, as well as by relationships between organisms and the physical environment. The carrying capacity of an ecosystem is the maximum number of organisms that an area can support on a sustained basis. The density of a population may produce such profound changes in the environment that the environment becomes unsuitable for the survival of that species. For instance, overgrazing of land may make the land unable to support the grazing of animals that lived there. Objectives: Graph data on the Kaibab deer population of Arizona from 1905 to 1939 Determine factors responsible for the changing populations Determine the carrying capacity of the Kaibab Plateau Background Before 1905, the deer on the Kaibab Plateau were estimated to number about 4000. The average carrying capacity of the range was then estimated to be about 30,000 deer. On November 28th, 1906, President Theodore Roosevelt created the Grand Canyon National Game Preserve to protect the "finest deer herd in America." DATA TABLE Unfortunately, by this time the Kaibab forest area had already been overgrazed by sheep, cattle, and horses. Most of the tall grasses had been eliminated. The first step to protect the deer was to ban all hunting. In addition, in 1907, The Forest Service tried to exterminate the predators of the deer. Between 1907 and 1939, 816 mountain lions, 20 wolves, 7388 coyotes and more than 500 bobcats were killed. Signs that the deer population was out of control began to appear as early as 1920 - the range was beginning to deteriorate rapidly. The Forest Service reduced the number of livestock grazing permits. By 1923, the deer were reported to be on the verge of starvation and the range conditions were described as "deplorable." The Kaibab Deer Investigating Committee recommended that all livestock not owned by local residents be removed immediately from the range and that the number of deer be cut in half as quickly as possible. Hunting was reopened, Year Deer Population 1905 4,000 1910 9,000 1915 25,000 1920 65,000 1924 100,000 1925 60,000 1926 40,000 1927 37,000 1928 35,000 1929 30,000 1930 25,000 1931 20,000 1935 18,000 1939 10,000 and during the fall of 1924, 675 deer were killed by hunters. However, these deer represented only onetenth the number of deer that had been born that spring. Over the next two winters, it is estimated that 60,000 deer starved to death. Today, the Arizona Game Commission carefully manages the Kaibab area with regulations geared to specific local needs. Hunting permits are issued to keep the deer in balance with their range. Predators are protected to help keep herds in balance with food supplies. Tragic winter losses can be checked by keeping the number of deer near the carrying capacity of the range. DATA 1. Graph the deer population data. Place time on the X axis and "number of deer" on the Y axis Analysis 1. During 1906 and 1907, what two methods did the Forest Service use to protect the Kaibab deer? 2. Were these methods successful? Use the data from your graph to support your answer. 3. Why do you suppose the population of deer declined in 1925, although the elimination of predators occurred? 4. Why do you think the deer population size in 1900 was 4,000 when it is estimated that the plateau has a carrying capacity of 30,000? 5. Based on these lessons, suggest what YOU would have done in the following years to manage deer herds. 1915: 1926: 6. It is a criticism of many population ecologists that the pattern of population increase and subsequent crash of the deer population would have occurred even if the bounty had not been placed on the predators. Do you agree or disagree with this statement. Explain your reasoning. 7. What future management plans would you suggest for the Kaibab deer herd? 6. Assessment - The teacher understands and uses multiple methods of assessment to engage learners in their own growth, to monitor learner progress, and to guide the teacher’s and learner’s decision making. The following is the test that was given to the students in the General level class to assess them on the Ecology chapter. The test was made up to give students a change in how they are usually assessed. Instead of regular multiple choice or true/ false questions, the assessment was designed to have students answer questions based on different images and diagrams. It was used as a change of pace for the students and they performed very well on the assessment. Name: ___________________________ Picture 1 – use the picture to identify the biotic and abiotic factors Biotic Factors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Abiotic Factors 1. 2. 3. 4. Picture 2 1. Which level of organization includes many individuals of 1 type of animal? 2. Which level includes large pieces of the world? 3. What is the smallest level of organization that includes several types of animals? 4. What is the largest level of organization? Picture 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Who is the herbivore in the food chain? Who is the top consumer in the food chain? Who is the producer in the food chain? Not including the sun, how many steps in the food chain are there? Name a carnivore in the food chain. Picture 4 1. List a food chain with 5 steps from within the web. 2. 3. 4. 5. Label the row that consists of autotrophs. Label each consumer as an herbivore or carnivore. Who has the ability to eat the most different living things from the food web. Name a type of consumer missing from the food web. Picture 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What level of the pyramid contains the herbivores? What level of the pyramid has the fewest organisms? What level of the pyramid must have the most organisms? What level of the pyramid contains the autotrophs? What would happen if the trees no longer existed in this ecosystem? Picture (s) 6 Label each picture as the type of consumer it is. (Carnivore, Herbivore, Scavenger, Omnivore, or Decomposer) A. B. C. D. E. F. H. Picture 7. G. I. J. 1. What produces fossil fuels in the carbon cycle? 2. Name 3 things that release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. 3. Who can use the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere Picture 8 – label each # on the diagram with the correct term from the water cycle. Choices: Precipitation, Transpiration, Evaporation, Ground Water, Condensation, and Run Off. Picture 9 1. 2. 3. 4. List 2 things that add phosphorus to the soil. Who uses phosphate? Where is inorganic phosphorus available? What happens to excess phosphorus in the soil? 7. Planning for Instruction - The teacher plans instruction that supports every student in meeting rigorous learning goals by drawing upon knowledge of content areas, curriculum, cross-disciplinary skills, and pedagogy, as well as knowledge of learners and the community context. The following is an example of the planning that was used for the chapter on plants. It breaks down what is covered in each section and states the essential questions that students should be able to answer by the end of the chapter. It also states the objective for each section and lists the activities that go along with each. Using this planning allows teachers to be able to design instruction around what needs to be accomplished. Using goals allows the teacher to make sure each student meets the objectives set forth at the beginning of the unit. Chapter # 22 Chapter Title Introduction to Plants Essential Question What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? Lab #1 Planting various types of plants Lab #2 Section # 22.1 Section Title What is a Plant? Guiding Question What are characteristics of plants? Objective - Describe what plants need to survive - Describe how the first plants evolved - Explain the process of alternation of generations Activity - dichotomous key 22.2 Seedless Plants What are the characteristics of seedless plants? - Identify the characteristics of green algae - Describe the adaptations of bryophytes - Explain the importance of vascular tissue 22.3 22.4 Seed Plants Flowering Plants What are the characteristics of seed plants? What are the characteristics of flowering plants? - Describe the reproductive adaptations of seed plants - Identify the reproductive structures of gymnosperms - Identify the reproductive structures of angiosperms - Identify some of the ways angiosperms can be categorized - 20-Plant diversity: Ferns and their relationship to other plants - 25-Plant Diversity - dissect -6-2-How can Conifers be identified? - dissect - 27-Flowers and Fruit 8. Instructional Strategies - The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage learners to develop deep understanding of content areas and their connections, and to build skills to apply knowledge in meaningful ways. The following is a project that was given to complete during the third marking period. Students were given three options to complete that would demonstrate their knowledge of various topics. Giving students different options allows them to choose the task that would give them the best opportunity to do well. Having students complete the project gives them a better connection to the material and has them apply their knowledge in meaningful ways. 3rd Marking Period Project CP Biology Choose one of the following: 1. Know your Ancestors (DIORAMA) For this assignment you may choose ANY extinct creature and tell us about the animal and why it died out. Explain what conditions it was adapted to, what niche it occupied, predator/prey, etc. Using what you know about adaptations to explain why it died out. You must also show evolution at work. Research what animals are closely related to this extinct animal. Make a DIORAMA (3-D scene) showing the creature in its environment, and what creatures (extinct or alive) are descended from this animal. Must be at least shoe box sized (adult shoe)… 2. Children’s Book For this assignment you will write a children’s book about a baby animal finding his/her niche. It should be full of pictures and should tell the tale about how a baby animal of your choosing is born, develops with its mother and siblings (if applicable) and then goes off to survive on its own. This story may be in 1st or 3rd person. You must color it and the writing (if not typed) MUST be neat and organized. The storyline should be clear and there should be NO GRAMMATICAL ERRORS. You should include these ideas: Niche, adaptations, characteristics of that particular species, predator prey relationships, accurate traits and habits of the organism, scientific name of the organism, etc.) The storyline needs to flow smoothly, so it should be long enough to develop your character, details the trials of its life and a strong conclusion. BE NEAT!!! BE CREATIVE!!! 3. Sell a Biome For this assignment you need to advertise and sell a biome. You can choose a biome of your choice and sell it to your audience (class). You need to let us see the biome, tell us the main flora and fauna located there, where it is located, biotic and abiotic factors, and any other information you think important. You may put it on a poster, make a video, slide show…I give you creative freedom. You will be presenting these projects to the class for a grade. Be proud of your work. Make sure everything is neat, NOT on lined paper, not crumpled or folded and is pleasing to the eye. If you have any other ideas for a project, check with me for approval before beginning. DUE DATE: ________________________ 9. Professional Learning and Ethical Practice - The teacher engages in ongoing professional learning and uses evidence to continually evaluate his/her practice, particularly the effects of his/her choices and actions on others (learners, families, other professionals, and the community), and adapts practice to meet the needs of each learner. 10. Leadership and Collaboration - The teacher seeks appropriate leadership roles and opportunities to take responsibility for student learning, to collaborate with learners, families, colleagues, other school professionals, and community members to ensure learner growth, and to advance the profession. The following form is what is used during the PLC meetings with teachers. Once a week, we would sit down with the other college prep teachers and go over various things such as activities and assignments used during chapter, test scores, and planning. The purpose of the meetings is to make sure all of the teachers are on the same page so no one falls behind. As we go through the meeting, one teacher would fill out the form to make sure we knew what was covered in the meeting. This also allowed the science supervisor to track the progress of the classes and make sure the appropriate materials and topics are being covered. PLC MEETING REPORT SCIENCE DEPARTMENT Rodney Velardi – B230 Ext. 1638 PLC GROUP NAME_______________________________________________________________ DATE & TIME OF MEETING________________________________________________________ Sign-in Print Name 1)___________________________________________________________________________________ 2)___________________________________________________________________________________ 3)___________________________________________________________________________________ 4)___________________________________________________________________________________ 5)___________________________________________________________________________________ 6)___________________________________________________________________________________ 7)___________________________________________________________________________________ 8)___________________________________________________________________________________ 9)___________________________________________________________________________________ 10)__________________________________________________________________________________ Purpose/Goal of meeting: _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ What was accomplished? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Future Meeting Topics/Agenda: _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________