Test 1, 2007
advertisement

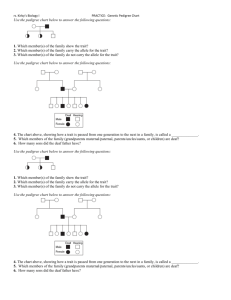
Test 1, Fall 2007 Part One. Short Answers Answer 5 of the following 6 questions completely in the space provided. You must show all work in order to receive full credit for the question. Make sure to define all gene symbols, and to indicate allele dominance relationships in your definitions. Name___________________________________ 1) An unaffected man whose father expresses a recessive trait marries an unaffected woman with a brother expressing the same recessive trait. The man's mother, youger brother and sister are all unaffected. The woman's parents are both unaffected. a) Draw the pedigree of this family in the space below, indicating all genotypes. b) What is the probability that the newlyweds' first child will express the trait? c) What is the probability that the newlyweds will have two heterozygous children? 2) A true-breeding red snapdragon was crossed to a true-breeding white snapdragon. The F1 progeny were red. When the F1 were selfed, the following F2 progeny were observed: Total 1850 red 670 pink 831 white 3351 (a) Using your own clearly defined genetic symbols, give the appropriate parental, F1 ,and F2 genotypes in order to explain the above results. (b) What phenotypic ratio would be expected from a testcross of an F1 snapdragon? (c) Suppose the white phenotype is now lethal. What phenotypic ratio would be expected from a cross between F1 individuals? 3) The following coat colors are known to be determined by alleles at one locus in horses: palomino cremello chestnut = golden coat with lighter mane and tail = almost white = brown The following table gives ratios obtained in matings of the above varieties: Cross 1 2 3 Parents cremello x cremello chestnut x chestnut cremello x chestnut Offspring all cremello all chestnut all palomino 4 palomino x palomino 1/4 = chestnut 1/2 = palomino 1/4 = cremello Assign gene symbols for the genetic control of coat color on the basis of these data. Diagram the last two matings, giving the genotypes of all individuals. 4) Normal diploid somatic (body) cells of the mosquito, Culex pipiens, contain six chromosomes (two copies each of three chromosomes, that are designated by the capital letters A, B and C). Assign the symbols , , and to the three homologous chromosomal pairs. The "m" superscript indicates that the homologue is maternally derived, while the "p" indicates a paternally derived homologue. (a) In each of the nuclei below, draw the expected configuration of all chromosomes, making sure to label each homolog using the symbols defined above, Mitotic Metaphase Metaphase of Meiosis I Metaphase of Meiosis II (b) The stage at which "sister chromatids go to opposite poles" immediately follows which of the above stage(s) (more than one answer can be correct)? (c) Assuming that all nuclear DNA is restricted to chromosomes and that the amount of nuclear DNA essentially doubles during the S phase of interphase, how much nuclear DNA would be present in each nucleus listed above? Note: assume that the G1 nucleus (just prior to S phase) of a mosquito cell contains 3.0 X 10-12 grams of DNA. 5) In the house mouse coat color is genetically controlled. The results of a series of matings involving yellow, tan, black and blackish-tan are shown. Give a complete genetic explanation of these results, including the genotypes of all individuals. Cross Parents Offspring 1 yellow x yellow 391 yellow : 132 black 2 tan x yellow 214 tan : 210 yellow 3 yellow x yellow 284 yellow : 108 tan 4 yellow x yellow 306 yellow: 110 blackish-tan 5 blackish-tan x blackish-tan 110 black: 210 blackish-tan:101 tan 6 blackish x tan all blackish-tan 7 black x blackish-tan 141 black: 144 blackish-tan 6) Two plants are crossed; their genotypes are A/A;B/b;C/c and a/a;B/b;c/c. What phenotypic ratio would be expected among the progeny of this cross, given the following conditions: Assume that allele A codes for color with A being green and a being white; the B allele codes for pod size with B being big and b being small; and allele C codes for wrinkled leaves with C being wrinkled and c being smooth. a) All three genes display complete dominance. b) All three genes display incomplete dominance, with the Aa, Bb and Cc phenotypes of pale green, medium, and crinkled, respectively. Part 2: All students must answer this question. You and your lab partner decide to test several members of the Borden family, who are depicted in the pedigree below, for the presence of an RFLP associated with high susceptibility to MODI-1 Type 2 Diabetes (the trait depicted in the pedigree). Each family member's DNA was digested with Eco RI, run out on an agarose gel using standard procedures, and Southern blotted. Finally, a DNA probe was used to assay for the presence or absence of a marker gene (A) known to be very closely linked to the MODI-1 susceptibility gene. Answer all of the questions on the next page based on the resulting data: Figure 1. The Borden Family Pedigree II-1 II-2 II-3 II-4 III-2 III-4 III-5 III-6 III-7 III-8 Figure 2. RFLP analysis of Borden family DNA. The identity of each family member in the analysis is indicated by the pedigree number above each well. a) Is this trait inherited as a dominant or as a recessive allele? Explain b) Is this trait autosomal or X-linked? Explain c) Write the genotypes of each family member on the pedigree above. d) Which of the two molecular alleles - A' or A'' - is linked to the MODI-1 susceptibility allele? Explain. e) What is an RFLP? f) Individuals III-4 and III-5 come to you wanting to know what the probability is that their children will carry the MODI-1 allele. What do you tell them? Make sure you address any issues involved in using linked markers for genetic testing, rather than the gene itself.