printer-friendly sample test questions

Content Benchmark P.12.A.1
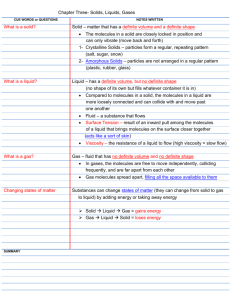
Students know different molecular arrangements and motions account for the different physical properties of solids, liquids, and gases. E/S
Sample Test Questions
1 st Item Specification: Given a diagram, choose the molecular arrangement that best describes a solid, liquid, or gas.
Depth of Knowledge Level 1
1.
Use the following diagrams to answer the question below.
Diagram 1
Diagram 3
Diagram 2
Diagram 4
Which of the diagrams best describes the molecular arrangement of oxygen?
A.
Diagram 1
B.
Diagram 2
C.
Diagram 3
D.
Diagram 4
2.
Use the following diagrams to answer the question below.
Diagram 1
Diagram 3
Diagram 2
Diagram 4
Which of the diagrams best describes the molecular arrangement of a mineral?
A.
Diagram 1
B.
Diagram 2
C.
Diagram 3
D.
Diagram 4
Depth of Knowledge Level 2
3.
What is the molecular arrangement like in a liquid such as rubbing alcohol and why?
A.
The molecules are close together because of their strong intermolecular attractions and low kinetic energy.
B.
The molecules are randomly packed together, but the molecules can slip and slide over each other.
C.
The molecules are close together because the kinetic energy is dominant over the potential energy within the molecules.
D.
The molecules are far apart because of their weal intermolecular attractions and high kinetic energy.
4.
What is the molecular arrangement like in wood and why?
A.
The molecules are close together because of their strong intermolecular attractions.
B.
The molecules are randomly packed together because the molecules can slip and slide over each other.
C.
The molecules are close together because the kinetic energy is dominant over the potential energy within the molecules.
D.
The molecules are far apart because of their small intermolecular attractions.
2 nd Item Specification: Recognize the differences between solids, liquids, and gases.
Depth of Knowledge Level 1
5.
Which of the following describes the differences between solids and liquids?
A.
Both have a definite shape, but only solids have a definite volume.
B.
Both have a definite volume, but only liquids have a definite shape.
C.
Solids have definite volume and shape, but liquids only have a definite volume.
D.
Liquids have a definite volume and shape, but solids only have a definite shape.
6.
Which of the following best describes the differences between liquids and gases?
A.
Both have a definite volume, but only liquids have a definite shape.
B.
Both have a definite shape, but only gases have a definite volume.
C.
Gases have a definite volume only and liquids do not have either.
D.
Liquids have definite volume only and gases do not have either.
Depth of Knowledge Level 2
7.
A student wants to test a mystery substance to find out what state of matter it is. Which characteristics can be used to determine its state?
A.
Volume, density, compressibility, and flow.
B.
Volume, density, compressibility, and mass.
C.
Shape, flow, and temperature.
D.
Shape, density, and temperature.
8.
A student has run tests on a mystery substance and has found that is has a definite volume, high density, and flows easily. Which state of matter is it and why?
A.
It is a solid because it has a definite volume and high density.
B.
It is a liquid because it has a definite volume and high density.
C.
It is a solid because it has a definite volume and flows easily.
D.
It is a liquid because it has a definite volume and flows easily.
3 rd Item Specification: Analyze the motion of particles in solids, liquids, and gases.
Depth of Knowledge Level 1
9.
Which of the following correctly describes the motion of particles in a solid?
A.
They do not move at all.
B.
They move rapidly around in random patterns.
C.
They vibrate in a set pattern.
D.
They flow easily, but slowly around each other.
10.
Which of the following correctly describes the motion of particles in a gas?
A.
They do not move at all.
B.
They move rapidly around in random patterns.
C.
They vibrate in a set pattern.
D.
They flow easily, but slowly around each other.
Depth of Knowledge Level 2
11.
What is happening to the particles of a solid as it changes phase into a liquid?
A.
They slow down and spread apart because energy is being added.
B.
They slow down and become closer because energy is being removed.
C.
They speed up and spread apart because energy is being added.
D.
They speed up and become closer because energy is being removed.
12.
What is happening to the particles of a gas as it changes phase into a liquid?
A.
They slow down and spread apart because energy is being added.
B.
They slow down and become closer because energy is being removed.
C.
They speed up and spread apart because energy is being added.
D.
They speed up and become closer because energy is being removed.
4 th Item Specification: Explain properties of the states of matter using kinetic-molecular theory.
Depth of Knowledge Level 1
13.
Which of the following describes a state of matter that has a fixed molecular arrangement and particles that are close together?
A.
A substance that has a strong attraction between particles and low kinetic energy.
B.
A substance that has a strong attraction between particles and high kinetic energy.
C.
A substance that has little attraction between particles and high kinetic energy.
D.
A substance that has little attraction between particles and low kinetic energy.
14.
Which of the following describes a state of matter that has a random molecular arrangement and particles that are far apart?
A.
A substance that takes the shape of its container and is NOT easily compressed.
B.
A substance that has a definite shape and is easily compressed.
C.
A substance that takes the shape of its container and is easily compressed.
D.
A substance that has a definite shape and is NOT easily compressed.
Depth of Knowledge Level 2
15.
According to the kinetic-molecular theory, the particles in Ideal gases
A.
behave like tiny discrete particles in a state of constant, random motion.
B.
behave like hard, spherical objects in a state of constant, patterned motion.
C.
lose some energy when they collide with each other or with the walls of the container.
D.
have a strong force of attraction between the particles and the walls of the container.
16.
Which of the following is not part of the kinetic molecular theory of gases?
A.
Attractive and repulsive forces between gas molecules are negligible.
B.
Gases consist of molecules in continuous random motion.
C.
Collisions between gas molecules do not result in loss of energy.
D.
Matter is conserved in ordinary chemical reations.
Content Benchmark P.12.A.1
Students know different molecular arrangements and motions account for the different physical properties of solids, liquids, and gases. E/S
Answers to Sample Test Questions
1.
B, DOK level 1
2.
A, DOK level 1
3.
B, DOK level 2
4.
A, DOK level 2
5.
C, DOK level 1
6.
D, DOK level 1
7.
A, DOK level 2
8.
D, DOK level 2
9.
C, DOK level 1
10.
B, DOK level 1
11.
C, DOK level 2
12.
B, DOK level 2
13.
A, DOK level 1
14.
C, DOK level 1
15.
A, DOK level 2
16.
D, DOK level 2