Physical Science Final Study Guide
advertisement
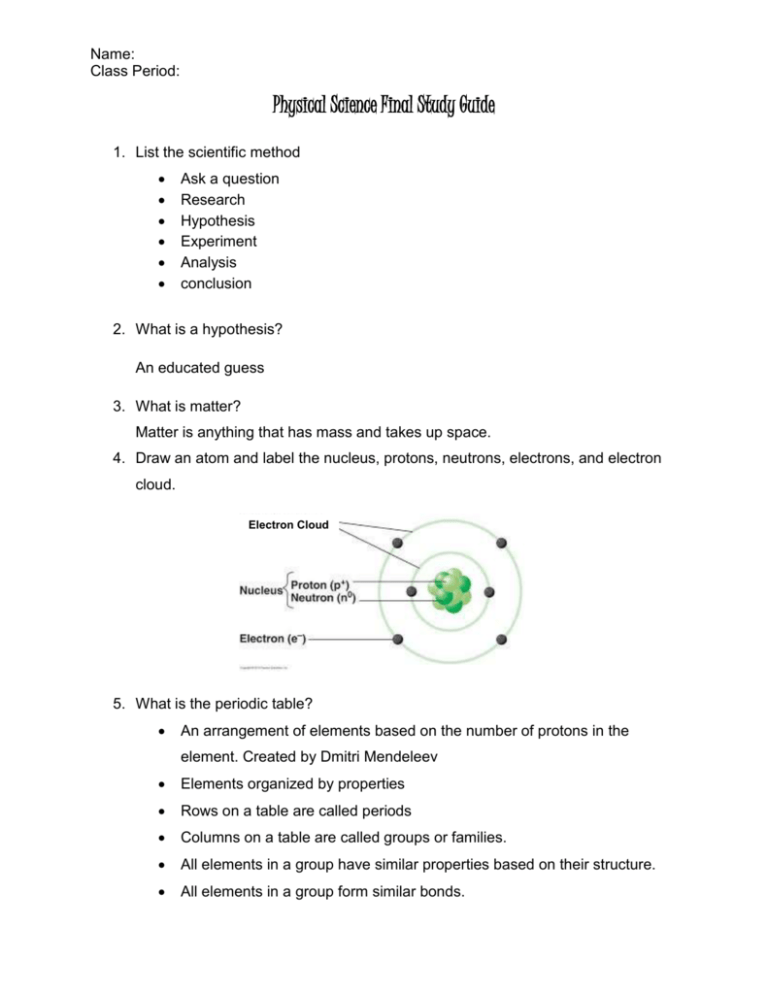
Name: Class Period: Physical Science Final Study Guide 1. List the scientific method Ask a question Research Hypothesis Experiment Analysis conclusion 2. What is a hypothesis? An educated guess 3. What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. 4. Draw an atom and label the nucleus, protons, neutrons, electrons, and electron cloud. Electron Cloud 5. What is the periodic table? An arrangement of elements based on the number of protons in the element. Created by Dmitri Mendeleev Elements organized by properties Rows on a table are called periods Columns on a table are called groups or families. All elements in a group have similar properties based on their structure. All elements in a group form similar bonds. Name: Class Period: 6. Define the following: Element symbol: a one or two letter symbol (the first letter is always capitalized) that stands for a particular element. Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. Atomic Mass/ Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the atom. The periodic table displays the average number of protons and neutrons for all atoms of the element. 7. Use the periodic table to find the numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons for atoms of the following elements. Note: many of the atoms on this practice chart are isotopes of elements. You will not have to deal with isotopes on the final (for example: on the final, Sodium would have a mass number of 23, the same as on the periodic table) Element Mass Atomic Symbol Number Number Boron B 11 Sodium Na Gallium Name of Element Protons Neutrons Electrons 5 5 6 5 24 11 11 13 11 Ga 68 31 31 37 31 Yttrium Y 89 39 39 50 39 Copper Cu 64 29 29 35 29 Technetium Tc 98 43 43 55 43 8. What is a metal? What are the properties of metals? Where are they found on the periodic table? Metals have a metallic luster and are good conductors of heat and electricity. They are malleable (easily bent) and ductile (easily drawn into wires). Metals are located on the left side of the periodic table. Most elements are metals. Name: Class Period: 9. What is a metalloid? What are the properties if metalloids? Where are they found on the periodic table? Have characteristics of metals and nonmetals. All are solid at room temperature. Semi- conductors; used to make electric circuits. Metalloids are found on the “stair step line” on the periodic table 10. What is a nonmetal? What are the properties of nonmetals? Where are they found on the periodic table? Nonmetals are dull in appearance, poor conductors of heat and electricity, and are usually gasses or liquids at room temperature. Solid nonmetals are brittle. Nonmetals are found on the right side of the periodic table 11. Tell where the following are on the periodic table and describe them: Alkali metals - Group 1 Shiny, malleable and ductile. React rapidly and violently with oxygen and water Alkaline earth metals- Group 2 Shiny, malleable, and ductile. Combine readily with other elements- not found alone in nature Transition metals - Elements in groups 3- 12 Occur in nature as uncombined elements Oxygen Family/ Chalcogens: Group 16 on the periodic table. Nonmetals and metalloids Halogens: Group 17 Seven electrons in their outer energy level. Needs to gain one electron from a metal Form salts, ionic compounds between halogens and metals. Nobel Gases: Group 18 on the periodic table. Exist as isolated atoms. Stable because they have 8 electrons in their outermost energy level. No known natural compounds Name: Class Period: 12. What is a pure substance? What are the two types of pure substances? Matter that has the same composition and properties throughout is called a substance. Pure substances can be elements or compounds. 13. What is a mixture? When two or more substances (elements or compounds) come together but don’t combine to make a new substance, they are mixtures. The identity of the substances is not changed. Mixtures can be separated. 14. What is a homogenous mixture? Homogenous- “the same throughout” Cannot see different parts in this kind of mixture. 15. What is a heterogeneous mixture? see parts of a heterogeneous mixture. 16. Draw the Following Ionic Bonds. Be sure to include the charges of the ions: Potassium and Chlorine Aluminum and Bromine Br Al Name: Class Period: Magnesium and Iodine 17. Draw the Lewis Structure (Dot diagram) of the following elements: Sodium Strontium Aluminum Carbon Phosphorus Name: Class Period: Oxygen Fluorine Argon 18. Draw the following covalent bonds and write the chemical formula: Chlorine + Chlorine Oxygen + 2 Hydrogen Oxygen + Oxygen Name: Class Period: 19. What are the 5 signs a chemical change is occurring? Bubbles (production of a gas) Production of an odor/ smell Color change Change in temperature Production of a precipitate (solid) 20. A chemical reaction begins with substances called reactants and ends with substances called products. 21. The substances to the left of the arrow are reactants. The substances to the right of the arrow are products. 22. How can you tell if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic? Heat is produced in an exothermic reaction (it is a product) The reaction will feel hot. Heat is absorbed in an endothermic reaction (it is a reactant) The reaction will feel cold. 23. What are the steps to balancing a chemical reaction? Draw a line down the middle (at the arrow) Count the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation Balance the equation by adding coefficients in front of the elements/ compounds. Check that the reaction is balanced by multiplying the coefficients by the subscripts. 24. What is the Law of Conservation of Matter? Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. 25. Balance the following chemical reactions: __4__P +___5_ O2 → _____ P4O10 ___2__ Mg + _____O2 →__2__ MgO _2__HgO → __2_Hg + _____O2 Name: Class Period: __2__Al2O3 →__4 _ Al + _3 _O2 _____Cl2 + __2 _NaBr →__2__ NaCl +_____ Br2 26. Define solubility: measure of how much solute can be dissolved in a certain amount of solvent. Substances that dissolve in another substance are called soluble in that substance; substances that do not dissolve in another substance are termed insoluble in that substance. 27. What is a saturated solution? A saturated solution contains all of the solute it can hold under a given condition. 28. What is an acid? Acids- substances that dissolve in water and release positively charged hydrogen ions that combine with water molecules to form positively charged hydronium ions. 29. What are some characteristics of acids? Acids taste sour, conduct electricity, are corrosive, and react with certain metals. 30. What is a base? B. Bases- substances that accept hydrogen ions; when dissolved in water, a hydroxide ion forms. 31. What are some characteristics of bases? 32. Bases taste bitter, feel slippery, are corrosive, and conduct electricity. 33. List some common acids: Lemons, vinegar, battery acid, carbonic acid 34. List some common bases: Soap, bleach, cleaning products, blood 35. What is the pH scale. pH is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is and relates to the concentration of hydronium ions and hydroxide ions. The scale goes from 1 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic) Name: Class Period: 36. Acids have a (high or low) pH 37. Bases have a (high or low) pH 38. Solutions with a low pH have a lot of ____H+__ ions. 39. Solutions with a high pH have a lot of ___OH-___ ions. 40. What is a neutralization reaction? the interaction between the H+ of an acid and the OH- of a base to form water and a salt; antacids can help neutralize excess acid in the stomach. 1. Fill in the chart below: Variable Speed (s)/ Velocity (v) Formula Units Speed= distance/ m/s time V= p/m m/s2 Acceleration (a) Final speed- initial speed time Momentum (p) Kg* m/s P= mv Mass (m) Kg M= p/V 41. What is the speed of a sailboat that is traveling 100 meters in 120 seconds? 0.83 m/s Name: Class Period: 42. As a shuttle bus comes to a normal stop, it slows from 9.00m/s to 0.00m/s in 5.00s. Find the average acceleration of the bus. -1.8 m/s2 43. Calculate the momentum of a 700g ball that is rolling down a ramp at 4.6m/s. 3.22kg * m/s or 3220 g*m/s 44. If a 40 Kg object has a momentum of 400Kg*m/s, how fast is it traveling? 10m/s 45. Define the following types of friction: Static friction- the type of friction that prevents an object from moving when force is applied. Sliding friction is due to the microscopic roughness of two surfaces; it slows down a sliding object. Rolling friction between the ground and a wheel allows the wheel to roll. 46. Define the following: Newton’s first law of motion: An object will remain at rest or move with constant speed unless a force is applied. Newton’s second law of motion: states that an object acted upon by a net force will accelerate in the direction of the force, and that the acceleration equals the net force divided by the object's mass. Newton’s third law of motion: states that forces always act in equal but opposite pairs. 47. What is the formula for Newton’s second law? 48. What are the units for: Force N Mass kilograms Acceleration m/s2 Name: Class Period: 49. What is the acceleration of softball if it has a mass of 0.5 kg and hits the catcher's glove with a force of 25 N? 50m/s2 50. Define the following types of energy: Radiant- light energy/ energy from electromagnetic waves Thermal- Energy that increases as temperature increases Potential- Energy Stored Due to its position is potential energy. Kinetic- Energy From motion is kinetic energy. Nuclear- The nucleus of an atom contains nuclear energy. Chemical- the energy stored in chemical bonds. Electrical- Energy from electricity (from the flow of charges) 51. What is the definition of energy? Energy is the ability to causes change. 52. What is the law of conservation of energy? energy is never created or destroyed; it merely changes form. 53. Label where the kinetic energy is the greatest and where the potential energy is the greatest on the following diagram of a pendulum. Potential Energy is greatest Potential Energy is greatest Kinetic Energy is Greatest Name: Class Period: 54. What is work? occurs when a force causes an object to move in the same direction that the force is applied. 55. What is power? how quickly work is done. 56. What is the formula for work? Work= force x distance 57. What is the formula for power? power= work done/ time needed 58. Why can you never get as much output work as the input work you put into a machine? Friction converts work to heat. 59. Explain what each of the following mechanical advantages mean and give an example of a machine with that mechanical advantage: A mechanical advantage of 1 – only the direction of the force is changed Example: fixed pully A mechanical advantage greater than 1- the force is multiplied (force must be applied over a longer distance) Example: Ramp A mechanical advantage of less than 1- force is exerted over a shorter distance. Example: Wedge 60. Fill in the following chart: Simple Machine Definition a flat, sloped surface. Inclined Plane any rigid plank that pivots Lever about a point inclined plane wrapped Screw around a cylinder or post Inclined plane that moves- Wedge Name: Class Period: two circular objects of Wheel and Axle different sizes that rotate together. grooved wheel with a roper Pulley or chain wrapped around it. 61. It took a 500.0-newton ballerina work of 250 joules to lift herself upward through the air. How high did she jump? Distance= 0.5 meters 62. Suppose a force of 100 newtons is used to push an object a distance of 5 meters in 15 seconds. Find the work done and the power for this situation. Work = 500 Joules Power= 33.3 Watts 63. Draw a transverse wave and label the crest, trough, amplitude, and wavelength. 64. What type of wave is a sound wave? How is it formed? A sound wave is a compressional wave. It is produced by vibrations. 65. Draw a compressional wave and label the compressions and rarefactions. Name: Class Period: 66. Label the following electromagnetic spectrum with the correct type of electromagnetic wave (X ray, microwave, radio wave, visible light, gamma ray, ultraviolet wave, and infrared wave) 67. What is the order of visible light from lowest frequency to highest frequency? Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet (ROY G BIV)