Unit 2 Review – The Biological Basis of Human Behaviour
advertisement
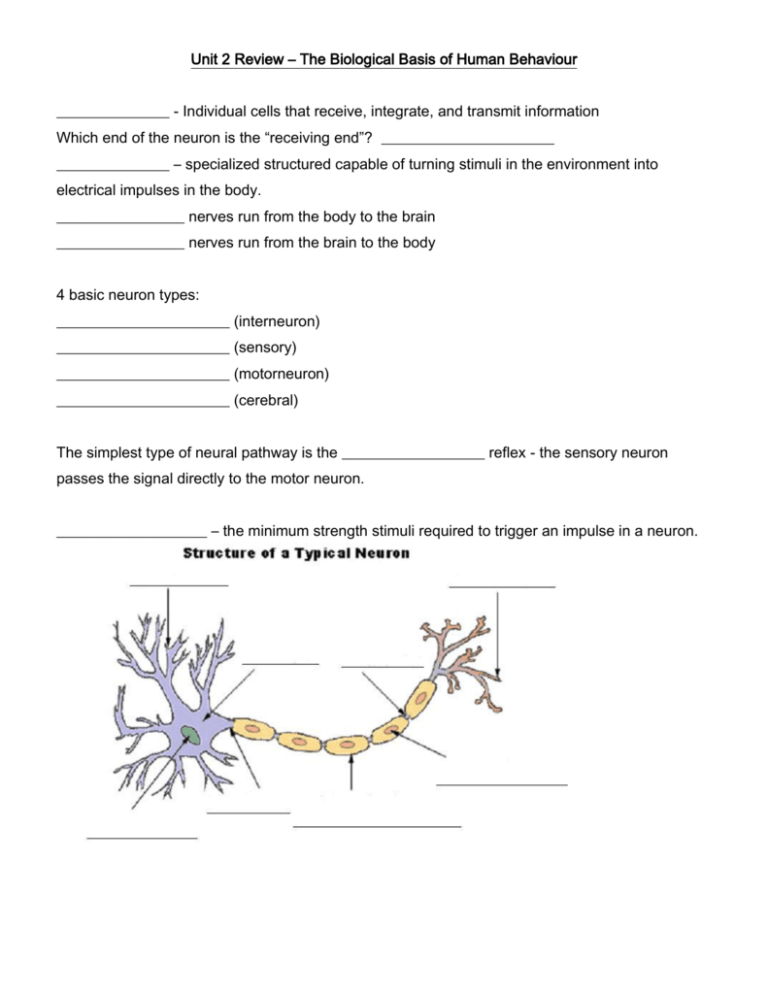
Unit 2 Review – The Biological Basis of Human Behaviour _______________ - Individual cells that receive, integrate, and transmit information Which end of the neuron is the “receiving end”? _______________________ _______________ – specialized structured capable of turning stimuli in the environment into electrical impulses in the body. _________________ nerves run from the body to the brain _________________ nerves run from the brain to the body 4 basic neuron types: _______________________ (interneuron) _______________________ (sensory) _______________________ (motorneuron) _______________________ (cerebral) The simplest type of neural pathway is the ___________________ reflex - the sensory neuron passes the signal directly to the motor neuron. ____________________ – the minimum strength stimuli required to trigger an impulse in a neuron. • ____________________ neurons carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) into the central nervous system. • ____________________ neurons (motoneurons) carry signals from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. • ____________________ connect various neurons within the brain and spinal cord. • Threshold – the minimum intensity required to trigger a chain reaction in a neuron. (55 millivolts in mammals) Neuron Functioning The signal that travels the length of the neuron is actually a change in the _______________ of the outside of the axon. The resting charge on the cell is _______ millivolts. This charge is created by a membrane around the cell that keeps positively charged __________ ions (Na+) on the outside of the cell and negatively charged ________________ ions (K-) in the inside. Once the threshold is achieved in the cell body, the protein “________” of the axon open and Na+ ions rush in. For ___ millisecond, the outside of the axon body becomes ____ and the interior becomes _____. The polarity of the axon body is ___________ as the threshold is achieved. The gates quickly ___________ and ______+ ions slowly leak out and the cell begins to actively pump ______+ ions back out. This returns the cell to it’s resting state. The ____________________ of the cell produces electric currents that stimulate the ___________________ value in neighboring regions as the impulse travels down the axon. _____________________ Law – the stimulus does not provide the energy of the for the nervous impulse. This means that a stronger sensation is caused by a_____________________________________, not a___________________________. Synaptic Transmission 1920 – ____________________ proved the existence of chemical substances that communicated between body structures by stimulating a _______________ in a jar of water and then pouring that water over another jar and observing the effect. The second ___________________ reacted to the fluid by ____________________ ______________________________________________. Proving that transmission from one neuron to the next involved some kind of chemical. _____________________ – the gap between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of the receiving neuron. _________________________________ – tiny sacs of neurotransmitter that erupt into the synapse when a signal is triggered. _______________________________ - chemical substance that is released at the terminal end of the neuron that travel across the synapse and have an excitory or inhibitory effect on the adjacent neuron. As each neurotransmitter crosses the synapse, it lands on specialized _________________________________ on the ________________________ of the next neuron. The receptors then lower the ______________________________ of the neuron. As each neurotransmitter reaches a receptor, the _________________________ is lowered more and more until the ______________________ is reached and an ________________________ is triggered. __________ and ________ model – each neurotransmitter is paired with a specific receptor cell and will not react to another. Excess transmitter in the synapse is gathered and reabsorbed in a process known as ________________________. Neurotransmitters and their Function List four neurotransmitters and Function explain their function ___________________________ Yeah, Dopamine ___________________________ GABA List five kinds of drugs and explain how they work MAOIs _________________________ _________________________ Curare ___________________________ Function Hormones _________________________ – the optimal state of the body maintained by the endocrine system Link the hormone to the gland to the role Hormone Gland Testosterone ______________ _________________ Ovaries Cortical steroids ______________ Adrenaline ______________ Oxytocin ______________ ______________ Thyroid Progesterone ______________ Purpose Brain structures and localization Central Nervous System – comprised of the _______________________ and ___________________ the role of the CNS is to _____________________________ __________________________. Peripheral Nervous System – its role is to _______________________________ _____________________________________________________________. 2 Functions of the PNS: ____________________ division – controls the skeletal system and transmissions from the sense organs ____________________ division – serves to control basic life processes. 2 structures attached to the brain stem: 3 portions of the brain: Hindbrain is comprised of the: _________________ - heartbeat, circulation, respiration… _________________– balance and muscular coordination Midbrain is comprised of the: ________________________ – activates other parts of the brain and regulates ____________. Forebrain is comprised of the: Thalamus –________________________________________________________________ Hypothalamus – ____________________________________________________________ Cerebral cortex –____________________________________________________________ which is divided into four lobes – _______________,_______________,_________________, and ______________________. Limbic system – in charge of ________________________ and _________________ Cortex divided into 2 zones: ___________________ areas – receives signals from sensory organs and transmit signals to the muscles ___________________ areas – remaining 2/3rds of the cortex – higher mental functions; speech, memory, thinking, and planning Motor ________________ – a schema of the body represented on the cortex Sensory _________________ – a schema of the body as it is represented on the cortex for sensory attention. Visual cortex, auditory cortex, and association areas can be discovered by _________________, _________, _________, and _________ scans. Brain disorders – define each term: Aphasia:_____________________________________________________________________ Apraxias:_____________________________________________________________________ Agnosia: _____________________________________________________________________ Split-Brain functioning:__________________________________________________________ Unilateral neglect:______________________________________________________________ The association areas of the cerebral cortex can be mapped through all of the following processes EXCEPT... a) PET scans b) Lesioning c) CAT scans d) Drug therapy Jane has suffered a stroke that has damaged her motor projection region of her temporal lobe, which of the following symptoms would you expect her to have? a) Difficulty breathing normally b) Trouble remembering names c) Inability to organize objects in her environment spatially d) A limp What part of the brain does a teenager presumably lack according to Yerglin and Todd which causes them to lack good judgements of future consequence? a) b) c) d) visual cortex limbic system hippocampus prefrontal cortex After his car accident, Fred can no longer form words, or comprehend language. He most likely has: a) Aphasia b) Apraxias c) Agnosia d) Unilateral neglect Stanley has recently had a large portion of his brain removed due to a tumour, now when his family brings flowers to his bedside, he says “Thank you for these colourful, multifolded, satiny objects with long green projections sticking out from their bottoms!” Stanley’s strange response can be most likely attributed to: a) Aphasia b) Apraxias c) Agnosia d) Unilateral neglect What is one weakness of Computed Tomography images (CT scans) a) it does not show enough detail to see tumors or lesions b) it is dangerous to inject things like radioactive dyes c) it cannot show structural changes in the brain d) it does not show brain activity Analyze the following image. What kind of imaging technology is presented above? a) fMRI b) MRI c) Electroencephalogram d) PET scan If you had metal implants or a pacemaker, which of the following medical scans could be damaging to you? a) fMRI b) EEG c) PET d) none of the above, they are all safe Genetic Psychology Analyze the following data chart carefully Rate of concordance of schizophrenia Monozygotic male 0.35 Monozygotic female 0.36 Dizygotic male 0.05 Dizygotic female 0.06 According to the above chart… a) there is a strong indication that schizophrenia is a result of environmental factors b) there is a strong indication that schizophrenia is a result of genetic factors c) there is a strong indication that schizophrenia is acquired (you catch it) rather than innate (you’re born with it) d) nothing conclusive was found with the data According to the above chart… a) girls get schizophrenia more often than males b) boys get schizophrenia more often than girls c) there is no significant difference between boys and girls when it comes to schizophrenia d) schizophrenia is acquired from the mother’s side of the family Evolutionary Psychology If we accept that behaviours can be linked in some way to ____________________________ Then….. Based on the principles of _______________ __________________________ it follows that behaviours that are ____________________________ would cause a greater chance of passing on _______________ to the next generation whereas behaviours that are ________________________ would not. According to Lu, Chang et al. 2012, if a man approaches a woman and asks her to dance while staring at her hips… a) he’s interested in a long term relationship in which he will invest heavily in any potential offspring b) he’s interested in dancing c) he’s only after one thing (wink wink) and when he gets it he’s OUT like bellbottoms! d) he’s interested in your friend, not you According to Fussell and Stollery (2012), when a man gets cheated on, he will only dump his partner if they actually had sex with someone else, on the other hand – a woman who gets cheated on will… a) dump the guy whether sex occurred or not b) stay with the guy because she is interested in his long term investment in her offspring c) find someone else to cheat on with in revenge to increase the variety of her potential mates d) neglect her own offspring because she doubts its true origins Possible long answer questions… How do biological conditions influence our behavior? Give at least three ways and cite specific examples Should schools bring back corporal punishment? Choose a side in this debate and defend your position using the information we have learned in this unit. Can we help who we are and how we behave or do we really not have a choice in what we do? Give your best, most thought our answer and justify your position with specific references to the material from this unit.