CHEM 1000 Discussion Worksheet: Chemical Compounds
advertisement
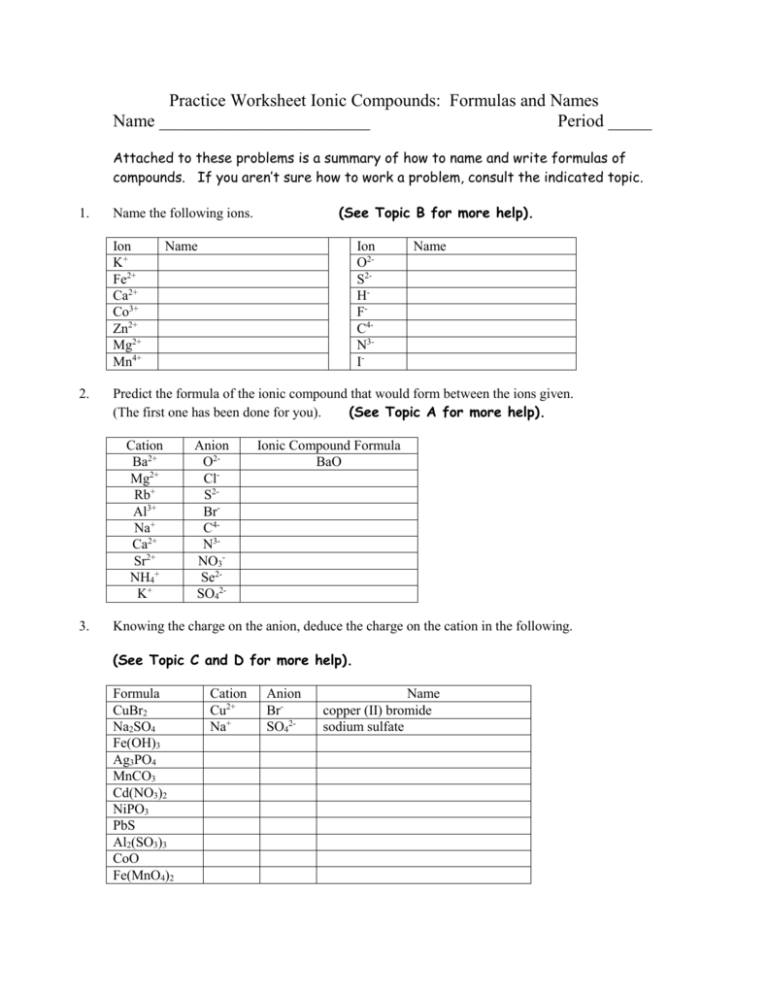
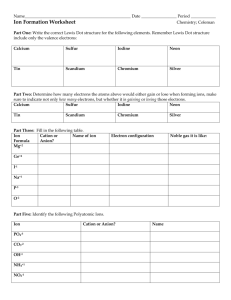
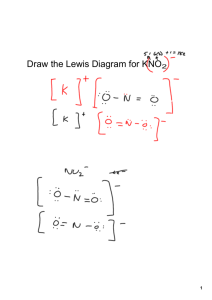
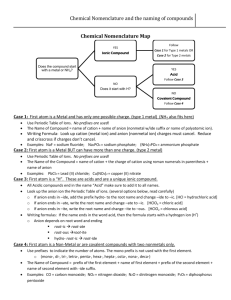
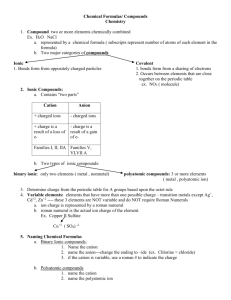
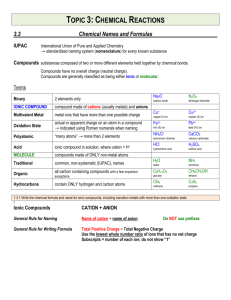
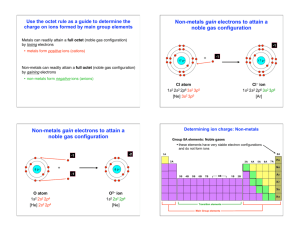
Practice Worksheet Ionic Compounds: Formulas and Names Name ________________________ Period _____ Attached to these problems is a summary of how to name and write formulas of compounds. If you aren’t sure how to work a problem, consult the indicated topic. 1. Ion K+ Fe2+ Ca2+ Co3+ Zn2+ Mg2+ Mn4+ 2. Name Ion O2S2HFC4N3I- Name Predict the formula of the ionic compound that would form between the ions given. (The first one has been done for you). (See Topic A for more help). Cation Ba2+ Mg2+ Rb+ Al3+ Na+ Ca2+ Sr2+ NH4+ K+ 3. (See Topic B for more help). Name the following ions. Anion O2ClS2BrC4N3NO3Se2SO42- Ionic Compound Formula BaO Knowing the charge on the anion, deduce the charge on the cation in the following. (See Topic C and D for more help). Formula CuBr2 Na2SO4 Fe(OH)3 Ag3PO4 MnCO3 Cd(NO3)2 NiPO3 PbS Al2(SO3)3 CoO Fe(MnO4)2 Cation Cu2+ Na+ Anion BrSO42- Name copper (II) bromide sodium sulfate 4. a) Fill in the chart to indicate whether the combinations will describe an ionic compound or a covalent (molecular) compound. metal + nonmetal nonmetal + nonmetal NH4+ + other nonmetals b) Determine whether each of the compounds is molecular or ionic. Then supply the missing formula or name. (See Topics A & D for more help). Name the following ionic compounds: 1) NH4Cl _____________________________________ 2) Fe(NO3)3 _____________________________________ 3) TiBr3 _____________________________________ 4) Cu3P _____________________________________ 5) SnSe2 _____________________________________ 6) GaAs _____________________________________ 7) Pb(SO4)2 _____________________________________ 8) Be(HCO3)2 _____________________________________ 9) Mn2(SO3)3 _____________________________________ 10) Al(CN)3 _____________________________________ Write the formulas for the following compounds: 11) chromium (VI) phosphate _____________________________________ 12) vanadium (IV) carbonate _____________________________________ 13) tin (II) nitrite _____________________________________ 14) cobalt (III) oxide _____________________________________ 15) titanium (II) acetate _____________________________________ 16) vanadium (V) sulfide _____________________________________ 17) chromium (III) hydroxide _____________________________________ 18) lithium iodide_____________________________________ 19) lead (II) nitride _____________________________________ 20 silver bromide _____________________________________ A. Predicting Ionic Compound Formulas An ionic compound is neutral overall: (+) charge of cations + (-) charge of anions = 0 If the charges of the cation and anion don’t add up to be zero, then sum to zero or “criss-cross” the charges (make sure you reduce the charges to lowest terms before you criss-cross” them). Cc+ Aaex. B. C. Ba2+ Ca Ac O2- → sum to zero → BaO Fe3+ O2- → “criss-cross” → Fe2O3 The cation is written first. When using a subscript for a polyatomic ion, put the entire polyatomic ion in ( ). Naming Ions Cation: Use element name “as is” or use a Roman Numeral to specify charge Anion: Replace end with “ide” ex. Li+ is the “lithium” ion ex. Mn2+ is “manganese(II)” ex. C4- is carbide (carbon + ide) Predicting Charge of cation from a Formula Cations other than group I, group II, silver, cadmium, zinc and aluminum can have variable charge. Since an ionic compound is neutral overall, the charge on the metal cation can be determined based on the anion charge: Total charge of cations + Total charge of anions = 0 D. Ex. PbO: The charge on O is –2, so the charge on Pb must be +2. FeBr3: The total anion charge is 3x(-1) = -3, so the charge on Fe must be +3. (“Reverse” criss-cross!) Naming Chemical Compounds 1. Ionic Compounds a) Name the metal or the polyatomic ion “ammonium”. b) Then the anion, ending in “ide” (or polyatomic ion name) CaCl2 CaCO3 FeO (NH4)2CO3 calcium chloride calcium carbonate iron(II) oxide ammonium carbonate