Personality factors in anomalous experience.
advertisement
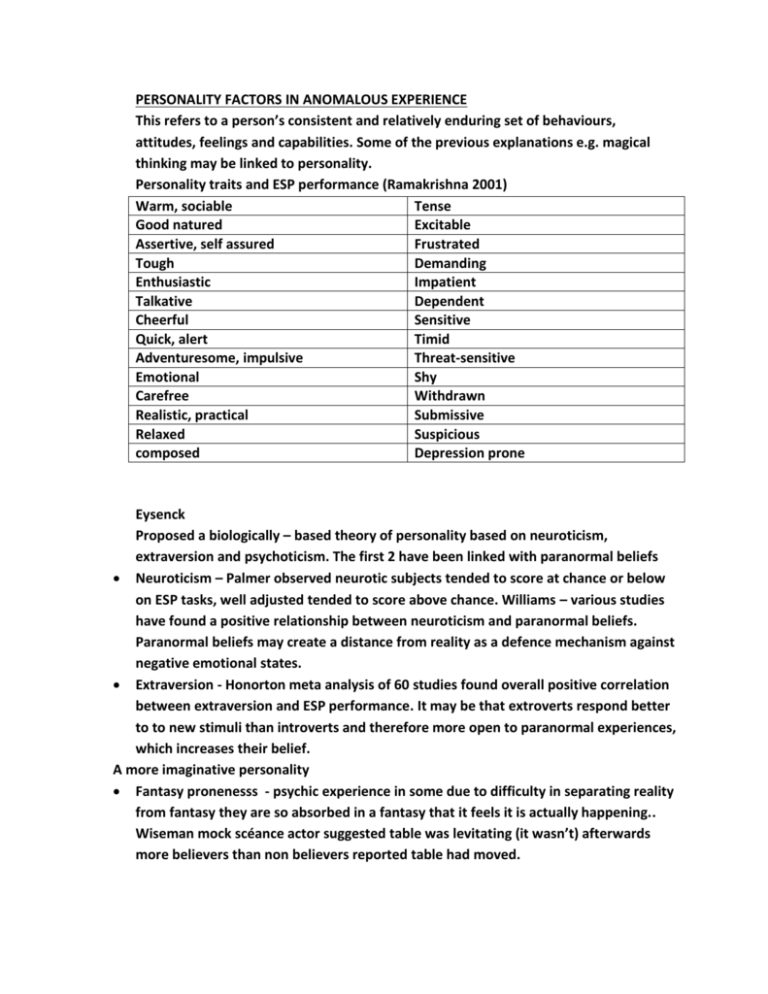
PERSONALITY FACTORS IN ANOMALOUS EXPERIENCE This refers to a person’s consistent and relatively enduring set of behaviours, attitudes, feelings and capabilities. Some of the previous explanations e.g. magical thinking may be linked to personality. Personality traits and ESP performance (Ramakrishna 2001) Warm, sociable Tense Good natured Excitable Assertive, self assured Frustrated Tough Demanding Enthusiastic Impatient Talkative Dependent Cheerful Sensitive Quick, alert Timid Adventuresome, impulsive Threat-sensitive Emotional Shy Carefree Withdrawn Realistic, practical Submissive Relaxed Suspicious composed Depression prone Eysenck Proposed a biologically – based theory of personality based on neuroticism, extraversion and psychoticism. The first 2 have been linked with paranormal beliefs Neuroticism – Palmer observed neurotic subjects tended to score at chance or below on ESP tasks, well adjusted tended to score above chance. Williams – various studies have found a positive relationship between neuroticism and paranormal beliefs. Paranormal beliefs may create a distance from reality as a defence mechanism against negative emotional states. Extraversion - Honorton meta analysis of 60 studies found overall positive correlation between extraversion and ESP performance. It may be that extroverts respond better to to new stimuli than introverts and therefore more open to paranormal experiences, which increases their belief. A more imaginative personality Fantasy pronenesss - psychic experience in some due to difficulty in separating reality from fantasy they are so absorbed in a fantasy that it feels it is actually happening.. Wiseman mock scéance actor suggested table was levitating (it wasn’t) afterwards more believers than non believers reported table had moved. Suggestibility – these people are more easily hypnotised. Hergovich suggested this may be linked with paranormal beliefs because some involve deception, and suggestible people are more prone to accept these phenomena as real e.g. psychic mediumship. Creative personality – Thalbourne, meta – analysis of 15 studies found a correlation between creative personality and paranormal beliefs. Other possibilities Schizotpy personality traits related to schizophrenia Irwin and Green found a link Evaluation. Research appears to imply belief in paranormal is pathological and links have not be found with all mental disorders e.g. bipolar disorder. Link with schizotpy not surprising as a characteristic is ‘having magical or superstitious belief’. Auton – some research accentuated the positive e.g. positive correlation between self actualisation and psi belief. Locus of control – people with external locus of control more likely to believe in paranormal than those with internal locus of control AO2 Correlations tend to depend on hoe belief is measured. Many studies use Paranormal Belief Scale, which has 7 sub scales e.g. psi, traditional religious beliefs. each of these sub –scales may produce different correlations. Neuroticism. Watson and Watt focused on superstition sub-scale. Found neuroticism was only related to certain paranormal beliefs – bad luck superstition. They noted that actual questions used in PBS to assess belief in superstition were related to negative superstitions. Suggesting previous research may lack validity because of the way paranormal relief is assessed. Psychoticism. – Francis tested 20000 UK children aged 13 – 15 and found high psychoticism did correlate with some paranormal beliefs – e.g. astrology and PK but not traditional religious beliefs. Locus of control - Tobacyk relationship between belief and locus of control depends on type of belief. Superstition and spiritualism positive for external PK negatively. Davies however found positive correlation with internal locus and belief. Unreliability of results may be in part due to the way belief is measured. Groth-Marnat and Pegden found greater external locus of control associated with spirituality and precognition, and internal associated with superstition. Link to false memories. People with strong imaginations, fantasy prone or suggestible envision events e.g. UFO’s and then believe them to be true as susceptible to false memories – a memory of something that didn’t happen but feels as if it is real. French and Wilson gave 100 participants a news coverage questionnaire. 4 of the 5 items were real – 1 fictitious. When questioned afterwards 36% claimed they had seen the fictitious footage and these scored higher on paranormal belief and experience. Clancy – people who claimed to have experienced an alien abduction were also found to be more susceptible to false memories, possible that some reports are false memories. Psychopathological or filling a need. Are beliefs a symptom of underlying mental illness or fulfilling a psychological need. Mental illness. A number of personality factors linked to psi are characteristics of mental disorders. Link with schizotpy not surprising because one characteristic is “having magical or superstitious beliefs” A psychological need. Relationships found with childhood trauma, fantasy proneness and paranormal beliefs. the belief may provide a welcome ‘illusion’ of control. Auten examined personality traits in believers and non-believers and found no difference on traits considered to be non-pathological. So argued belief is not indicative of psychopathology. Some research has found positive correlations e.g. between belief and self- actualisation.