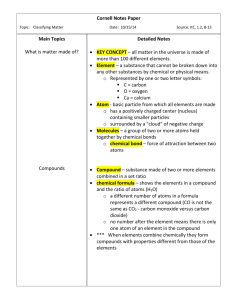
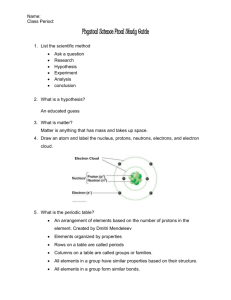
Chemistry Guided Notes
advertisement
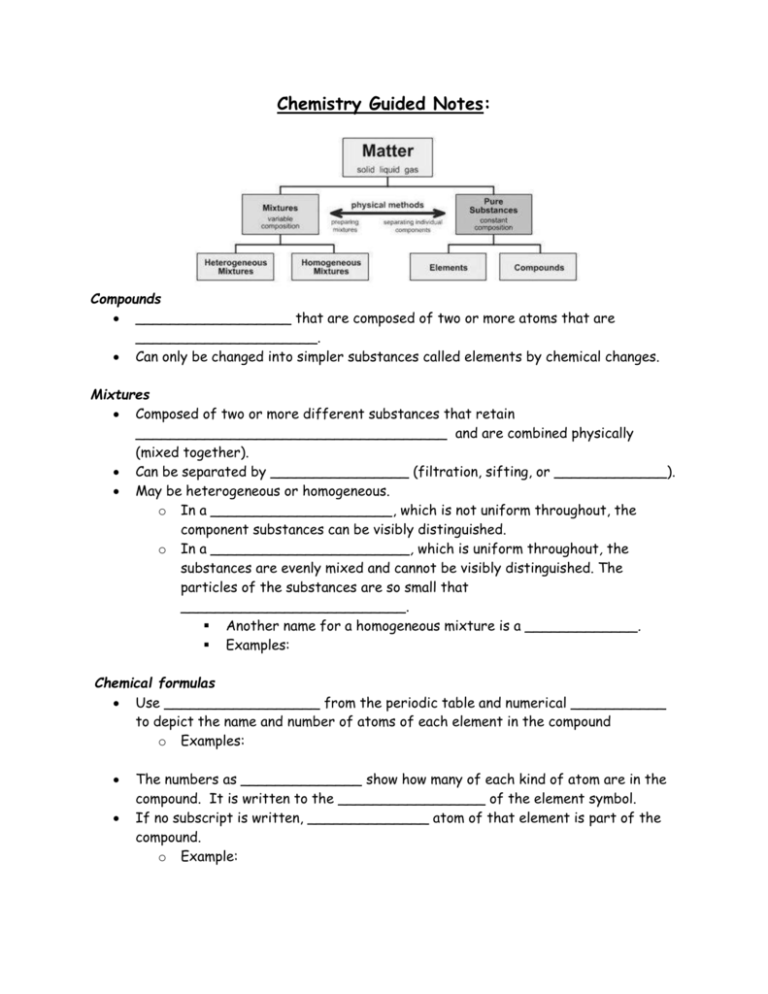
Chemistry Guided Notes: Compounds __________________ that are composed of two or more atoms that are _____________________. Can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes. Mixtures Composed of two or more different substances that retain ____________________________________ and are combined physically (mixed together). Can be separated by ________________ (filtration, sifting, or _____________). May be heterogeneous or homogeneous. o In a _____________________, which is not uniform throughout, the component substances can be visibly distinguished. o In a _______________________, which is uniform throughout, the substances are evenly mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that __________________________. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a _____________. Examples: Chemical formulas Use __________________ from the periodic table and numerical ___________ to depict the name and number of atoms of each element in the compound o Examples: The numbers as ______________ show how many of each kind of atom are in the compound. It is written to the _________________ of the element symbol. If no subscript is written, ______________ atom of that element is part of the compound. o Example: N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, and H2 are _____________________ where all of the atoms of the molecule are the same element. Ionic Bonds Formed when _______________ and ________________ chemically bond to form a new substance. ______________ are transferred from the metals to the nonmetals. Covalent Bonds Formed when nonmetals bond with ____________________ Electrons are _______________ Physical and Chemical Properties: Can be used to classify and identify substances. _________________ and _________________ are two major groups of elements that have different physical properties. Physical properties of metals include: ___________________—Having a shiny surface or reflecting light brightly ___________________—Heat and electricity move through them easily ___________________—Ability to be hammered into different shapes ___________________—Ability to be drawn into a wire ___________________—Heavy for their size Physical properties of nonmetals include: _____________—Not shiny ___________________—Heat and electricity do not move through them easily _____________—Break or shatter easily (solids) Physical properties: Can be observed and measured without changing the kind of matter being studied. ________________________ o The temperature at which a solid can change to a liquid o Unchanging under constant conditions Example: ______________________ o The temperature at which a liquid changes from a liquid to a gas. o _______________ begins when bubbles form throughout, grow larger, rise to the surface, and burst. o As long as the substance is _________________the temperature of the liquid remains constant (at the ________________). o Density o The relationship between the __________ of a material and its _________ o Substances that are _____________ contain more matter in a given volume. o The density of a substance is _____________________ no matter how large or small the sample of the substance. o Example: o o o o o o o o _____________________ is unchanging under constant conditions for a given substance. Example: Generally, metals have a ________________ density than nonmetals. Density is the _________ of a substance per unit of ___________. Density of a substance changes with _____________________ due to the difference in the particle arrangement in solids, liquids and gasses. The volume and density of a particular substance is dependent upon its _______________________________________. It is calculated using the formula: Volume Measured in _______________________ Can be calculated using basic math formulas or the ________________________________ Mass Measured in _____________ The composition of a substance does not change when one measures mass and volume. Example: If the mass of an object is 20 grams and the volume of the same object is 10 mL, what is the density of the object? ________________________ o The ability to act as an electrical conductor or an electrical insulator is based on the solid’s ability to complete an electric circuit, i.e., conduct electricity. o Materials with high conductivity are called electrical __________________ because they allow current to flow easily. o Materials with low conductivity are called electrical __________________ because they do not allow current to flow. Example: Most metals are electrical ________________ while nonmetals are electrical _________________. __________________ o Can be used to help identify a substance, along with other properties. o By itself, it is not a significant identifier of a substance. o Absence of ________________ is also a physical property. __________________ o The relative resistance of a metal or other material to denting, scratching, or bending. __________________ o The property of reacting to the forces exerted by magnets ____________________________ Can be recognized only when substances react or do not react chemically with one another, that is, when they undergo a change in composition. Can be used to help identify a substance Ability to burn o Involves a substance reacting quickly with ______________ to produce light and heat. Ability to rust o Involves a substance reacting _____________with oxygen. The process is called rusting. Memorize the following: Element Hydrogen Symbol Element C Copper Nitrogen Symbol Si Al O Silver Chlorine Au Mg Iron Zinc He Ca Potassium Phosphorus Na I Fluorine Chemical Formula Chemical Name NaCl Type of Bond Ionic Water C6H12O6 Oxygen Gas Covalent Covalent Nitrogen Gas Covalent CO2 Fe2O3