Acids/Bases/Equilibrium Study Guide
advertisement

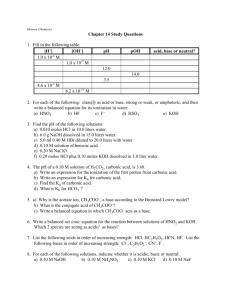
Acids/Bases/Equilibrium Study Guide Equations that will be provided: That means you need to know how to use your calculator!!! [H+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14M pH = -log[H+] [H+] = 10-pH pOH=-log[OH ] [OH-] =10-pOH Topics Covered: □ Properties of acids/bases □ Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids/bases (conjugate acids and bases) □ Naming acids (ate-ic acid, ite-ous acid, ide-hyro-ic acid) and bases □ Calculate pH, pOH, [H+] or [OH-] when given the appropriate information (Equations provided above) □ Determine whether a substance is acidic or basic with pH, pOH, [H+] or [ OH-] □ Predict products of neutralization reactions □ Calculate, perform, and describe titrations □ Reversible reactions and equilibrium – What does equilibrium mean? □ How can we make a reaction occur faster? □ Calculate Concentration (know the equation) □ Strong acids/bases vs. Weak acids/bases Practice Problems: 1. What are three characteristics of acids? Three of bases? 2. In the following reactions, label the Bronsted-Lowry acids, bases and their conjugates: A. NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OHB. HF + H2O F- + H3O+ 3. Write the formula of the conjugate acid of each Bronsted-Lowry base: ClO-2, H2O, H2PO4-1, NH3 4. If a solution has a pH of 4.5, what is the [H+] and [OH-]? Is this solution acidic, basic, or neutral? Explain. (3.2x10-5M, 3.2x10-10M) 5. Why is pH of “7” considered neutral? 6. What would be the pH of a 0.00000793M HCl solution? (5.1) 7. What is the pH and pOH of 0.0349 M KOH? (12.5, 1.5) 8. What does neutralizing mean? How do you neutralize an acid? What is the neutralization point? 9. What is an indicator? What is an example of an indicator? 10. If 19.65 mL of HCl is neutralized by 37.2 ml of 0.45M KOH, what is the molarity of the acid? (0.85 M) 11. How many mL of 3M H2SO4 will you need to neutralize 120ml of 1.3 M NaOH? (26mL) 12. What is the difference between strong/weak acids? And concentrated/diluted acids and bases? 13. What is the pH of a 0.0365 M solution of HNO3? (1.44) 14. What is the pOH of a 0.0000365 M solution of HNO3? (9.56) 15. Complete the following reactions: (Don’t forget the definitions of acids and bases) HC2H3O2 + NaOH HC2H3O2 + NH3 HC2H3O2 + H2O H2PO4- + H2O 16. Describe 2 ways you could speed up a reaction (Explain what happens on the molecular level) 17. If you make 3.2 M H2SO4 with 23 g of H2SO4, what volume (in mL) do you have? (73 mL) 18. Name the following: H2SO3, H3PO4, H3N 19. What is the “equal” part in equilibrium? 20. What is the pH of 0.000987 M H2SO4? (2.7) 21. 98.2 mL of 0.00047 M NaOH is neutralized by 12.34 mL of H2SO4. What is the pH of the acid? (2.43)