file
advertisement

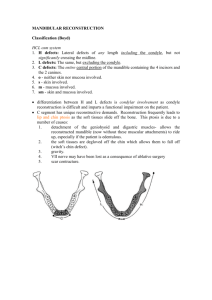
DESMOPLASTIC FIBROMA OF THE MANDIBLE IN PEDIATRIC PATIENT: RESECTION AND RECONSTRUCTION WITH FIVE YEAR FOLLOW UP Introduction and objectives The desmoplastic fibroma (DF) of bone is considered a benign yet locally aggressive tumor of fibroblastic origin, comprising less than 1% of all bone tumors. Any bone can be affected, recent reviews show a total of 152 gnathic cases in english literature. The objectives of this article are to report a case of DF in the mandible of a pediatric patient, and make an update about the most important features of this lesion. Methods A 3y 7m old boy was sent for maxillofacial evaluation of a painless mass in his right cheek. Computed tomography informed an expansive intraosseous lesion in the right mandibular body and ramus. Internal structure of the tumor showed mixed density. Cortical bone was thin without periosteal reaction. The patient was admitted for surgery by a combined team of pediatric, plastic and maxillofacial surgeons. Operation consisted in hemimandibulectomy and immediate reconstruction with free fibula flap. Pathological examination identified DF of the jaw. At a 5 year period of follow up, clinical and imaginological examination show no recurrence of the tumor. Discussion An important number of DF cases reported presented in younger people, but only a few correspond to patients less than 4 years old. Surgery with complete excision is the treatment of choice in order to decrease recurrence and morbidity. Mandibular reconstruction in these cases is mandatory to ensure correct craniofacial development. Conclusions Fibro-osseous lesions of the maxillofacial bones share overlapping clinical, radiographic and histopathologic features that may difficult the diagnosis. DF often mimics other pathologies of the jaws; the differential diagnosis must consider entities with the same clinical presentation, and radiolucent images in the radiographic exams. Complete resection and reconstruction with a fibula flap demonstrated to be a satisfactory treatment option, with low morbidity and excellent results in a pediatric patient.