theme 6 LA 2014 bhambri
advertisement

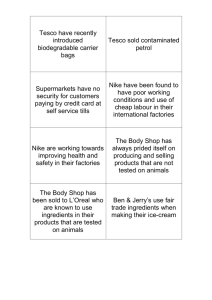
Los Angeles EMBA Arvind Bhambri Theme 6 2014 Friday, August 29, 2014 Values and Global Strategy (1) Apple came under heavy criticism when harsh labor practices at Foxconn, a major Apple supplier, became headline news. This experience is not unique to Apple; instead, any global company that operates in multiple countries through subsidiaries or partners faces similar scrutiny. To understand the challenges of operating in multiple countries with different legal and societal standards, we will start with a case on Nike. Like many other companies, Nike expanded its international sourcing by working with independent contractors to access low cost labor in its overseas plants. What started as a “simple” and fairly common corporate practice suddenly escalated into emotional high profile media criticism about human rights and globalization. We will use the Nike case and some recent Economist articles on Foxconn and other companies to discuss the values and ethical dimensions of global strategies. Discussion Questions 1. Does Jeff Ballinger have a convincing argument about Nike? Does Nike have a convincing response? 2. How well has Nike handled the publicity surrounding its labor practices? Could or should the company have done anything differently? 3. What is a “fair” wage in Vietnam? In Indonesia? How should Nike think about it? Should Nike pay a competitive local wage or does it have an obligation to pay more? Why? 4. What should Apple’s approach be in addressing labor issues with Foxconn? Readings: Hitting the Wall: Nike and International Labor Practices HBSP 9-700-047 Hitting the Wall: Nike and International Labor Practices Spreadsheet Supplement HBSP XLS304 Values in Tension: Ethics Away from Home by Thomas Donaldson, HBR 96502 Foxconn: When workers dream of a life beyond the factory gates. Economist, December 12, 2012. Home or abroad? Herd instinct. Economist, January 19, 2013. Saturday, August 30, 2014 Values and Global Strategy (2) Yesterday, we discussed how MNCs should address pressures that, if handled improperly, can hurt a company’s brand and reputation. Today, we will take a different, more proactive view. Do MNCs, in view of their vast reach and deep resources have a responsibility to make a substantive positive impact on society? If so, how should companies balance corporate profitability with corporate social responsibility? And how should this balance alter their approach to global strategy? Discussion Questions 1. Can major food and beverage companies such as PepsiCo play a constructive role in addressing social and ecological costs associated with the industry (e.g., obesity and environmental degradation)? Why or why not? 2. Do large global corporations have a special responsibility in this area? 3. How has the food and beverage industry responded to criticisms? 4. What is your assessment of PepsiCo’s initiatives? To what extent should sustainability and corporate social responsibility be more or less central to PepsiCo’s global strategy? 5. What recommendations would you make to Nooyi and to PepsiCo? Readings: PepsiCo, Profits, and Food: The Belt Tightens 9-314-055 Bhambri Materials: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Hitting the Wall: Nike and International Labor Practices HBSP 9-700-047 Hitting the Wall: Nike and International Labor Practices Spreadsheet Supplement HBSP XLS304 Values in Tension: Ethics Away from Home by Thomas Donaldson, HBR 96502 Foxconn: When workers dream of a life beyond the factory gates. Economist, December 12, 2012. 6. Home or abroad? Herd instinct. Economist, January 19, 2013. 7. PepsiCo, Profits, and Food: The Belt Tightens 9-314-055