ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LEARNING GOALS TIER 1 Explain what an
advertisement

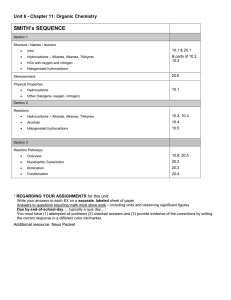
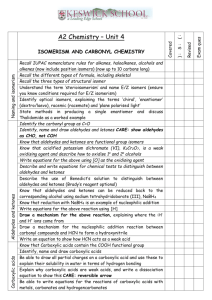
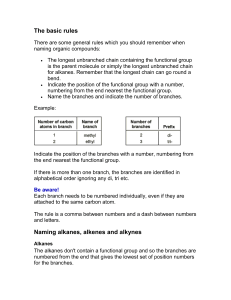
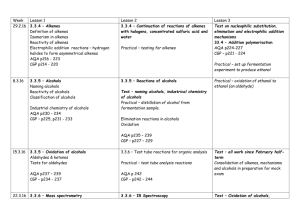
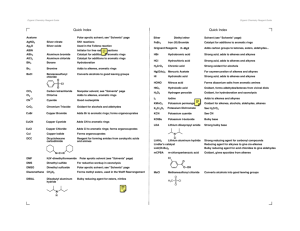
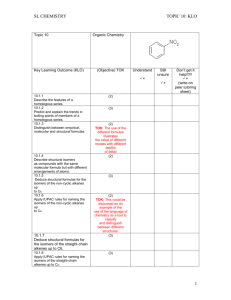
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LEARNING GOALS TIER 1 Explain what an empirical formula is Explain what a molecular formula is Explain what a structural formula is Explain what an isomer is Know the prefixes used in organic chemistry up to ten Explain what is meant by a homologous series TIER 2 Recognize the following functional group: alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, esters, carboxylic acid, benzene rings, amino groups and halides Identify primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms in alcohols and halogenalkanes Identify between an alkane, alkene and alkyne TIER 3 Deduce structural formulas for isomers of non-cyclic alkanes up to six carbons Apply the IUPAC rules for isomers of the straight-chain alkane up to six carbons Deduce structural formulas for alkenes and alkynes with only one double and triple bond respectively. Apply the IUPAC rules for naming alkenes and alkynes with only one double and triple bond respectively. TIER 4 Deduce structural formulas for compounds up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional groups: alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, esters, carboxylic acid, benzene rings, amino groups and halides Apply the IUPAC rules for naming compounds up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional groups: alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, esters, carboxylic acid, benzene rings, amino groups and halides TIER 5 Predict and explain trends in boiling points of members of a homologous series Discuss the volatility and solubility in water of compounds containing the functional groups: compounds up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional groups: alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acid, and halides . Describe using equations the complete and incomplete combustion of alkanes Describe using equations the reactions of methane and ethane with chlorine and bromine Describe using equations the reaction of alkenes with hydrogen and halogens Describe using equations, the reactions of symmetrical alkenes with hydrogen halides and water Distinguish between alkanes and alkenes using bromine water Describe using equations the complete combustion of alcohol Describe using equations the oxidation of alcohols Describe using equations the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols Describe using equations the substitution reactions of halogenoalkanes with sodium hydroxide TIER 6 Explain the reactions of methane and ethane with chlorine and bromine in terms of a free radical mechanism Outline the polymerization of alkenes Outline the economic importance of the reaction of alkenes Explain the substitution reactions of halogenoalkanes with sodium hydroxide in terms of SN1 and SN2 mechanisms Deduce reaction pathways given the starting materials and the product.