Emotional Health
advertisement

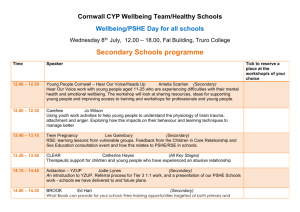
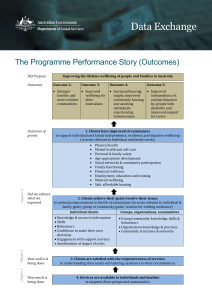
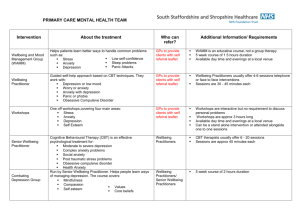
TEACHER & RESOURCES STUDENT TO NOTES ACCOMPANY ‘BEING VICTOR’ UNIT 4: DEPRESSION Curriculum Areas PSHE, Tutorial LESSON 1: EMOTIONAL HEALTH Age Group 11-16 To support the on-line teen soap ‘Being Victor’, TrueTube have developed a series of 20 lesson plans that fit into 5 themes in the PSHE curriculum. The themes are: 1 2 3 4 5 Relationships Online Identity Sex & Promiscuity Depression Young Carers There are 4 lessons in each Unit. Each lesson can be used separately and can be completed by a class in 45-60 minutes, or extended and adapted to suit personal priorities and curriculum needs. This pack contains a Teacher Sheet and a Student Sheet for: Unit 4: Depression Lesson 1: Emotional Health Like all lessons in the Being Victor lesson pack series, this lesson uses as its stimulus the CTVC series Being Victor and a range of issue-based films from the TrueTube website. Both provide entertaining and engaging media to involve the target youth audience in frank discussions and explorations of the social and moral issues that are important in their lives. It is suggested that this Lesson be incorporated into schemes of work in PSHE and/or used, as appropriate, in tutorial sessions. To facilitate this, the Lesson can be completed in 45 minutes but could also be extended and adapted to suit personal priorities and curriculum needs. Being Victor is the story of Vinnie Dupe and his online alter-ego Victor Sage. A ten-week online live action teen drama, it follows the lives of Vinnie and his friends as they cope with college, family, work and the nightmarish rules of teenage life. The content of the drama has been developed to tackle hard issues and give young people a forum to stimulate thought, dialogue and debate around these issues. The series is accompanied by Victor’s Blog that went live 10 weeks before broadcast in order to help create the back-story it continues live alongside the episodes. http://www.victorsblog.co.uk TrueTube is a free, award-winning, website which uses real-life stories and issues to encourage teenagers to explore and debate the world of morality, ethics, politics and religion. TrueTube brings to life the subjects at the heart of Secondary Education using short-form, web-based video and multimedia technology. The site encourages teenagers to find their voice as they explore their own value systems and those of their peers around the corner and across the world. Teachers can use the site as a catalyst to encourage classroom discussion and as a tool to aid learning through audio-visual media. As well as the resources here, the site offers a range of targeted teaching resource packs which include Lesson plans and Lessons which fit with the QCA2007 curriculum. Because streaming media in an educational environment is not always practical, most of the films on TrueTube are downloadable as MPEG-4’s. These files are automatically associated with QuickTime and you will need this in order to play back films you have downloaded. To access the films and learn more about True Tube visit: www.truetube.co.uk 1|Page The aims of these sites support the stated aims of the National Curriculum at Key Stages 3 and 4 PSHE: Personal wellbeing. ‘Personal wellbeing helps young people to embrace change, feel positive about who they are and enjoy healthy, safe, responsible and fulfilled lives. Through active learning opportunities students recognise and manage risk, take increasing responsibility for themselves, their choices and behaviours and make positive contributions to their families, schools and communities. As students learn to recognise, develop and communicate their qualities, skills and attitudes, they build knowledge, confidence and self-esteem and make the most of their abilities. As they explore similarities and differences between people and discuss social and moral dilemmas, they learn to deal with challenges and accommodate diversity in all its forms. The world is full of complex and sometimes conflicting values. Personal wellbeing helps students explore this complexity and reflect on and clarify their own values and attitudes. They identify and articulate feelings and emotions, learn to manage new or difficult situations positively, and form and maintain effective relationships with a wide range of people. Personal wellbeing makes a major contribution to the promotion of personal development.’ National Curriculum Programmes of Study PSHE: Personal Wellbeing The full list of Units and Lessons for the Being Victor lesson plan series is: Unit 1 Relationships Teacher Notes Lesson 1 Belonging Lesson 2 Peer Pressure Lesson 3 Friends and Family Lesson 4 Resolving Differences Unit 2 Online Identity Teacher Notes Lesson 1 Better Than Real Life Lesson 2 Meeting Online Lesson 3 Online Behaviour Lesson 4 Cyberbullying Unit 3 Sex and Promiscuity Teacher Notes Lesson 1 Attitudes to Sex Lesson 2 Risky Business Lesson 3 Designing the Sex Education Curriculum Lesson 4 Saying ‘No’ and Meaning It Unit 4 Depression Teacher Notes Lesson 1 Emotional Health Lesson 2 Understanding Depression Lesson 3 Emotional Intelligence Lesson 4 The Reality of Suicide Unit 5 Young Carers Teacher Notes Lesson 1 What is Caring? Lesson 2 The Effects of Caring Lesson 3 Awareness Lesson 4 Support for Carers 2|Page TEACHER NOTES 4.1 Theme: DEPRESSION Lesson 1 of 4: EMOTIONAL HEALTH Curriculum Area PSHE, Tutorial Age Group 11-16 The following notes give specific background and pointers for teaching the activities as well as the Key Concepts (National Curriculum) covered. Symbols Used in student notes/activity outlines True Tube film(s) Written task Group work Work sheet Learning Objectives Research emotional health and understand how it can change according to circumstances Identify and categorise the factors that can have a positive or negative effect on emotional health Begin to think about the things you can do to help maintain emotional balance. Curriculum References KEY STAGE 3 1.1 Personal identities a. Understanding that identity is affected by a range of factors, including a positive sense of self. b. Recognising that the way in which personal qualities, attitudes, skills and achievements are evaluated affects confidence and self-esteem. c. Understanding that self-esteem can change with personal circumstances, such as those associated with family and friendships, achievements and employment. 1.2 Healthy lifestyles b. Understanding that physical, mental, sexual and emotional health affect our ability to lead fulfilling lives, and that there is help and support available when they are threatened. KEY STAGE 4 1.1 Personal identities a. Understanding that identity is affected by a range of factors, including a positive sense of self. b. Recognising that the way in which personal qualities, attitudes, skills and achievements are evaluated affects confidence and self-esteem. c. Understanding that self-esteem can change with personal circumstances, such as those associated with family and friendships, achievement and employment. 3|Page 1.2 Healthy lifestyles b. Understanding that our physical, mental, sexual and emotional health affect our ability to lead fulfilling lives and that there is help and support available when they are threatened. Discussion Points Look together at the definition of emotional health on Sheet 4.1 What is Emotional Health? Another definition offered by the Samaritans states that: Emotional health is part of our overall health, concerned with the way we think and feel. It refers to our sense of well-being, and our ability to cope with life events. Emotional health is about our ability to acknowledge and respect our own emotions as well as those of others. People are not born with good or poor emotional health, it depends on the circumstances they grow up in, as well as the knowledge and skills and experience they collect throughout life and how they use those. Emotional health is not the same as happiness. Happiness is an emotion that can come and go very quickly. Emotional health is like a toolkit which equips you to get the most out of life. The Samaritans also state that many people refer to mental health when they mean mental illness. To avoid this confusion, refer to emotional health. Explore the sorts of factors that can have a negative impact on emotional health. Categorise these according to whether they are social (death, stress, family disagreements or lack of support, falling out with friends, money problems), psychological (anxiety, stress over work, loneliness, lack of confidence, self-criticism) or physical (illness, drink, drugs, diet, exercise, accident). Share some of the words that people feel comfortable to volunteer describing positive and negative feelings. You could write these as a continuum on a board or flipchart: i.e. most negative words on the far left, most positive on the far right and more neutral words in between. Explain that everyone feels low sometimes, but that it is how we deal with it that’s important to emotional wellbeing. Ask the class to explain why they think emotional health is important. This might include the ability to: deal with stress and bounce back from a negative experience; perform well at school; adapt to change; build strong relationships and support others; achieve a work life balance; feel good about themselves. You might want the class to create posters suggesting what young people can do to maintain a sense of emotional balance. Reading/Extras Discuss with the class the things that they do to maintain emotional balance and a sense of wellbeing. Ask them to share the things that give them pleasure and make them feel good about themselves. Key Charities – Useful Information and Support http://www.samaritans.org http://www.supportline.org.uk http://www.youngminds.org.uk http://www.mind.org.uk http://www.depressionalliance.org http://www.depression.com http://www.kidshealth.org/teen 4|Page STUDENT SHEET Unit 4 Lesson 1 Depression: Emotional Health Curriculum Area PSHE, Tutorial Emotional Health Learning Objectives Research emotional health and understand how it can change Total Time 45 minutes according to circumstances Identify and categorise the factors that can have a positive or negative effect on emotional health Begin to think about the things you can do to help maintain emotional balance. Resources: Access to TrueTube website either on individual PCs (or on whiteboard) Access to the internet Sheet 4.1 What is Emotional Health? 15 minutes Introduction 1. 2. 20 minutes Main Activity 1. 2. 10 minutes In pairs, watch some of the TrueTube films listed on Sheet 4.1 What is Emotional Health? Create a table to describe the factors that can have a negative or positive impact on emotional health. In pairs list five words that describe you when you’re feeling positive, and able to cope well with life. For example, relaxed. Now write five words that describe you when you’re feeling less positive. These words probably represent the continuum of your mental health. Most of the time we’re somewhere between the two: when something really good happens we’re at the positive end and when challenges become too difficult we find ourselves at the negative end. Emotional health and wellbeing depends on finding ways to deal with problems in order to maintain emotional balance. Plenary and Reflection 1. 2. 5|Page We often ask people we meet how they are and this generally refers to their physical well-being. If someone asks after your emotional health, what do you think they mean? How might you answer? Look at the definition of emotional health from the Samaritans’ website. This is reproduced on Sheet 4.1 What is Emotional Health? Look at some other definitions online and agree a class definition. What factors do you think most influence your sense of emotional wellbeing? If you want, you could share these thoughts with a trusted partner. As a class, discuss why taking care of your emotional health is just as important as staying physically fit. Sheet 4.1 What is Emotional Health? According to the Samaritans ... [www.samaritans.org/your_emotional_health] Emotional health is about how balanced and confident we feel emotionally. If something happens and we feel low emotionally, getting back on track can be difficult. People do not automatically have either good or poor emotional health. Your emotional health depends on the circumstances you grow up in, the knowledge and skills and experience collected throughout life, and how these are used. You can think of emotional health as being a sort of sliding scale. We’re all somewhere on the emotional health scale, and people will go up and down this scale – that’s part of life and an important part of being emotionally healthy. In a more positive place: relaxed, happy, content, easy going, laid back, chatty, friendly, fun In a more negative place: upset, sad, withdrawn, irritable, angry, argumentative, guilty, quick tempered, tearful Many factors can have an impact on our emotional health. Watch some of the TrueTube films below and list the social, physical and psychological factors that have affected the young people’s mental health and the impact it has had on their lives. From Harming Myself to Helping Others [3:18] Body and Health – Mental Health Roller Coaster Life [2:40] Body and Health – Mental Health Out of the Abyss [2:40] Body and Health – Mental Health Doom and Gloom of the New Year [1:35] Body and Health – Well Being Abortion and Depression [3:11] Global – Human Rights Losing my Brother [4:55] Body and Health – Life & Death Learning to Grieve [4:59] Relationships – Loss Headings for List Social factor Psychological factor - relationships, family, friends, acquaintances - thoughts and feelings Physical factor - health and fitness What factors influence your sense of emotional well-being most? 6|Page Impact - how the factors in the young people’s lives affect them day to day