1st Semester Final Study Guide
advertisement

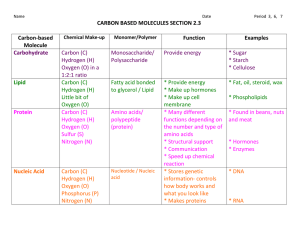
Ecology What is an ecosystem? Give an example. What is ecology? What is a biotic factor? Give examples. What is an abiotic factor? Give examples. What is biodiversity? What ecosystem has the highest biodiversity of any ecosystem on Earth? What is the difference between a producer and a consumer? What is an autotroph? What is a heterotroph? Why do all ecosystems depend on producers? What is photosynthesis? What is the difference between photosynthesis and chemosynthesis? What is an herbivore? What is a carnivore? What is an omnivore? What is a detritivore? What does a decomposer (they are detritivores) do? What is the difference between a specialist and a generalist? What are the trophic levels in a food web or a food chain? What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Describe the flow of energy from one trophic level to another in a food web – how much energy is lost between each trophic level? How does habitat differ from the concept of ecological niche? Know the definitions of habitat and niche that I gave in class. How does the stability of an ecosystem depend on its producers? What are the two processes used by producers to obtain energy? Carbon, Hydrologic, and Nitrogen Cycles Fossil fuels are a key part of which cycle? What is a biotic carbon sink? Please explain and be able to give examples. What is an abiotic carbon sink? Please explain and be able to give examples. When hydrocarbons such as oil are trapped deep underground, we describe them as what type of carbon? What is the major source of carbon pollution? Which greenhouse gas is most affected by human activity? How does the increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere result in global warming? What happens when water vapor released by evaporation and transpiration condenses? What is transpiration? How does it contribute to the hydrologic cycle? What is infiltration and what important role does it play in the hydrologic cycle? How are infiltration and groundwater connected? What happens during the process of nitrogen fixation? What are the nitrogen fixers? What are the four forms of nitrogen in the process of nitrogen fixation? Name the two forms of nitrogen that plants can use. What is the main cause of the large dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico? What role do we, here in Iowa, play in causing the dead zone? What are the most important sources of nitrate pollution? How does nitrate pollution affect aquatic ecosystems? How does climate change affect corals and coral reefs? Biochemistry What is a polymer made up of? Is glucose considered a monomer or a polymer? Why? 1 What are the four main groups of carbon-based molecules? What are the elements that make up carbohydrates? What is the monomer that makes up lipids? How is a saturated fat different from an unsaturated fat? What carbon-based molecules are made of amino acid monomers? What carbon-based molecules are made up of nucleotide monomers? In what kind of molecule are the instructions for building proteins found? Enzymes are catalysts in living things. What are the two biological functions of enzymes? Estrogen is a steroid, of what carbon-based molecule is it made? What does an exothermic reaction do that an endothermic reaction doesn’t? What is happening when a chemical reaction is said to be at equilibrium? In the following chemical reaction, indicate which is/are the product(s) and which is/are the reactants: CO2 + H2O H2CO3. What carbon based macromolecule do plants produce from glucose for the purpose of support? What is activation energy – what is its role in a chemical reaction? What happens to an enzyme catalyst during a chemical reaction? The lock and key model of enzyme function illustrates which important characteristic of enzymes (see book or notes for illustration)? What atoms are the primary building blocks of all life on Earth? How many bonds can carbon form with other atoms? What kind of bonds are they? Starch is a polymer made by plants from glucose. For what do plants use starch? The most common organic (carbon-based) compound on Earth is what compound? Which nucleic acid is responsible for building proteins? For what is C6H12O6 the chemical formula? Cell Theory and Cell Membranes What characteristics do all cells share? Where is the DNA of a prokaryote found? Where is the DNA of a eukaryote found? What kind of organisms are prokaryotes? What kind of cells do we possess? What structure helps to maintain the shape of a cell? What organelle is the site of protein assembly? What organelle takes the assembled proteins from the ribosomes; folds them; and then modifies them by adding other molecules to them? What organelle sorts, packages, and delivers proteins to where they need to go? What organelles have their own DNA, ribosomes, and supply their cells with energy? In what organelle are the instructions for the production of proteins found? What do we call the instructions (in what molecule are they coded)? Would poison that kills human cells by blocking pores in the nuclear membrane also kill bacteria? Explain your reasoning. What organelle is involved in defending a cell against intruders such as bacteria and viruses? How are atoms and cells similar? What is cytoplasm? How does your book describe it? Amino acids that are used to build proteins are found where in the cell? An electron microscope reveals the detailed structure of a cell with membrane-bound organelles. What kind of cell are you looking at? Name two major features that are unique only to plant cells? What do each do? What invention played a revolutionary role in the discovery of cells by early scientists? What are the three principles of cell theory? 2