Earth Science vocab sheet
advertisement
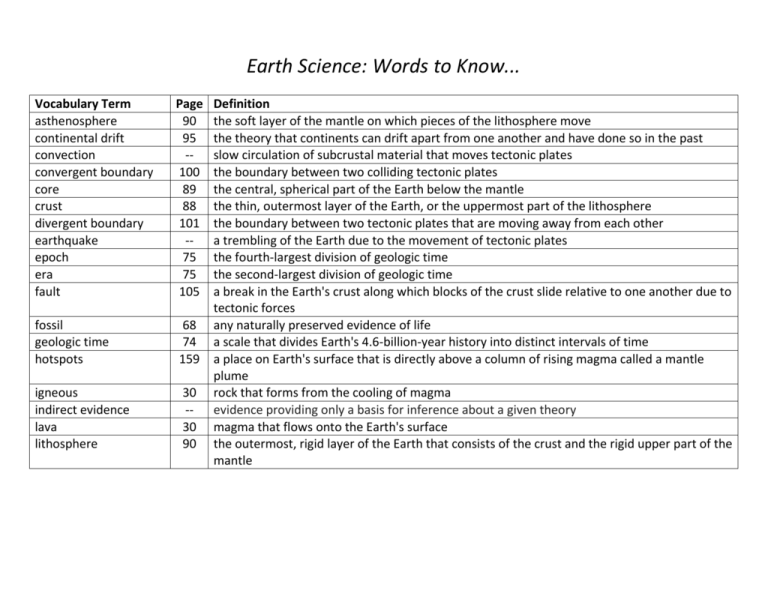
Earth Science: Words to Know... Vocabulary Term asthenosphere continental drift convection convergent boundary core crust divergent boundary earthquake epoch era fault Page 90 95 -100 89 88 101 -75 75 105 fossil geologic time hotspots 68 74 159 igneous indirect evidence lava lithosphere 30 -30 90 Definition the soft layer of the mantle on which pieces of the lithosphere move the theory that continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past slow circulation of subcrustal material that moves tectonic plates the boundary between two colliding tectonic plates the central, spherical part of the Earth below the mantle the thin, outermost layer of the Earth, or the uppermost part of the lithosphere the boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other a trembling of the Earth due to the movement of tectonic plates the fourth-largest division of geologic time the second-largest division of geologic time a break in the Earth's crust along which blocks of the crust slide relative to one another due to tectonic forces any naturally preserved evidence of life a scale that divides Earth's 4.6-billion-year history into distinct intervals of time a place on Earth's surface that is directly above a column of rising magma called a mantle plume rock that forms from the cooling of magma evidence providing only a basis for inference about a given theory magma that flows onto the Earth's surface the outermost, rigid layer of the Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle Earth Science: Words to Know... Vocabulary Term magma mantle metamorphic Page 29 89 30 mineral model pangea period plate tectonics 4 --75 99 Richter scale ring of fire rock rock cycle sedimentary seismology transform boundary volcano Wegener --26 28 30 120 101 148 -- Definition the hot liquid that forms when rock partially or completely melts the layer of the Earth between the crust and the core rock that forms when the texture and composition of preexisting rock changes due to heat or pressure a naturally formed, inorganic solid with a crystalline structure a representation of what is thought to be true based on evidence the "supercontinent" that once incorporated all Earth's landmasses the third-largest division of geologic time the theory that the Earth's lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around on the top of the asthenosphere a numerical scale for expressing the magnitude of an earthquake the area of the Pacific basic where there are large amounts of volcanoes and earthquakes a solid mixture of crystals of one or more minerals or other materials the process by which one rock type changes into another rock type rock that forms when sediments are compacted and cemented together the study of earthquakes the boundary between two tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally a mountain that forms when molten rock, called magma, is forced into the Earth's surface the geophysicist and meteorologist who proposed the theory of plate tectonics