The Integumentary System - Roden`s Anatomy & Physiology
advertisement

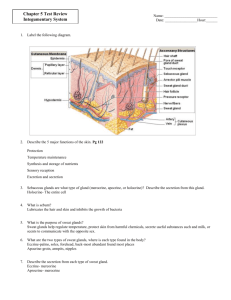
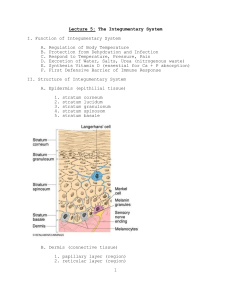
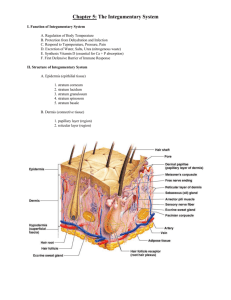
The Integumentary System Organs include: Hair, Skin, Nails and associated structures (vessels, nerves, glands) Skin structure I. Intro A. Main layers - from superficial to deep 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Hypodermis- not always considered as part of skin layers (but we will) II. Functions A. Protection] B. Sensation C. Movement without energy D. Excretion E. Vitamin D production 1. Skin absorbs vitamin D from the sun 2. Vit D moves into blood stream 3. Travels to kidney and liver 4. Converted to calcitriol 5. Calcitriol enters blood stream and regulates calcium and phosphorous F. Immunity G. Healing Wounds H. Body temperature homeostasis – vasoconstriction & vasodilation II. Epidermis A. keratinized stratified squamous ________________ B. avascular C. renews itself totally every 35-45 days D. main cell types 1. keratinocytes a. produce keratin - waterproofing protein b. originate in deep layers & get pushed to surface while becoming keratin filled c. cells are connected to each other by __________________________ and ___________________________ (two types of membrane specializations) d. cell production and keratinization accelerated in places of high friction and may form a callus 2. melanocytes a. produce melanin which colors skin & filters UV to protect DNA from mutation b. same number in everyone, but different amounts of pigment produced c. UV increases melanin production d. freckles & pigmented moles caused by: _______________________ E. Skin color 1. Determined by combo of: A. B. C. 2. Pigments A. melanin - 3 types (black, brown, yellow) B. Carotene - yellow to orange 1. lipid soluble vitamin A precursor 2. accumulates in ___________________and ______________ cells C. Hemoglobin 1. ________ color of oxygenated blood 2. more obviously detected in ____________ skin F. Diagnostics 1. skin color is often used as a first line diagnostic tool 2. Influenced by ______________ or _______________ states. 3. List color of skin AND possible causes for each of the following: a. cyanosis b. erythema c. albinism d. pallor e. jaundice f. bronzing g. bruises (hematomas) G. 5 strata (deep to superficial) 1. stratum basale a. highly ____________ b. ~25% melanocytes 2. stratum spinosum a. slightly mitotic b. contain Langerhan’s cells (macrophages) c. several layers of _________ sided cells )looks spiny) 3. stratum granulosum a. also contain Langerhan’s cells b. keratohyalin (helps form ____________) 4. stratum lucidum a. ONLY found mainly in palms & soles where epidermis is thicker b. completely keratinized c. contains closely packed, clear cells that contain gel-like substance ____________ 5. stratum corneum a. also completely keratinized b. tough, waterproofing protection c. __________ layer d. made up of _______ cells II. Dermis A. ____________layer of skin A. strong, flexible CT - 2 layers 1. papillary layer - contains ______________CT a. dermal papillae indent into epidermis 1. form fingerprints 2. important for grip 3. contains blood vessels 4. __________________ corpuscle – nerve (touch) receptors 2. reticular layer - ___________ ________________ CT a. Contains blood vessles, nerves, glands, adipose b. Collagen – prevents overstretching and tearing of skin c. Elastin – allows skin to stretch 1. Stretch marks - dermal tears VI. Hypodermis A. not usually considered part of skin B. also referred to as subcutaneous layer 1. site of subcutaneous injections - very vascular so medication can be absorbed into bloodstream over time C. attaches skin to underlying structures, shock absorption, insulation D. ________________ corpuscles - nerve endings responsible for sensitivity to deep pressure touch and high frequency vibration Skin Appendages I. Hair A. minor protective functions (retain heat, decrease sunburn, eyelashes protect eyes) B. structure of hair - chief regions 1. _________ – extends above the skin’s surface 2. follicle – extends into dermis 3. root – lies within the follicle 4. bulb – contains CT, vessels and nerves 5. sebaceous gland – lubricates hair 6. ________________ _________ _____________ – attached to follicle and contracts to move hair (hair growth, goosebumps) C. hair grows from root outward 1. influenced by: (in this order) a. ______________ - main influence b. hormones c. blood flow 2. baldness ( alopecia ) a. male pattern baldness - sex linked recessive genetic trait b. thinning – can be caused by medications, nutrition, stress, etc. D. pigment 1. caused by proportions of 3 melanin types 2. dark hair – true melanin 3. blonde and red – melanin with __________ and ___________ 4. gray/white hair - melanin replaced by air bubbles in shaft II. Nails A. Scale-like modifications of the epidermis B. Heavily keratinized C. Stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed to form nail matrix 1. Responsible for growth ( matrix region) D. Lack of pigment makes them colorless E. Lunula “___________ ___________” – area of cell growth (white semicircle at base of nail) F. Cuticle – area of skin that covers base of nail III. Sweat Glands A. eccrine glands - duct opens to skin surface 1. know sweat composition & pH 2. regulated by sympathic NS to assist in ______________________________ B. apocrine glands - duct opens into hair follicle 1. axillary & anogenital region - begin to function at puberty 2. know sweat composition C. ceruminous glands 1. external 1/3 of ear canal 2. produce ___________________________________ (cerumen) IV. Sebaceous (oil) glands A. functions 1. waterproofing 2. softens & lubricates skin and hair 3. bactericidal effect B. secretion stimulated by hormones Burns I. general info A. Define: ____________________________________________________ caused by heat, electricity, radiation, chemicals B. Two main dangers 1. ___________________________________ - loss of fluids & electrolytes lead to renal shutdown, circ. shock 2. ___________________________________ - mechanical barrier destroyed & immune system deficient C. Rule of Nines - know diagram - used to estimate percent of body burned so correct amount of body fluid can be replaced II. Partial thickness burns A. first-degree burn 1. epidermal damage 2. localized redness, swelling, pain 3. usually heal in 2-3 days - no scarring B. second-degree burn 1. damage to epidermis and dermis & structures within 2. appearance of blisters 3. skin regeneration in 3-4 weeks - some scarring 4. danger of infection III. Full thickness burns (third-degree) A. epidermis, dermis, hypodermis & all structures within are completely destroyed B. usually painless at site of burn due to destruction of sense receptors C. appear grayish-white, tan, brown, black, or deep cherry red D. surrounded by areas of 1st and 2nd degree burns - which are painful E. numerous treatments SKIN CANCER I. Intro A. B. C. D. caused by damage to _________________________ - chemical, radiation ____________________________ cell growth - benign vs. malignant ____________________________ cancers are skin cancers Know basic description of each II. Basal cell carcinoma A. affect cells in stratum basale 1. cannot produce ________________________________ 2. boundary lost between dermis and epidermis B. _________________________% of all skin cancers - least malignant C. seldom _____________________________________ - treated surgically or with radiation - 99% cure rate if early D. Signs 1. Pale marks 2. Reddish patches 3. Round, smooth growth with raised edge 4. Shiny bumps 5. Sores that don’t heal III. Squamous cell carcinoma A. 2nd most common B. higher risk – fair skin, light hair, blue/green eyes C. can metastasize if left untreated D. 1500 - 2000 deaths/year E. originates in __________________________________________________ F. Signs same as basal cell carcinoma IV. Malignant melanoma A. least common, most serious B. originates in _____________________________________________ C. metastasizes rapidly through lymphatic system D. early detection critical - 5 year survival rates 1. caught early - 90% 2. larger but localized - 55% 3. metastasized - 14% E. occurs at younger age mid to late teens - 20s to 30s - fastest rate of increase F. usually originates in mole 1. ABCD rule for detection ABCDV. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Prevention A. Incidence - ___________________________________ is main cause of all skin cancers B. Risk factors 1. Clothing 2. Location a. 1 in 7 Americans will develop a skin cancer b. SW U.S. - Sun Belt - 30% of population 3. Skin type a. light skinned esp. blonds, redheads, and those who tend to burn or freckle b. basal cell & squamous cell associated with cumulative sun exposure c. melanoma associated with acute exposure (sunburn) - burns alter DNA 4. types of UV a. UV-A - falls evenly throughout day a. resp. for aging, wrinkling, tanning, depletes collagen, burns cornea b. penetrates deeper - possible immune sys. damage b. UV - B - falls during midday - resp. for burning – melanoma C. Prevention 1. Wear sunscreen whenever outside or cover up 2. avoid midday sun between 10-2 and beware of reflected light 3. higher altitudes - every 1000 ft above sea level, radiation increases 4-5 % 4. Be cautious about tanning beds 5. Medications - tetracycline (antibiotics), Retin A, birth control, antidepressants, diuretics, and anti-inflammatories cause photosensitivity 6. avoid sunburns 7. examine skin regularly - remember ABCD rule – have full body check by dermatologist once a year OTHER DISORDERS A. Contact Dermatitis (________________) 1. inflammation, red, itchy skin 2. contact with allergen or irritant (ie. Poison ivy) 3. not contagious 4. over the counter meds; sometimes Rx 5. Prevention a. avoid _____________ and __________________ B. Blisters 1.epidermal cell injury or separation of epidermis from dermis C. Warts 1. Benign neoplasms, but can turn __________________ 2. Contagious 3. Remove by freezing, drying, laser therapy, chemicals D. Boils 1. Bacterial infection that infects hair follicles 2. Large, inflamed, pus-filled lesions E. Tinea 1. __________ infections (ringworm, jock itch, athlete’s foot) 2. Reddish discoloration, scaling, crusting 3. Treat with antifungal agent 4. Prevent recurrence by keeping skin dry F. Impetigo 1. Caused by bacterial infection 2. Mostly _____________ 3. Reddish discoloration turns into blisters and yellowish crusts 4. If turns systemic, it is life threatening G. Psoriasis 1. Cause is unknown, probably genetic 2. Triggered by trauma, infection, stress 3. Cutaneous inflammation, scaly lesions due to excessive rate of epithelial cell growth H. Urticaria (hives) 1. Raised, red lesions caused by blood vessel leakage 2. Severe itching 3. Causes (hypersensitivity, allergic reactions, physical irritants, systemic disease) I. Scleroderma 1. _____________________ disorder 2. Affects blood vessels and CT 3. Hard skin lesions 4. More common in ____________ J. Decubitus Ulcers (bedsores) 1. pressure sores 2. Lack of blood flow causes tissue damage K. Acne 1. clogged _____________________ follicles from abnormal shedding of skin cells 2. bacteria build-up in sebaceous glands 3. enhanced by hormones 4. over the counter meds; sometimes Rx 5. Prevention a. avoid using oils, greasy mosturizers, facewash, and makeup b. wash hands before applying makeup c. use non-scented ordinary mild soap d. keep hands away from face