ch23 and 24 notes abbrev
BIOLOGY NOTES
CHAPTER 23 and 24 INVERTEBRATES
MRS. TERHUNE
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS:
1.
2.
1.
What are the characteristics of Animals?
2.
What are the characteristics of the phyla within the Animal Kingdom?
Characteristics of Animals:
3.
4.
Life Cycle of an Animal
Sperm (n) + Egg (n)----->Zygote (2n) ----->Blastula-----> Gastrula-----> Larva -----> Adult
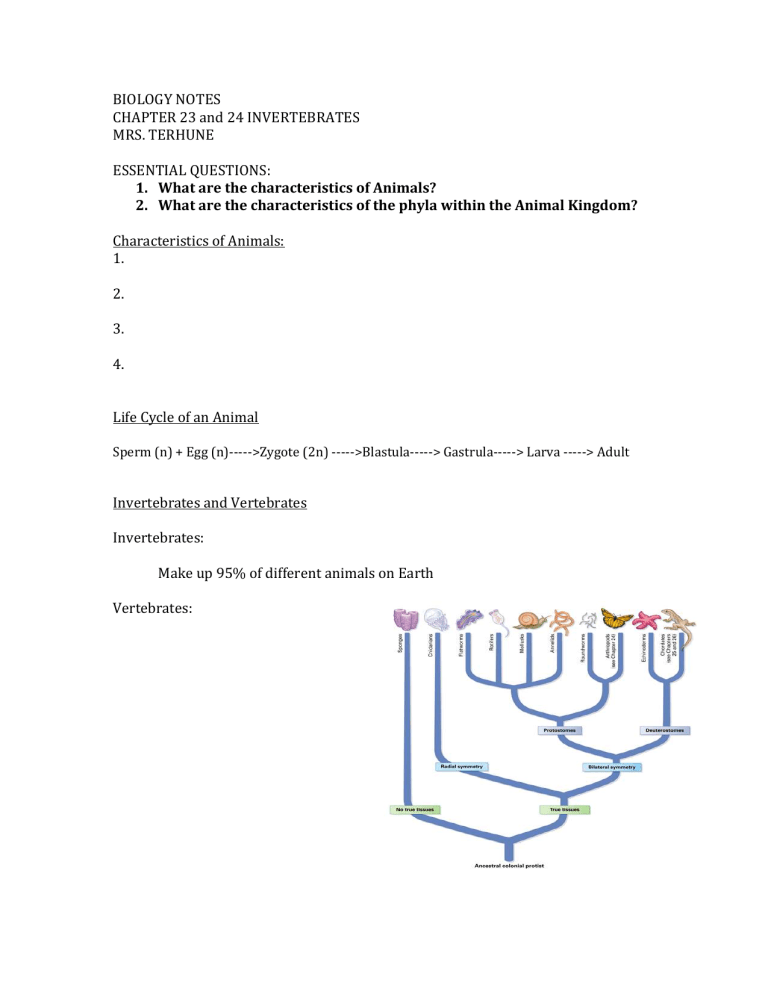
Invertebrates and Vertebrates
Invertebrates:
Make up 95% of different animals on Earth
Vertebrates:
SPONGES (PHYLUM PORIFERA) (23.2)
Characteristics
Structure (Body plan):
Outer layer:
Inner layer:
Ingestion:
Collar Cells:
Ameobocytes:
Reproduction:
Budding(asexual):
Regeneration(asexual):
Sexual:
Movement:
Sessile:
Evolution:
Evolved early from_______________________
PHYLUM CNIDARIA (Hydra, Jellies, Sea anenomies, Coral) (23.3)
2 Characteristics ALL Cniderians Share:
1.
2.
Stinging Cells
Cnidocytes:
Nematocyst:
Body Form
Polyp:
Medusa:
Nutrition:
Tentacles:
*Some have medusa and poly stage, some only have polyp
Gastrovascular Cavity
Classes of Cnidarians
Examples
Hydrozoa Scyphozoa Anthazoa
PHYLUM
PLATYHELMINTHES(Flatworm s) aka Planarians (23.4)
Body Plan:
Bilateral Symmetry:
3 Tissue Layers:
1.
Ectoderm:
2.
Mesoderm:
3.
Endoderm:
Acoelmate:
Digestion:
Gastrovascular Cavity:
Major Characteristics:
Movement:
Eyespots:
Nervous System:
Classes of Platyhelminthes
See pictures in class
PHYLUM NEMATODA (ROUNDWORMS) (23.5)
Body Plan
Have ____________________ symmetry and 3 tissue layers like flatworms
Different from flatworms and Cniderians because:
Complete Digestive Tract:
Pseudocoelm:
Diversity
- Most are _____________________________.
- Some are ________________________ and live in the tissues of plants and animals.
Ex:
Phylum Annelida (Annelids) aka Segmented Worms (23.6)
Annelid means “little rings”
Body Plan
Have bilateral symmetry and 3 tissue layers
Closed Circulatory System:
Coelom
Earthworm Anatomy
Pharynx:
Crop:
Gizzard:
Clitellum:
Setaea
Example:
Phylum Mollusca (Molluscs) (23.7)
Examples:
Body Plan
Foot:
Mantle:
Mantle Cavity:
Radula:
Coelom:
3 cavities:
1.
2.
3.
Open-Circulatory System:
Class of Mollusks
Gastropoda
Description:
Bivalvia Cephalopoda
Phylum Echinodermata (Echinoderms) (23.8)
Examples:
Body Plan
Symmetry:
Water Vascular System:
Tube Feet:
Feeding
Reproduction
Regeneration
Sexual
Classes of Echinoderms
- See pictures on powerpoints
Animal Diversity
EVOLUTION
How did animals evolve to live on land?
CAMBRIAN EXPLOSION
What happened during the Cambrian period?
Arthropods (Chapter 24)
Body Plan
Head:
Thorax:
Abdomen:
Jointed Appendages:
Exoskeleton
Purpose:
Composed of:
Difference between endoskeleton and exoskeleton:
Molting:
Adaptations in Body System
Open Circulatory System
Nervous System
Ganglia
Compound Eyes
Single-lens
Breathing
Aquatic
Terrestrial
Tracheae:
Spiracles:
DIVERSITY
Where did arthropods evolve from?
How are they different?
The original arthropods that are now extinct are called__________________________
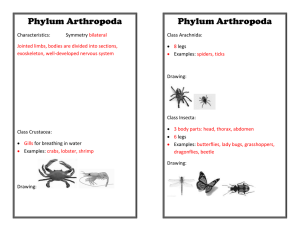
CLASSIFICATION: Phylum Arthropoda
Subphylum Cheliceriformes
Class Arachnida
Examples=
Subphylum Uniramia
Class Diplopoda
Examples=
Class Chilopoda
Examples=
Class Insecta
Examples=
Subphylum Crustacea
Examples=
Subphylum Trilobitomorpha= extinct
Class Arachnida (Arachnids)
Examples:
Body Plan
- 2 body sections
1.
2.
- 2 pairs of mouthparts:
Chelicarae
Pedipalps
Malphighian Tubules
Book lungs
DIVERSITY
SPIDERS
Hunters:
Weavers:
spinnerets:
All produce silk, but not all produce _________________
SCORPIONS
Hunt during the __________________
Live in ______________________
Pedipalps are _______________________
Used for_________________
Poisonous ________________, not a bite
MITES AND TICKS
Parasites:
Plants or animals
Cause________________ Disease
Live off host by:
Free-living:
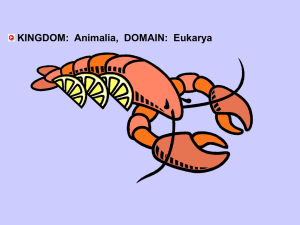
CLASS CRUSTRACEA (Crustaceans)
DECAPOD
Exoskeleton:
BARNACLES
Carapace:
Mandible:
COPEPODS
ISOPODS
CLASS INSECTA
BODY PLAN
3 main body parts:
Wings:
Maliphighian tubules:
Trachael System:
Compound eyes:
ADAPTATIONS
Flight:
Metamorphasis:
Incomplete:
Complete:
CLASS DIPLOPODA
CLASS CHILOPODA