sampletest1
advertisement

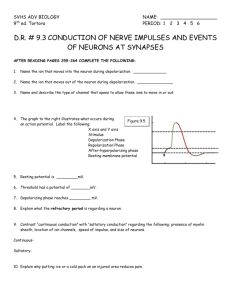
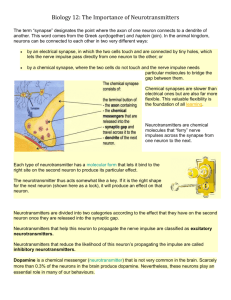
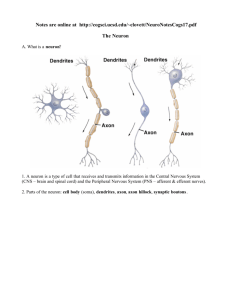
Sample Test 1 1 Which of the following are found in only myelinated neurons? a. Dendritic spines b. Nodes of Ranvier c. Dendritic buds d. Axon hillocks e. Terminal buttons 2 Which of the following are thought to play a role in the blood-brain barrier? a. astroglia b. oligodendroglia c. satellite cells d. a and b e. a and c 3 Myelination a. causes cancer b. penetrates the blood-brain barrier c. occurs only on Schwann cells d. increases the speed of axonal transmission e. increases the speed of synaptic transmission 4 At rest, a. A neuron has a membrane potential of about -70 mV b. The electrical charge outside the neuron is 70 mV less than inside the neuron c. A neuron is polarized d. All of the above e. a and c 5 When a neuron is at rest, there are more a. Na+ ions outside the neuron than inside the neuron b. K+ ions outside the neuron than inside the neuron c. Cl- ions outside the neuron than inside the neuron d. a and c e. b and c 6 Na+ ions are continuously forced into neurons by a. Their high internal concentration b. Their high external concentration c. The negative resting potential d. b and c e. none of the above 7 Action potentials originate at the a. Terminal buttons b. Synapses c. Axon hillock d. Node of ranvier e. Nucleus 8 A neuron fires when a. Its sodium-potassium pumps are stimulated b. There is an EPSP c. There is an IPSP d. The degree of depolarization of the axon hillock exceeds the threshold of activation e. Its buttons are stimulated 9 Action potentials are initiated by the a. Opening of voltage-activated sodium channels b. Closing of ligand-activated chloride channels c. Closing of ligand-activated potassium channels d. Opening of ligand-activated potassium channels e. Closing of voltage-activated calcium channels 10 Action potentials spreading down an axon do not change direction because right behind the action potentials is a wave of a. Potassium b. Depolarization c. Absolute refractoriness d. Sodium e. Cytoplasm 11 Conduction of action potentials in myelinated axons a. Is faster than in unmyelinated axons b. Is slower than in unmyelinated axons c. Requires more energy than in unmyleinated axons d. a and c 12 Neurotransmitter release occurs through the process of a. excitotosis b. exocytosis c. synthesis d. metabolism e. endocytosis 13 The release of neurotransmitter molecules is often triggered by a. an efflux of sodium ions b. an influx of calcium ions c. the sodium-potassium pump d. the arrival of an AP at the axon hillock e. the release of calcium ions from the buttons 14 Ionotropic receptors are linked to a. ribosomes b. neurotransmitters c. vesicles d. G proteins e. ligand-activated ion channels 15 Metabotropic receptors are linked to a. ligand-activated ion channels b. signal proteins and G proteins c. ionotropic receptors d. vesicles e. receptor subtypes 16 In comparison to ionotropic receptors, metabotropic receptors a. are more prevalent b. produce longer lasting effects c. produce effects that are more diffuse d. produce effects that take longer to develop e. all of the above 17 Autoreceptors a. are ligands for their neuron's own neurotransmitter b. are located on postsynaptic membranes c. do not bind to neurotransmitter molecules d. commonly found in synaptic vesicles 18 GABA, glycine, aspartate and glutamate are a. amino acid neurotransmitters b. small-molecule neurotransmitters c. transmitters at fast-acting, directed synapses d. building blocks of proteins e. all of the above 19 Monoamines are divided into two groups a. aminoacids and peptides b. peptides and proteins c. peptides and polypeptides d. catecholamines and indolamines e. catecholamines and dopamine 20 All catecholamines are synthesized from a. tyrosine b. tryptophan c. dopamine d. norepinephrine e. epinephrine 21 Neuromodulators are neurotransmitters that a. are always inhibitory b. are usually excitatory c. increase or decrease the sensitivity of other neurons to the local effects of other neurotransmitters d. are not amino acids e. c and d