Bonding, Geometry, and Hybridization HW PSI AP Chemistry Nam
advertisement

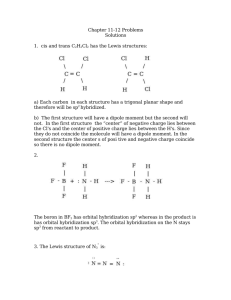
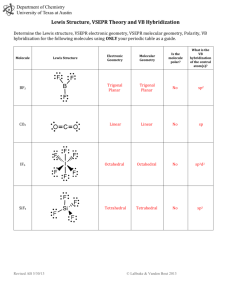
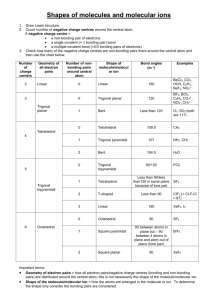
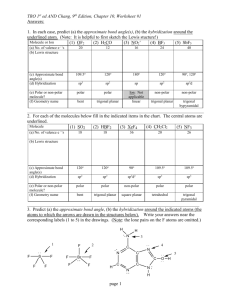
Bonding, Geometry, and Hybridization HW PSI AP Chemistry Name_______________________ 1. According to the VSPER theory, if there are five electron domains in the valence shell of an atom, they will be arranged in a(n) ______________ geometry. A) octahedral B) linear C) tetrahedral D) trigonal planar E) trigonal bipyramidal 2. The electron-domain geometry and molecular geometry of iodide trichloride are ____________ and _____________, respectively. A) trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal planar B) tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal C) trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped D) octahedral, trigonal planar E) T-shaped, trigonal planar 3. The molecular geometry of the CS2 molecule is __________. A) linear B) bent C) tetrahedral D) trigonal planar E) T-shaped 4. The molecular geometry of the PHCL2 molecule is __________. A) bent B) trigonal planar C) trigonal pyramidal D) tetrahedral E) T-shaped 5. The molecular geometry of the SF2 molecule is __________. A) linear B) bent C) trigonal planar D) tetrahedral E) octahedral 6. The molecular geometry of the PF4+ ion is __________. A) octahedral B) tetrahedral C) trigonal pyramidal D) trigonal planar E) trigonal bipyramidal 7. The Cl-Si-Cl bond angle in the SiCl2F2 molecule is approximately __________. A) 90° B) 109.5° C) 120° D) 180° E) 60° 8. The molecular geometry of the H3O+ ion is __________. A) linear B) tetrahedral C) bent D) trigonal pyramidal E) octahedral 9. According to valence bond theory, which orbitals on bromine atoms overlap in the formation of the bond in Br2? A) 3s B) 3p C) 4s D) 4p E) 3d 10. The electron-domain geometry of a sulfur-centered compound is trigonal bipyramidal. The hybridization of the central sulfur atom is __________. A) sp B) sp2 C) sp3 sp3 D) sp3d E) sp3d2 11. The hybridization of orbitals on the central atom in a molecule is sp. The electron-domain geometry around this central atom is __________. A) octahedral B) linear C) trigonal planar D) trigonal bipyramidal E) tetrahedral 12. The hybridization of orbitals on the central atom in a molecule is sp2. The electron-domain geometry about this central atom is __________. A) octahedral B) linear C) trigonal planar D) trigonal bipyramidal E) tetrahedral 13. The hybridization of the carbon atom in carbon dioxide is __________. A) sp B) sp2 C) sp3sp3 D) sp3d E) sp3d2 14. The hybridization of the central atom in the XeF4 molecule is __________. A) sp B) sp2 C) sp3sp3 D) sp3d E) sp3d2 15. The electron-domain geometry of the AsF6- ion is octahedral. The hybrid orbitals used by the As atom for bonding are __________ orbitals. A) sp2d2 B) sp3 C) sp3d D) sp3d2 E) sp2 16. There are __________ σ and __________ π bonds in the H-C≡C-H molecule. A) 3 and 2 B) 3 and 4 C) 4 and 3 D) 2 and 3 E) 5 and 0 17. There are __________ σ and __________ π bonds in the H2C=C=CH2 molecule. A) 4, 2 B) 6, 4 C) 2, 2 D) 2, 6 E) 6, 2 18. There is/are __________ σ bond(s) in the molecule below. A) 1 B) 2 C) 12 D) 13 E) 18 19. The Lewis structure of carbon monoxide is given below. The hybridizations of the carbon and oxygen atoms in carbon monoxide are __________ and __________, respectively. :C≡O: A) sp, sp3 B) sp2, sp3 C) sp3, sp2 D) sp, sp E) sp2, sp2 20. ClF3 has "T-shaped" geometry. There are __________ non-bonding domains in this molecule. A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) 4 21. The electron domain and molecular geometry of BrO2- is _________. A) tetrahedral, trigonal planar B) trigonal planar, trigonal planar C) trigonal pyramidal, linear D) tetrahedral, bent E) trigonal pyramidal, seesaw 22. The O-C-O bond angle in the CO32- ion is approximately __________. A) 90° B) 109.5° C) 120° D) 180° E) 60° 23. The molecular geometry of the left-most carbon atom in the molecule below is __________. A) trigonal planar B) trigonal bipyramidal C) tetrahedral D) octahedral E) T-shaped 24. The molecular geometry of the right-most carbon in the molecule below is __________. A) trigonal planar B) trigonal bipyramidal C) tetrahedral D) octahedral E) T-shaped 25. The central iodine atom in the ICl4- ion has __________ nonbonded electron pairs and __________ bonded electron pairs in its valence shell. A) 2, 2 B) 3, 4 C) 1, 3 D) 3, 2 E) 2, 4 26. The electron-domain geometry and the molecular geometry of a molecule of the general formula ABn will always be the same if __________. A) there are no lone pairs on the central atom B) there is more than one central atom C) n is greater than four D) n is less than four E) the octet rule is obeyed 27. A molecule has the formula AB3 and the central atom is in a different plane from the surrounding three atoms. Its molecular shape is __________. A) tetrahedral B) trigonal pyramidal C) linear D) T-shaped E) bent 28. Of the molecules below, only __________ is polar. A) SbF5 B) AsH3 C) I2 D) SF6 E) CH4 29. Of the molecules below, only __________ is nonpolar. A) CO2 B) H2O C) NH3 D) HCl E) TeCl2 30. Of the molecules below, only __________ is nonpolar. A) BF3 B) NF3 C) IF3 D) PBr3 E) BrCl3 31. Name and draw the molecular structure (including bond angles) for each of the following. a. XeF2 b. IF3 c. IF4+ d. SF5+ 32. Name and draw the molecular structure (including bond angles) for each of the following. a. BrF5 b. KrF4 c. IF6+ 33. Which of the molecules or ions in number 1 above have dipole moments? 34. Which of the molecules or ions in number 2 above have dipole moments? 35. The addition of antimony pentafluoride (SbF5) to liquid hydrogen produces a solution called a superacid. Superacids are capable of acting as acids toward many compounds that we normally expect not to act as bases. For example, in the following reaction, HF acts as a base: SbF5 + 2HF SbF6- + H2F+ Write Lewis structures for and predict the molecular structures and polarities of the reactants and products in this reaction. 36. The molecules BF3, CF4, CO2, PF5, and SF6 are all nonpolar, even though they all contain polar bonds. Why? 37. Consider the structural formula for acetic acid, HC2H3O2 or CH3COOH. Indicate the type of hybridization used by each of the carbon and oxygen atoms. H O H C C H O H 38. Consider the structural formula for the acetate ion, C2H3O2– or CH3COO–. Indicate the hybridization used by each of the carbon and oxygen atoms. H O H C C H O Practice questions: 39. Which hybridization is associated with a steric number of 3? ( steric number is equal to the number of atoms the central atom is connected to ) a) sp d) sp3d b) sp2 e) sp3d2 c) sp3 40. The molecule BrF3 has a steric number of ___ on the central atom? a) 3 b) 4 c) 5 d) 6 41. What is the hybridization of Br in BrF3? a) sp d) sp3d b) sp2 e) sp3d2 c) sp3 42. How many equivalent sp3d orbitals are there? a) 3 b) 1 c) 5 d) 6 43. What type of hybridization is associated with a square planar molecular shape? a) sp3 d) sp3d b) sp2 e) sp3d2 c) sp 44. What shape for electron pairs is associated with sp3d2 hybridization? a) linear d) tetrahedral b) square planar e) octahedral c) bent 45. What hybridization is predicted for phosphorus in the PCl3 molecule? a) sp2 b) sp3 c) sp d) sp3d2 46. A double bond contains ___ sigma bond(s) and ___ pi bond(s). a) 0, 2 b) 1, 2 c) 2, 0 d) 1, 1 47. What angle exists between orbitals in sp3d2 hybrid orbitals? a) 90.0° d) 120.0° b) 180.0° e) 78.5° c) 109.5° 48. Which of the following elements is most likely to display sp3d hybridization? a) oxygen d) carbon b) nitrogen e) boron c) phosphorus 49. How many sigma () and pi () electrons pairs are in a carbon dioxide molecule? a) four and zero d) two and four b) three and two e) one and three c) two and two 50. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atoms in CH3OH and CO2, respectively? a) sp3, sp3 d) sp2, sp2 b) sp3, sp2 e) sp3, sp c) sp2, sp3 51. All of the following species contain two -bonds EXCEPT a) SCN d) OCS b) CO e) NO c) H2CCO 52. Which response contains all the characteristics that should apply to BF3? 1. trigonal planar 2. one unshared pair of electrons on B 3. sp2 hybridized boron atom 4. polar molecule 5. polar bonds a) 2, 4, and 5 d) 1, 3, and 5 b) 1, 3, and 4 e) 3, 4, and 5 c) 1, 2, and 3 Free response Questions 1. (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for CO32-, CO2, and CO, including resonance structures where appropriate. (b) Which of the three species has the shortest C-O bond length? Explain the reason for your answer. (c) Predict the molecular shapes for the three species. Explain how you arrived at your predictions. 2. Explain why molecules of NF3 are polar, but those of BF3 are not. 3. CF4 XeF4 ClF3 (a) Draw a Lewis electron-dot structure for each of the molecules above and identify the shape of each. (b) Use the valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model to explain the geometry of each of these molecules. 4. Use simple structure and bonding models to account for each of the following. (a) The bond length between the two carbon atoms is shorter in C2H4 than in C2H6. (b) The H-N-H bond angle in NH3 is 107.5º. (c) The bond lengths in SO3 are identical and shorter than a sulfur-oxygen single bond. (d) The I3- ion is linear. 5. NO2 NO2- NO2+ Nitrogen is the central atom in each of the species given above. (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structure for each of the three species. (b) List the species in order of increasing bond angle. Justify your answer. (c) Select one of the species and give the hybridization of the nitrogen atom in it. (d) Identify the only one of the species that dimerizes and explain what causes it to do so. 6. Explain each of the following observations in terms of the electronic structure and/or bonding of the compounds involved. (a) At ordinary conditions, HF (normal boiling point = 20°C) is a liquid, whereas HCl (normal boiling point = -114°C) is a gas. (b) Molecules of AsF3 are polar, whereas molecules of AsF5 are nonpolar. (c) The N-O bonds in the NO2- ion are equal in length, whereas they are unequal in HNO2. (d) For sulfur, the fluorides SF2, SF4, and SF6 are known to exist, whereas for oxygen only OF2 is known to exist. 7. Consider the molecules PF3 and PF5. (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for PF3 and PF5 and predict the molecular geometry of each. (b) Is the PF3 molecule polar, or is it nonpolar? Explain. (c) On the basis of bonding principles, predict whether each of the following compounds exists. In each case, explain your prediction. i. NF5 ii. AsF5 8. Answer the following questions using principles of chemical bonding and molecular structure. 2– (a) Consider the carbon dioxide molecule, CO2, and the carbonate ion, CO3 . i. Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each species. 2– ii. Account for the fact at the carbon-oxygen bond length in CO3 is greater than the carbonoxygen bond length in CO2. (b) Consider the molecules CF4 and SF4. i. Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each molecule. ii. In terms of molecular geometry, account for the fact that the CF4 molecule is nonpolar, whereas the SF4 molecule is polar.