tissue grafting
advertisement

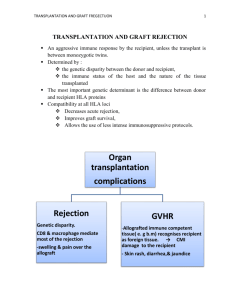
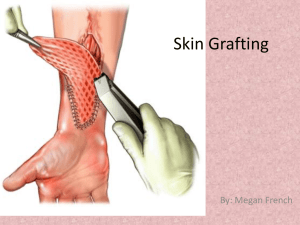
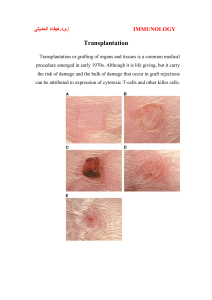
TISSUE GRAFTING Autografts Any tissue transferred from one site to another in the same individual (iliac bone from the pelvis is commonly used to supplement the fusion mass). Tissue taken from one part of an individual organism's body and then moved or transplanted to another location within that same organism. Rejection is rarely (if ever) a problem since the donor and recipient are the same individual. Skin transplants are a common example. Allograft Graft of a piece of tissue or organ from one individual to another of the same species Homograft: tissue or organ transplanted from a donor of the same species but different genetic makeup; recipient's immune system must be suppressed to prevent rejection of the graft Isografts A graft of tissue between genetically identical individuals Xenografts -zen´o-graft. A graft of tissue transplanted between animals of different species. Called also heterograft, heterologous graft, and heteroplastic graft. Xenotransplantation is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another such as from pigs to humans. (See Medical grafting.) Such cells, tissues or organs are called Xenografts (xenotransplants). The term allo transplantation refers to a same-species transplant. Graft retention – methods - To prevent tissue rejection drugs called ‘Immunosuppressants” are administered after the organ transplantation. The most commonly used drugs are Antimetabolites, Alkylating agents, Toxic antibodies etc. Radiation, Cyclosporin FK 506, Antilymphocyte globulins, Adrenal corticoids, Azothioprine etc are also used as Immunosuppressants. These drugs hinder the development of T lymphocytes. Graft rejection – methods- Tissue rejection is due to cell mediated immune system of T cells of the recipient consider the transplanted organ as ‘Non self’. The process of rejection starts after 10-14 days of transplantation. This is indicated by the accumulation of T cells in the blood vessels of the transplanted organ. This prevents normal blood flow to the organ leading to its rejection. The MHC also stimulates the production