Isotopes and Atomic Mass
advertisement
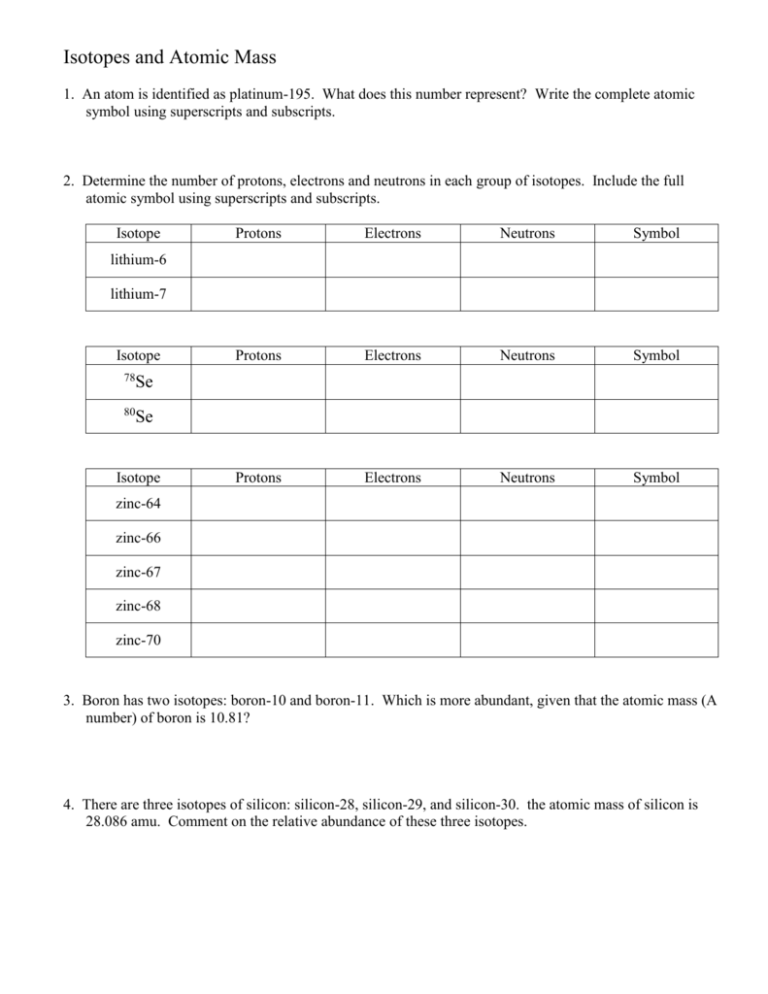
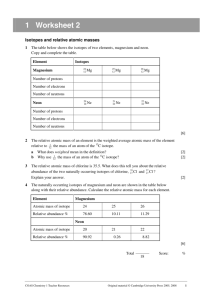
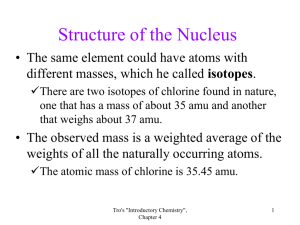
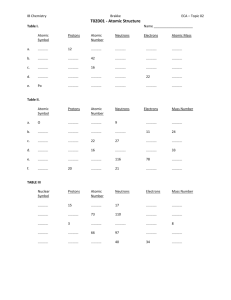
Isotopes and Atomic Mass 1. An atom is identified as platinum-195. What does this number represent? Write the complete atomic symbol using superscripts and subscripts. 2. Determine the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in each group of isotopes. Include the full atomic symbol using superscripts and subscripts. Isotope Protons Electrons Neutrons Symbol Protons Electrons Neutrons Symbol Protons Electrons Neutrons Symbol lithium-6 lithium-7 Isotope 78 Se 80 Se Isotope zinc-64 zinc-66 zinc-67 zinc-68 zinc-70 3. Boron has two isotopes: boron-10 and boron-11. Which is more abundant, given that the atomic mass (A number) of boron is 10.81? 4. There are three isotopes of silicon: silicon-28, silicon-29, and silicon-30. the atomic mass of silicon is 28.086 amu. Comment on the relative abundance of these three isotopes. 5. The average atomic mass of nitrogen is calculated from its relative abundance of its naturally occurring isotopes. Nitrogen-14 has a mass of 14.003 amu and has an abundance of 99.63%. Nitrogen-15 has a mass of 15.000 and is found 0.37% of the time. Calculate the average atomic mass for nitrogen. 6. The element copper has two naturally occurring isotopes: copper-63 and copper-65. The relative abundance and atomic masses are 69.2% for mass = 62.93 amu, and 30.8% for mass = 64.93 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass of copper. 7. Calculate the atomic mass of bromine. The two isotopes of bromine have atomic numbers (A number) and relative abundance of 78.92 amu (50.69%) and 80.92 amu (49.31%).