Forming Compounds - Homework Package
advertisement

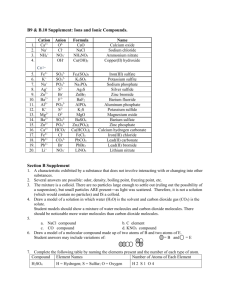
Forming Compounds - Homework Package SNC2D1 Grade 10 Academic Science 1. The Formation of Ions – complete the following table. Group Example & # of Lose or Bohr-Rutherford valence gain diagram electrons electrons? 1 Li 2 Be 13 (3) B 14 (4) C 15 (5) N 16 (6) O 17 (7) F 18 (8) He Ionic charge Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ______________________________________________ Conclusion: The atoms of the elements in each GROUP (i.e. column) share a common property – they all have the same number of ____________________ 2. What is the charge of each of the following common elements? Element Charge Element Charge Potassium +1 Calcium Sulphur Magnesium Mercury Bromine Phosphorus Barium Iodine Rubidium 3. Types of chemical bonds – is it ionic or molecular? Put a checkmark () in the appropriate column. Ionic Molecular CaCl2 Silver bromide CaO Dinitrogen monoxide CuCl2 Aluminum bromide CO Lead (II) oxide Cu2O Sodium chloride SO2 Carbon dioxide SnF2 Copper (II) chloride MgCl2 dihydrogen monoxide Li2O Carbon monoxide Na2O Zinc oxide PbI2 Aluminum oxide CO2 Copper (II) oxide FeCl2 Calcium chloride NaCl Potassium chloride SO3 Tin (II) chloride NaI Nitrogen dioxide KCl Sodium fluoride PbCl2 Sulphur trioxide K2O Lithium oxide N2O5 Zinc chloride Ionic Molecular IONIC BONDING Ionic bonding occurs when a ________________ and transfers one or more electrons to a _______________ in an effort to attain a stable ___________ of electrons. 1. Show the transfer of electrons using Bohr-Rutherford diagrams in the following combinations. K+F For example, the transfer of one electron from a sodium to chlorine atom can be depicted by the Bohr-Rutherford diagram below: Mg + I The attraction between the newly formed cation and anion is called the ionic bond. Be + S Example 2: Al and Cl Aluminum would need three chlorine atoms to get rid of its 3 valence electrons. The concept: The total positive charge and the total negative charge needs to equal ZERO in order to form a stable ionic compound. So…Al3+ is a stable cation, and Cl- is a stable anion. But there are more positive charges than negative charges if there is only one of each. So there needs to be a total of 3 negative charges to balance out the 3 positive charges that Al3+ has. Therefore, three chlorine ions are needed for every aluminum ion present. Na + O Al + Br Forming Ionic Compounds Anion Chemical Formula Name of Compound Cation Cation Anion Cation Anion Cation Anion Cation Anion Chemical Formula I- Li1 I1 LiI Lithium iodide Crisscross Anion Crisscross Li+ Lithium + Iodine Cation Potassium + Fluorine 2. Complete the following tables: Example 1: Elements Cation Elements Elements Anion Calcium + Bromine Name of Compound Elements Beryllium + oxygen Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Crisscross Chemical Formula Elements Name of Compound Calcium + nitrogen Crisscross Elements Cation Anion Aluminum + Chlorine Chemical Formula Name of Compound Crisscross Chemical Formula Elements Name of Compound Magnesium + phosphorus Crisscross Elements Magnesium + Sulphur Cation Anion Chemical Formula Name of Compound Crisscross Chemical Formula Elements Name of Compound Aluminum + oxygen Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Elements with Multiple Ionic Charges 1. Complete the following tables. Example 1: Name of Compound Cation Tin (II) iodide Sn2+ ISn1 I2 SnI2 Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Anion Cation Anion Copper (I) bromide Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Cation Anion Cation Anion Cation Anion Iron (III) chloride Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Tin(IV) fluoride Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Iron (II) oxide Crisscross Chemical Formula 2. Write the chemical names for the following compounds. a. CuCl2 Copper (II) chloride b. FeBr3 c. PbS d. SnO2 e. FeP f. CuI g. PbI2 h. FeCl2 i. SnF2 j. PbCl2 k. Cu2O 3. More practice! PART A: Write the chemical formula for the following compounds a. Copper (II) oxide b. Silver chloride c. Tin (II) chloride d. Cobalt (II) phosphide e. Sodium fluoride f. Lithium oxide g. Lead (II) oxide h. Iron (III) oxide i. Magnesium bromide j. Zinc oxide k. Chromium (II) bromide l. Nickel (III) oxide m. Lead (IV) oxide n. Aluminum nitride o. Lithium iodide p. Copper (II) chloride PART B: Write the chemical names for the following compounds a. NaCl b. MgCl2 c. FeCl3 d. FeO e. Mg3N2 f. Cu3N g. SnS2 h. AuCl3 i. Fe2O3 j. Cu3P2 k. CuF2 l. LiBr m. K3P Polyatomic Ions 1. Complete the following tables. Example 1: Name of Compound Cation Na+ Sodium phosphate Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Anion (PO4)3Na3 (PO4)1 Na3PO4 Cation Anion Cation Anion Calcium sulphate Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Copper (I) carbonate Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Cation Anion Cation Anion Tin (II) hydroxide Crisscross Chemical Formula Name of Compound Sodium chlorate Crisscross Chemical Formula 2. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Write the chemical names for the following compounds. KNO3 (found in gun powder) Potassium nitrate Ca(OH)2 (an ingredient in plaster) CaCO3 (in chalk) CuSO4 (a fungicide) KOH (used to make soap) Fe(NO3)3 (used in water treatment) Cu(ClO3)2 (used to colour fireworks) (NH4)3PO4 (ingredient in bread dough) 3. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Write the chemical formula for each of the following compounds. Potassium nitrate (used to colour fireworks purple) Barium sulphate (given prior to an X-ray of the intestine) Ammonium nitrate (common ingredient in fertilizer) Aluminum sulphate (used in preparing pickles) Potassium chlorate (an explosive) Copper (II) nitrate (used to colour ceramics) Lead (II) sulphate (found in car batteries) Tin (II) phosphate (used in the dyeing of silk) 4. More Practice! PART A: Write the chemical names for the following compounds. a. Li2CO3 b. Mg3(PO4)2 c. K2SO4 d. NaNO3 e. Al(OH)3 f. Pb3(PO4)2 g. Sn(ClO3)2 h. NaOH i. FeSO4 j. K3PO4 PART B: Write the chemical formulas for the following compounds. a. c. e. g. i. k. m. Magnesium sulphate Sodium chlorate Aluminum nitrate Sodium bicarbonate Copper (II) hydroxide Iron (II) phosphate Beryllium sulphate b. d. f. h. j. l. n. Copper (I) chlorate Magnesium hydroxide Lead (II) nitrate Aluminum carbonate Ammonium sulphate Cobalt (II) phosphate Barium nitrate Ionic Compounds – Review Write the chemical formulas and chemical names of the compounds produced from the listed ion in the grid below. Cl- Na+ NH4+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Zn2+ Fe2+ Al3+ Co3+ Fe3+ H+ Example: NaCl Sodium chloride CO32- OH- SO42- PO43- NO3- Molecular compounds - Covalent bonds Covalent bonding occurs when two more __________________ SHARE electrons, attempting to attain a stable octet of electrons at least part of the time. (Note: Hydrogen is stable with 2 electrons, not 8!) 1. Using Bohr-Rutherford diagrams, show how covalent bonding occurs in each of the following pairs of atoms. Atoms may share one, two, or three pairs of electrons (i.e. there can be a single bond, double bond, or triple bond between atoms). a. H + H (H2) b. F + F (F2) c. O + O (O2) d. N + N (N2) e. C + O (CO2) f. H + O (H2O) Naming molecular compounds using the prefix method: 1* 2 3 4 5 Prefix mono*MONO is only used with the 2nd non-metal! 2. Write the chemical formula for the following molecular compounds. a. Carbon dioxide CO2 b. Silicon dioxide c. Carbon disulfide d. Sulphur trioxide e. Carbon tetrachloride f. Diphosphorus trioxide g. Dinitrogen oxide h. Arsenic tribromide i. Phosphorus pentrabromide j. Dinitrogen tetroxide k. Silicon carbide l. Sulphur dioxide m. Dinitrogen monoxide n. Sulphur difluoride 3. Write the chemical name for the following molecular compounds. a. CF4 Carbon tetrafluoride b. PBr3 c. CS2 d. N2O2 e. H2O2 f. CO g. N2O3 h. SiC i. P2O5 j. SO3 k. SiO2 l. PCl5 m. N2O5 4. Ionic or Covalent For each of the following compounds, place a checkmark () under the appropriate column to state if it is IONIC or COVALENT and name the compound. Compound Example: BaS a. Rb3N b. N2S5 c. BeO d. HI e. SrCl2 f. FeCl3 g. P2S5 h. SCl2 i. Ag(NO3) j. As2S3 k. Cu(HCO3)2 l. SnO2 m. K3(PO4) n. NaCl o. CCl4 Ionic Covalent Chemical Name Barium sulphide Naming & writing chemical formulas for ionic & molecular compounds. 5. Write the chemical formula for the following compounds. Lithium bromide Carbon monoxide Arsenic trifluoride Mercury (II) sulfate Barium hydride Cobalt (III) chloride Calcium phosphate Phosphorus pentachloride Tin (IV) iodide Copper (I) oxide Sodium sulfide Dinitrogen trisulfide Iodine monobromide Beryllium bromide Lead (II) carbonate Lead (IV) oxide Selenium tribromide Potassium chlorate Barium nitrate Chromium (II) nitrate Ammonium sulfide Calcium bicarbonate Barium iodate Manganese (II) fluoride Sodium hydroxide Calcium hydroxide Ammonium sulfate Tricarbon tetraphosphide Chromium (III) oxide Iron (III) carbonate Hydrogen sulfide Magnesium nitride p. NO 2. Write the correct name for each of the following compounds NF3 Ag3N q. Na2(SO4) K2SO4 CrCl3 r. Na3P Au2O3 s. CO2 Co(NO3)3 KOH t. Fe2S3 Co(ClO3)2 u. BaSO4 P2S5 Li(NO3) v. K2O Ca3(PO4)2 Mg3(PO4)2 w. NaF CBr4 Si3N2 x. Na2CO3 SO2 Fe(ClO3)2 CaCl2 H2O y. NH4Cl