Unit 11: Acids & Bases Practice Problems/Review
advertisement

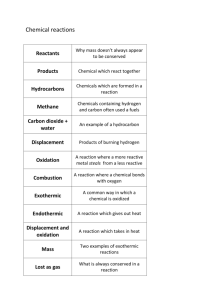
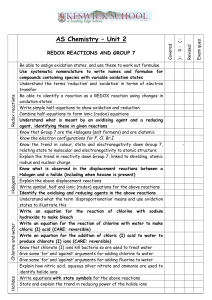
Name__________________________________ Period______ Unit 11: Acids & Bases Practice Problems/Review 1. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution, given the concentration of hydroxide ions is 1 x 10-5 M and the ion constant for water is 1 x 10-14. 2. When acids react with metals, they produce ______________________________ gas. 3. A basic solution contains more ___________________________________ ions than hydrogen. 4. What is the pH of blood, given the hydrogen ion concentration is 4.0 x 10-8 M? 5. In the Bronsted-Lowry model of acids and bases, an ________________________ is a hydrogen donor and a _______________________ is a hydrogen acceptor. 6. Which model states that an acid is a substance that contains hydrogen and ionizes to produce hydrogen ions? a. Arrhenius b. Bronsted-Lowry c. Lewis d. Hydrogen 7. What is the ph of 0.45 M of H2SO4? 8. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of 0.050 M H3PO4? 9.A solution that contains equal concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions is _______________________. 10. The pH scale allows scientists to define the acidity of a substance on a scale of _______________________. 11. An acid that can donate more than one hydrogen ion is called a _________________________________ acid. 12. Calculate the H concentration of an aqueous solution, given the concentration of OH– is 1 10–5 M and the ion product constant for water, KW is 1 10–14. 13. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution, given the pOH of the solution is 4.50 and the ion product constant for water, KW, is 1.00 10–14. 14. At 298 K, the H ion concentration of an aqueous solution is 1.00 10–5 M. What is the pH of the solution? 15. Calculate pH of an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride acid. Given the hydrogen ion concentration is 8.75 10–9 M. 16. The hydrogen ion concentration of a fruit juice is 2.5 10–5 M. What is the pH of the juice? 17. An aqueous solution has a pH of 2.7 at 298 K. Calculate the pOH of the aqueous solution. 18. Redox equations are ___________________________ when the total increase in oxidation numbers equals the total decrease in oxidation numbers. 19. Redox reactions involve the ________________________________ of electrons. 20. What is the oxidation number of chlorine in NaCl? 21. A/An _______________ agent is a substance that has the potential to cause another substance to be oxidized. 22. ____________________________ numbers are based on the distribution of electrons in a molecule. 23. Oxidation involves the ________________________________ of electrons. 24. Reduction involves the ________________________________ of electrons. 25. In a half-reaction, the charge on the reactant side must ____________________________ the charge on the product side. 26. For acidic solutions, __________________________________ ions are added to balance a halfreaction. 27. For basic solutions, ___________________________________ ions are added to balance a halfreaction. 28. Strong reducing agents are substances that easily _____________________________________ electrons. 29. The oxidation number of Na(s) is: 30. What is the oxidation number of oxygen? 31. What is the oxidation number of flouride? 32. What is the oxidation number of calcium? 33. What is the oxidation number of carbon? 34. Write the oxidation and reduction half-reactions for the redox reaction of Fe + F 35. Write the oxidation half-reactions for the redox reaction of 2 Silver(s) + Chlorine(g) Silver chloride. FeF ? 2 36. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution with a pOH of 4.5, given the ion product constant for water is 1.00 x 10-14. 37. At STP, the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 1.00 x 10-5 M. What is the pH of the solution? 38. Calculate the pH of a solution of HCl, given the hydrogen ion concentration is 8.87 x 10-9 M. 39. Calculate the pOH of a solution that has a pH of 2.7 at STP. 40. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of 0.650 M aqueous solution of Sodium hydroxide. The ionization product constant for water is 1.00 x 10-14. 41. Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration of a solution with a pH of 5.5, given the ion product constant for water is 1.00 x 10-14. 42. Explain what two type of solutions are being combined. Justify your answer. 43. Explain what two type of solutions are being combined. Justify your answer. 44. Using the pH scale, compare and contrast the nature of two solutions of your choosing. 45. How many times more acidic is acid rain compared to normal precipitation? 46. Examine the graph. Explain the point identified by the arrow. 47. Explain the variability on pH among the cities during years 1991 as compared to 1998. 48. Balance the following equation. 49. Identify the oxidized and reduced atoms in the following equation. 50. Calculate the net change in oxidation number of chlorine in the following redox reaction. 51. Balance the given redox reaction using changes in the oxidation number. 52. State what must be conserved in redox equations. 53. Determine the oxidation number of chlorine in NaCl. 54. Use the oxidation-reduction method to balance the given net ionic redox reaction. Cu(s) + NO3–(aq) + H+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + NO2(g) + H2O(l) 55. Place the appropriate coefficient in front of the formulas with the help of change in oxidation number, in the given net ionic redox reaction. TiCl62– + Zn Ti3+ + Cl– + Zn2+