Two Views of the Firm Two Views of the Firm
advertisement

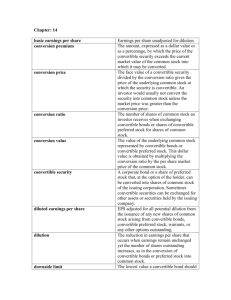
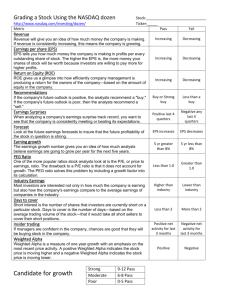
Two Views of the Firm Entity View Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity Two Views of the Firm Entity View Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity Proprietary View Assets – Liabilities = Owners’ Equity 1 Stock Repurchases • No gains or losses are recognized from the sale of a company’s treasury stock • Reasons for stock repurchases – Management believes the shares are undervalued and wants to boost the price – Management wants to distribute surplus cash to owners – Management needs shares for stock options Convertible Debt A bond which, at the buyers option, may be converted to common stock at a predetermined conversion price. Convertible Debt • Current GAAP specifies that convertible debt be recorded as debt only, with no value assigned to the conversion feature. • If the debt is converted the company may use one of two methods: – The book value method – The market value method 2 Earning Per Share • A critically important ratio because it is used to calculate price/earnings ratios. • This is the only financial ratio where the FASB mandates how it is calculated. • Earning Per Share information must appear on the face of the income statement. Earning Per Share The calculation of Earnings Per Share depends upon whether a firm has a simple capital structure or a complex capital structure. $ $ Simple Capital Structure • A simple capital structure exists when a company has no convertible securities and no options or warrants outstanding. • Firms with simple capital structures calculate only basic earnings per share. 3 Basic Earnings Per Share Net Income - Preferred Dividends EPS = Weighted Average Number of Common Shares Outstanding $ $ Complex Capital Structure A firm has a complex capital structure when its financing includes either securities that are convertible into common stock, or options and warrants which entitle holders to obtain common stock under specified conditions. Complex Capital Structure Firms with complex capital structures have an increased likelihood that additional common shares will be issued in the future. This possible increase in the number of shares is called potential dilution. 4 Complex Capital Structures Firms with complex capital structures must compute both basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share. $ $ Diluted Earnings Per Share For convertible securities use the if converted method. – Add to the numerator of basic EPS income adjustments due to dilutive financial instruments. – Add to the denominator of basic EPS newly issuable shares due to dilutive financial instruments. Diluted Earnings Per Share • For Stock Options and warrants use the treasury stock method. – Assume the options will be exercised if they are “in the money.” – Assume that the firm uses the proceeds of the exercise to purchase treasury shares at the average market price for the period. 5 Stock-Based Compensation The FASB allows a choice of methods. • Use the APB 25 approach which rarely recognizes compensation expense • Measure the fair value of the compensation and charge this amount to expense Stock-Based Compensation In the event the ABP approach is chosen, the company must disclose pro-forma net income and earnings per share as if the fair value method had been used. Stock-Base Compensation Fair Value Approach • Compensation cost (the option fair value) is measured only once, the grant date. • The compensation cost is charged to expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. • The offsetting credit is to paid-incapital from stock options. 6 7