Glossary of Reading Terms
advertisement

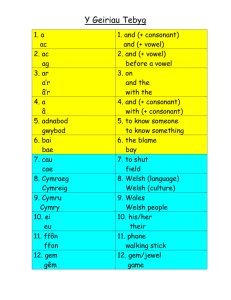
Glossary of Reading Terms Affix: A word element that is placed at the beginning (prefix), in the middle (infix), or at the end (suffix) of the root or word stem. Alliteration: The repetition of the same or similar sounds (usually consonants) that are close to one another (e.g. the timid, tiny tadpole). Antonym: A word which is the opposite of another word. Large is the antonym of small. Book Talk: When a teacher (or media specialist) gives a brief talk about a particular book to generate interest in the book. Consonant: a letter and a sound. Consonants are the letters of the alphabet except for the vowels a, e, i, o, u and sometimes y and w. Context Clues: Bits of information from the text that, when combined with the reader's own knowledge, allow the reader to "read between the lines," figure out the meaning of the text, or determine the meaning of unknown words in the text. Expository Writing: Text that explains an event, concept, or idea using facts and examples. Fluency: The ability to read at an appropriate rate smoothly. (Also the ability to read expressively if reading aloud.) Genre: A type or category of literature marked by conventions of style, format, and/or content. Genres include: mystery, fantasy, epic poetry, etc. Homonym: A word that has the same spelling or pronunciation as another but different meanings and/or origins. See homograph and homophone. Homophone: Two words that have the same pronunciation but differ in meaning or spelling or both. Example: pause and paws Idiom: a phrase or expression that is (usually) not taken literally. For example, "Don't let the cat out of the bag" means to not tell something one knows, to keep silent. Main Idea: The point the author is making about a topic. Topic and main idea are not the same. Metaphor: A figure of speech in which two things are compared by saying one thing is another. Narrative Writing: Generally, writing about an event in a personal way. Prefix: An affix that is added to the front of a word and changes its meaning. For example: un being placed in front of the word developed. Suffix: A group of letters added to the end of a word to form a new word. For example: when ful is added to the word help, a new word is formed: helpful. Syllable: a unit of sound or group of letters made up of a vowel sound or a vowel consonant combination. Syllables contain only one vowel. Synonym: A word that has the same meaning as another word. For example: big and large are synonyms. Syntax: the word order pattern in sentences, phrases, etc.