Lesson 15
advertisement

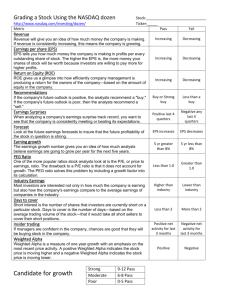
Slide 15A Walk’n on Wall Street Lesson 15 Slide 15B What Does That Mean? Term Definition portfolio a collection of investments. stock quote the price of one share of a stock. institutional investor organizations that pool sums of money from many members to invest in securities. mutual fund a professionally managed investment fund made up of a large pool of money received from many investors. Slide 15C What Does That Mean? Term Definition earnings per share EPS; the approximate amount of a company’s profit allocated per single share in the company. price-earnings ratio P/E Ratio; the ratio of a company's current share price compared to its earnings per share. rally a period of sustained increases in the prices of stocks or bonds usually following a period of flat or declining prices. trend a general direction of a market or security over time. Slide 15D What Does That Mean? Term Definition downgrade a negative change in the rating of a security upgrade a positive change in the rating of a security market cap the number of a company’s shares outstanding multiplied by the current share value. yield the cash return on an investment, expressed as a percentage of the current market value. net change abbreviated net chg; difference in dollars between the closing price of a security and the previous day’s closing price. Slide 15E Reminder Remember to visit http://c21student.com/flashc ards/ to access the online flashcards! Slide 15F Lesson 15 Objectives Compare an institutional and individual investor. Interpret technical data in a stock table. List ten fundamentals of stock valuation. Compare the G8, G7, and G20. Slide 15G What does this stock table tell you about HnnH stock? What do all those numbers, symbols, abbreviations, arrow, and technical information mean? Slide 15H A 52 W Hi/ Lo -shows volatility & trends B Stock = name of the company C Tkr = symbol -assigned by exchange D Dividend Slide 15I E Yld -cash return expressed as % of F current price EPS –company’s earnings divided by number of shares G P/E -share price divided by EPS H Vol -number of shares traded Slide 15J I Hi / Lo -comparison of share price J Close = final price of the day K Net chg = difference in dollars from L Market cap (small, mid, large) –share from prior day the prior day’s close price multiplied by total number of shares outstanding Slide 15K Another method to analyze value: Fun with Fundamentals Provide a deeper, analytical view with such things as company reports (especially earnings reports) Business plan, forecast and earnings reports Management strengths and strategies Pending products Industry and sector growth Slide 15L Downgrades and Upgrades Ratings, ratings, ratings Common stock ratings: strong buy, buy, hold, sell, or outperform or underperform Bonds = AAA down to D Ratings are upgraded or downgraded depending on the company’s performance, problems, or negative events Slide 15M The Big Picture An institutional investor is a professionally managed fund that pools and invests members’ money. Many factors go into analyzing a stock for value. Technical data is provided in a stock table. Stock tables look complicated but are actually easy to read, and are full of important information for comparing stock values. Stock fundamentals are also indicators of value. They include economic forecasts, earnings reports, annual reports, sector and industry growth outlook, management strengths and weaknesses, and a company’s pending products. The investment quality of stocks and bonds is professionally rated. To be financially literate in the 21st century you should understand basic stock valuation methods, and that stock markets are powerful engines driving the economy, as well as avenues to building personal wealth. Slide 15N Ponder and Predict One of President John F. Kennedy ‘s favorite sayings was A rising tide lifts all boats... Is this a metaphor for the stock market? Some people think it is. What do you think?