Unit 3 Chemistry – Reactions of Alkanes
advertisement

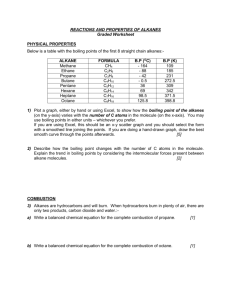
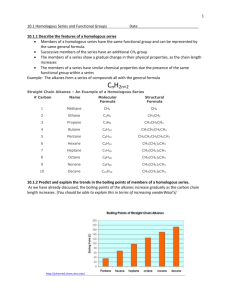
Unit 3 Chemistry – Reactions of Alkanes and alkenes Combustion alkanes are flammable and used as fuels complete combustion [reaction with excess oxygen from the air] produces water and carbon dioxide … there are rules for writing the balanced equation for the combustion reaction … unbalanced reaction equation … C2H6(g) + O2(g) balance the C atoms first … C2H6(g) + O2(g) balance the H atoms next … C2H6(g) + O2(g) finally, balance the O atoms … C2H6(g) + 3½O2(g) if necessary, multiply by 2 … 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) H2O(g) + CO2(g) H2O(g) + 2CO2(g) 3H2O(g) + 2CO2(g) 3H2O(g) + 2CO2(g) 6H2O(g) + 4CO2(g) alkenes undergo similar combustion … C3H6(g) + 4½O2(g) 3H2O(g) + 3CO2(g) Substitution of alkanes a substitution reaction of an alkane involves one or more of the H atoms on the alkane being replaced by a different atom or functional group substitution reactions involve:1. breaking the strong C–H covalent bond, 2. forming a new bond with the substituting atom Example: Chlorination of Ethane the effect of heat or UV light on a chlorine molecule is to break the Cl–Cl bond, forming .Cl- free radicals that attack the C–H bonds in the alkane one or more of the H atoms on the ethane are replaced by the attacking .Cl-, resulting in a mixture of chlorinated hydrocarbons. CH3CH3(g) + Cl2(g) CH3CH2Cl(g) + HCl(g) chloroethane CH3CH3(g) + 2Cl2(g) CH2ClCH2Cl(g) + 2HCl(g) 1,2-dichloethane General equation: R–H + Cl2 R–Cl + HCl ------------------------------------------------------------------------Reactions of Alkenes Properties of ethene [ 1st member of homologous series of alkenes ] unsaturated [has C=C]; non polar molecule flammable gas insoluble in water undergoes addition reactions Addition Reactions of Alkenes the C=C double bond makes alkenes more reactive that alkanes in an addition reaction, a small molecule [ such as Cl2, Br2, H2, H2O, HCl ] is able to add itself across the double bond, changing the double bond to a single bond and forming a single product CH2=CH2 + Br2 CH2(Br)CH2(Br) H H H H C=C H C H C H H Br Br – Br Br 1,2 dibromoethane Example: Addition of water to ethane ethane reacts with steam, using a phosphoric acid catalyst to make ethanol C2H4(g) + H2O(g) CH3CH2OH(g) H H H H H3PO4 C=C H C H 300oC C H H OH H H – OH ethanol Addition Polymerisation a large number of alkene molecules [monomers] can undergo a chain of addition reactions to form a very large molecule [polymer] this polymer forming addition reaction is called addition polymerisation R n H C=C H H R = -H …polyethene; R = -CH3 …polypropene; R = -C6H6 … polystyrene R H R H R ---– C– C– C– C– C –--H H H H H R = -Cl … polychloroethene [PVC] R = -OH … polyvinylalcohol [PVA] Reactions of Alkanes and Alkenes 1. Write the balanced molecular equation for the complete combustion of the following alkane and alkene in excess air:(a) 2,3-dimethyl pentane (b) 2,3-dimethyl but-1-ene ------------------------------------------------------------------------2. When propane and chlorine gas is mixed and exposed to ultraviolet light, a mixture of chlorinated alkanes, including 1,2-dichloropropane, is produced. (a) Name the reaction type that forms 1,2-dichloropropane. (b) What role does the UV light play in the reaction? (c) Draw the structural formula of 1,2-dichloropropane. (d) Write a balanced molecular equation for the reaction that forms 1,2-dichloropropane. (e) suggest how the 1,2-dichloropropane could be separated from the reaction mixture. ------------------------------------------------------------------------3. When propene and chlorine gas is mixed, a single reaction product 1,2-dichloropropane is formed. (a) Name the reaction type that forms 1,2-dichloropropane. (b) Write a balanced molecular equation for the reaction that forms 1,2-dichloropropane. (c) Compare the reactions that occur between propene and chlorine, and between propane and chlorine, explaining why a single reaction product is formed in the former and a mixture of reaction products is formed in the latter. -----------------------------------------------------------------------4. Explain how derivatives of ethene [XCH=CH2, where X = -OH, -Cl, -C6H5 etc.] are the basis for polymers such as PVA, PVC and polystyrene. -------------------------------------------------------------------------