Reading Notes - WordPress.com
advertisement

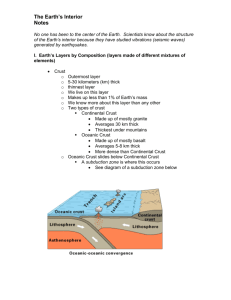
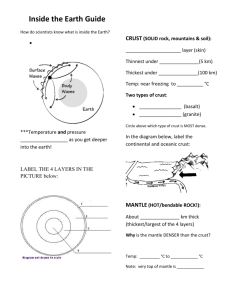
Reading Notes: Plate Tectonics Page 191-212 3 layers= Crust, mantle, core Compound= a substance composed of 2 or more elements Crust= the thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle 2 types= Continental and Oceanic Crust (oxygen, silicon, aluminium, etc.) Mantle= the layer of rock between the Earth’s crust and core Find out by mantle rock and ocean floor (volcanoes, magma) Core= the central part of the Earth below the mantle 5 physical layers Outer Core= liquid layer of the Earth’s core that lies beneath the mantle and surrounds the inner core Inner Core= solid, dense centre of our planet that extends from the bottom of the outer core to the centre of the Earth Lithosphere= divided into pieces called tectonic plates, the solid, outer layer of the Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle Mesosphere= the strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core Asthenosphere= the soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move Tectonic plate= a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle (like ice cubes in a bowl of punch) Know about earth layers by earthquakes which produce seismic waves shown by machine, seismograph, studied by seismologists Continental drift= the hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations (know because of fossils found in many places) One single, huge continent= Pangaea (all earth, Greek) Existed 245 million years ago, Laurasia and Gondwana= 180 million years ago Panthalassa= all sea Mid-ocean ridges= underwater mountain chains that run through Earth’s ocean basins Sea-floor spreading= the process in which new ocean lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies Evidence= Magnetic Reversals Magnetic Reversals= magnetic poles change places Plate tectonics= the theory that explains how large pieces of the Earth’s outermost layer, called tectonic plates, move and change shape Boundaries= place where tectonic plates touch Convergent Boundaries= the boundary formed by the collision of two lithospheric plates 3 types= continental-continental boundaries, continental-oceanic boundaries, oceanicoceanic boundaries Continental- oceanic collisions= subduction zone Divergent boundary= the boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other Forms new sea floor, mid-ocean ridges Transform boundary= the boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally San Andreas Fault in California Causes of tectonic plate motions= ridge push, convection, and slab pull Global Positioning system (GPS) measure the rate of tectonic plate movement, radio signals Stress= amount of force per unit area on a given material Deformation= process by which shape of a rock changes because of stress Compression= stress that occurs when forces act to squeeze an object (mountains may form) Tension= stress that occurs when forces act to squeeze an object (mid-ocean ridges) Folding= the bending of rock layers due to stress Types of fold= anticlines (upward-arching fold), synclines (down-ward troughlike folds), monocline (rock layers are folded so that both ends of the fold are horizontal Fault= a break in a body of rock along which one block slides relative to another Normal faults= hanging wall to move down relative to the footwall, tension Reverse Faults= hanging wall to move up relative to the footwall, compression Strike-slip faults= form when opposing forces cause rock to break and move horizontally Folded mountains= rock layers are squeezed together and pushed upward; convergent boundaries where continents have collided Fault- Block mountains= tension causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks; sedimentary rock layers are tilted up by faulting, produce mountains with sharp, jagged peaks Volcanic mountains= located at convergent boundaries where oceanic crust sinks into the asthenosphere at subduction zone; rock that is melted in subduction zone from magma, which rises into the Earth’s surface and erupts; form under the sea, islands; ring of fire Uplift= the rising of regions of the earth’s crust to higher elevations Subsidence= the sinking of regions of the Earth’s crust to lower elevations Rebound= process when one area rises without deforming Subsidence of cooler rocks Subsidence= occur when lithosphere becomes stretched in rift zone Rift zone= a set of deep cracks that forms between two tectonic plates that are pulling away from each other