File
advertisement

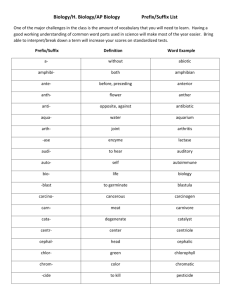
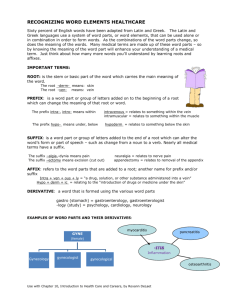
Chapter 10 NOTES - Medical Terminology Basics INTRODUCTION Greek influence –source for diagnosis and surgery related terms Latin influences – source for most anatomical terms Why use medical terminology? Understanding medical terminology adds precision, helps prevent medical mistakes 10.1 - WORD PARTS I. Overview Medical terms are made up of 2 or more parts each having unique meaning o Root: is fundamental element of every medical term & establishes basic meaning o Suffix: short element added to end of root to modify its meaning o Prefix: short element added before root to modify its meaning Health care professionals need only to familiarize themselves with the most commonly used word parts rather than attempt to memorize every possible medical term II. Root and Combining Form Root = basis for term’s meaning Most derived from Greek or Latin Compound word: word that contains more than one root o ie.) cardiovascular Vowel (usually o) is inserted between root & suffix that begins with a consonant to help with pronounciation o ie.) cardi + o + -logy = cardiology (“study of the heart”) o Root + combining vowel = combining form Many describe substances, organs, or colors (see table 10-1) III. Suffix Letter or combination of letters added to end of a root and modifies root’s meaning Can indicate that a word is a noun, adjective, singular or plural Typically adds meaning to the beginning of a word’s definition o Example: psych + o + -logy = psychology (“the study of the mind”) Often used to describe a symptom, a disease, or a surgical treatment (table 10-2) IV. Prefix Attached to beginning of a root word or combining form and modifies the root’s meaning Indicates position or direction o ie.) anti- = opposed to Indicates size or quantity of measurement o ie.) micro- = small Denotes time or rate of change o ie.) tachy- = fast or rapid 10.2 - DECODING MEDICAL TERMS 1. Break term into its building blocks o PREFIX + ROOT + SUFFIX echo- + cardio + -gram 2. Determine meaning of each part o echo- = “a returned or reflective sound” cardio = “heart” -gram = “record” 3. Join definitions of each part to create overall meaning of term (*remember the meaning of the suffix is ually moved to the front of the definiton) o “a record of the heart made by using returned or reflective sounds” Try it yourself! Decode hypodermal Break it apart= hypo + derm + al Indidivual meaning= below or deficient + skin + relating to Overall meaning= “relating to below the skin” 10.3 - SPELLING AND PRONUNCIATION Some words sound the same, but are spelled differently & have different meanings: o ileum (part of intestine) vs. ilium (part of hip bone) Some words sound similar, but are spelled differently & have different meanings: o abduction (to draw away from) vs. adduction (to draw towards) When letters are silent in a term, there is a risk of omitting them from a spelled word o (silent p in pterygium) Some combining forms have the same meaning but different origins that compete for usage o (hystero- vs. metro- vs. utero- all meaning “uterus”) Many words look the same & are easily confused Pay attention to context – use surrounding word to help determine meaning Pronunciation of word parts often changes when combined in different ways and based on region (see table 10-4) 10.4 - ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS Abbreviation: Shortened forms of a word or group of words o Save time and space o Can cause confusion when not universally understood o Usage varies in different institutions; follow policies of your institution Ex.) Preop= Preoperative or IV=intravaneous o Acronym: an abbreviation formed from the first letter of each word in a phrase Ex.) ASAP= As Soon As Possible or BP= blood Pressure Symbols: a form of efficient shorthand communication used in medical records or laboratory reports 10.5 - USING A MEDICAL DICTIONARY Specialized reference books used by health care professionals Meaning and pronunciation of terms Synonyms: words with the same meanings Origins of words (etymology) Useful appendices: measurements, clinical tests, drugs, diagnoses, body structures, information resources, & other topics Specialized, portable, CD, & online versions Medical acronyms & abbreviations book