File
advertisement

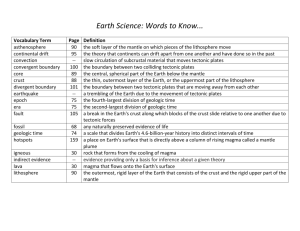
Section 1: Inside the Earth Earth's layers 1. Crust- less than 1% of earth's mass - 5 to 100 km thick and thin and solid layer above the mantle Types of crust: 1. oceanic- thinner but denser than continental because it contains twice as much as Fe, Ca, and Mg 2. continental crust- thicker but less dense than oceanic crust 2. Mantle- layer between the crust and core and contains most of Earth's mass (67%) -denser than crust because it contains more Magnesium How do scientists know about the composition of mantle? -from magma that flows out of active volcanoes on ocean floor 5 Physical Layers of the Earth 1. Lithosphere- outermost, rigid layer -made of crust and upper part of mantle and divided into tectonic plates 2. Asthenosphere- plastic layer of mantle -where tectonic plates move and made of solid rock flowing very slowly 3. Mesosphere- lower part of mantle -extends from bottom of asthenosphere to the core 4. Outer Core- liquid layer and 2,200 km thick 5. Inner core- solid dense center and 1,230 km thick - core is made mainly of Iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni) Tectonic Plates- block of lithosphere made up of the crust and outermost part of the mantle How do scientists know about deepest parts of the Earth? They study seismic waves caused by earthquakes. -Seismic waves travel at different speeds depending on density Seismograph- used to measure the density of Earth’s layers Check Points: 1. Identify the layers of the earth by their composition 2. Identify the layers of the Earth by their physical properties. Section 2: Continental Drift Alfred Wegener- wrote about Continental Drift Continental Drift- continents once formed a single landmass, broke up and drifted to present day locations -explained why fossils of same plant and animals are found on different sides of Atlantic Ocean Pangaea- Greek for "all earth"; single huge continent 245 million years ago - split into two huge continents Laurasia and Gondwana Sea- Floor Spreading- process by which new oceanic crust forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies Magnetic reversals- happen when Earth’s magnetic poles change places -used as evidence for sea-floor spreading Mid-ocean ridges- places where sea-floor spreading takes place GPS (Global Positioning System) - used to measure movement of tectonic plates Check Point: In your own words, define continental drift and sea-floor spreading Section 3: Plate tectonics Theory Plate tectonics- explains how tectonic plates move and change shape Boundary- where two tectonic plates meet 3 Types of boundaries 1. Convergent boundary- formed when two tectonic plates collide 2. Divergent boundary- when two tectonic plates move away from each other 3. Transform boundary- when two tectonic plates slide past each other 3 possible causes of Plate tectonics 1. Ridge Push- happens at mid-ocean ridge and oceanic crust slides downhill 2. Convection- hot rock within earth rises, cooler rock sinks 3. Slab Pull- when denser oceanic crust sinks, it pulls the rest of the tectonic plate with it Section 4: Earth's Deformation 1. Deformation- happens when the shape of a rock changes due to stress 2. Compression- when two tectonic plates collide at convergent boundary; forms mountains - stress that squeezes rock layers 3. Tension- when tectonic plates move away from each other - stress that stretches rock layers -occurs at divergent boundaries and forms at mid-ocean ridges Folding- bending of rock layers due to stress Fault- break in a rock along which one block slides relative to another Types of fault 1. Normal Fault- happens during tension when tectonic plates pull apart - hanging wall moves down, footwall moves up 2. Reverse fault- happens during compression when tectonic plates push rock together - hanging wall moves up, footwall moves down 3. Strike-slip fault- happens along transform boundary -when rocks break and move horizontally Types of mountains 1. Folded Mountain- highest mountain ranges in the world and forms when rocks are pushed together 2. Fault- Block Mountain- has sharp, jagged peaks and forms during tension(rock layers stretches) 3. Volcanic Mountain - forms at convergent boundaries along subduction zones - formed by magma that reaches earth’s surface Ring of Fire- where most active volcanoes are found Uplift- rising of parts of Earth's crust to higher elevations Subsidence- sinking of earth's crust Rift Zone- deep cracks that form between tectonic plates pulling away from each other Check Points 1. How do rift zones form? 2. What are the three types of faults?