Chapter 5 * Gases
advertisement

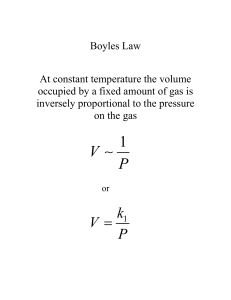
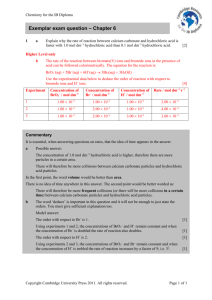
Chapter 5 – Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Distances between particles are so small they are assumed to be negligible. Particles are in constant motion therefore collisions are the cause of pressure. Particles do not attract or repel each other. Average kinetic energy of gas particles is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature. STP= standard temperature and pressure (273K=0°c and 1 atm) *at STP 1 mol of gas has volume of 22.4 L Boyle’s Law P₁V₁=P₂V₂ Volume of gas at constant temperature varies inversely with pressure. Charles’ Law - V₁/T₁=V₂/T₂ Volume of sample of gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to temperature in Kelvin’s. Avogadro’s Law - V₁/n₁=V₂/n₂ Equal volume of gases at same temperature and pressure have same number of particles. Gay-Lussac’s Law - P₁/T₁=P₂/T₂ Pressure of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume varies directly with the Kelvin temperature. Combined Gas Law - P₁V₁/T₁n₁=P₂V₂/T₂n₂ Ideal Gas Law - PV=nRT P=pressure (atm) where 760 torr=760mmHg=1atm v= volume (L) T=temperature (Kelvin) where K=°c+273 R= 0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K) n=moles (mol) Other Form of Equation - PV=(m/μ)RT m=mass (g) μ=molar mass (g/mol) Density Form of Equation - D=Pμ/RT (g/L) Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure - Ptotal = Pa+Pb+Pc... For a mixture of gases in a container, the total pressure exerted is the sum of the pressure of each gas if it were alone. Mole Fraction - Xa = na/ntotal = Pa/Ptotal The ratio of the number of moles of a given component to the total number of moles. Gas Collection Over Water - Ptotal = Pgas+Pvh2o Total pressure is equal to pressure of gas plus the pressure of water vapor. Math for Gas Molecules - KE=(3/2)RT KE units = J/Mol R= 8.31 J/mol·K Root Mean Square Velocity - Square Root of (3kT/m) or Square Root of (3RT/μ) r= 8.31 J/mol·K k= 1.381x10^-23 J/K Boltzmann’s Constant Urms units = m/s m=mass (kg) μ= molar mass (kg/mol) Diffusion - the mixing of gases equation : r₁/r₂ = square root of (μ₂/μ₁) where r = rate in units of volume / time Effusion - passage of gas through a tiny opening same equation as diffusion