Experiment M01 Melting point and boiling point determination
advertisement
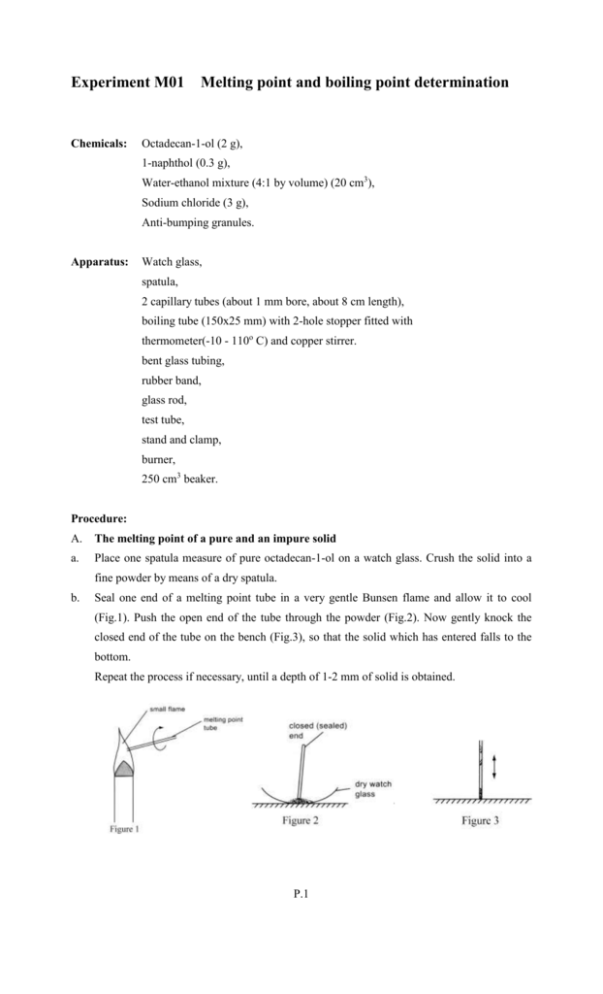
Experiment M01 Chemicals: Melting point and boiling point determination Octadecan-1-ol (2 g), 1-naphthol (0.3 g), Water-ethanol mixture (4:1 by volume) (20 cm3), Sodium chloride (3 g), Anti-bumping granules. Apparatus: Watch glass, spatula, 2 capillary tubes (about 1 mm bore, about 8 cm length), boiling tube (150x25 mm) with 2-hole stopper fitted with thermometer(-10 - 110o C) and copper stirrer. bent glass tubing, rubber band, glass rod, test tube, stand and clamp, burner, 250 cm3 beaker. Procedure: A. The melting point of a pure and an impure solid a. Place one spatula measure of pure octadecan-1-ol on a watch glass. Crush the solid into a fine powder by means of a dry spatula. b. Seal one end of a melting point tube in a very gentle Bunsen flame and allow it to cool (Fig.1). Push the open end of the tube through the powder (Fig.2). Now gently knock the closed end of the tube on the bench (Fig.3), so that the solid which has entered falls to the bottom. Repeat the process if necessary, until a depth of 1-2 mm of solid is obtained. P.1 Experiment M01 Melting point and boiling point determination Name: Seat No.: Date: Grade: c. Using rubber band, tie the tube to a thermometer, such that the base of the melting point tube is beside the thermometer bulb. Then set up the apparatus as shown in fig.4 d. Heat the water to about 45o C, stirring it constantly with the stirrer. After this, heat with a small non-luminous flame (not more than 4 cm high), so that the temperature rises slowly (about 2 degrees per minute). Watch for the temperature at which the powder just starts to melt. (Look for the first signs of melting - there is a crumbling and 'contraction' of the powder, followed by a 'damp' appearance.). Record this temperature. Note also the temperature at which all the solid has just turned into liquid. What is the melting point range of pure octadecan-1-ol? Is the melting point sharp? e. Mix thoroughly the rest of the crushed octadecan-1-ol in procedure a with about 1 of its 10 volume of 1-naphthol. Repeat the above procedures to find the melting point of the impure octadecan-1-ol. What is the melting point range of the impure octadecan-1-ol? Is the melting point higher or lower than that of the pure solid? Is the melting point as sharp or less sharp than that of the pure solid? P.2 Experiment M01 Melting point and boiling point determination Name: Seat No.: Date: Grade: B. The boiling point of a pure and an impure liquid 1 a. Fill of a boiling tube with distilled water. Add a few anti-bumping granules to the tube. Set 4 up the apparatus as shown in fig.5. Make sure that the thermometer bulb is completely immersed in water but does not touch the sides of the tube. b. Heat the tube gently until the water boils steadily. Record this steady temperature, what is the boiling point of distilled water. c. Fill 1 of a boiling tube with a water-ethanol mixture. Add a few anti-bumping granules to 4 the tube. Find the boiling point of the liquid mixture (as in steps a and b), after it has boiled for 1 minute. What is the boiling point of the impure water at this moment? Is this higher or lower than that of pure water? d. Add 2 spatula measures of sodium chloride to a boiling tube. Add water until the tube is 1 4 full. Stir with a glass rod until most of the solid dissolves. Add a few anti-bumping granules. Find the boiling point of the liquid mixture (as in steps a and b), after it has boiled for 1 minute. What is the boiling point of the impure water at this moment? Is this higher or lower than that of pure water? P.3