Carbon based molecules notes
advertisement

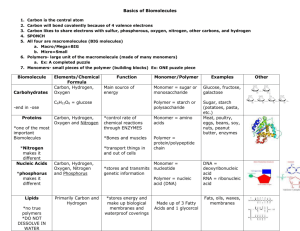
Name Date Period 3, 6, 7 CARBON BASED MOLECULES SECTION 2.3 Carbon-based Molecule Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chemical Make-up Monomer/Polymer Function Examples Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) in a 1:2:1 ratio Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Little bit of Oxygen (O) Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) Sulfur (S) Nitrogen (N) Monosaccharide/ Polysaccharide Provide energy * Sugar * Starch * Cellulose Fatty acid bonded to glycerol / Lipid * Fat, oil, steroid, wax Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) Phosphorus (P) Nitrogen (N) Nucleotide / Nucleic acid * Provide energy * Make up hormones * Make up cell membrane * Many different functions depending on the number and type of amino acids * Structural support * Communication * Speed up chemical reaction * Stores genetic information- controls how body works and what you look like * Makes proteins Amino acids/ polypeptide (protein) * Phospholipids * Found in beans, nuts and meat * Hormones * Enzymes * DNA * RNA Name Carbon-based Molecule Carbohydrate Date Chemical Make-up Provide energy Monomer/Polymer Monosaccharide/ Polysaccharide Lipid * Fat, oil, steroid, wax Fatty acid bonded to glycerol / Lipid * Phospholipids Protein Amino acids/ * Found in beans, polypeptide (protein) nuts and meat * Hormones * Enzymes Nucleic Acid Nucleotide / Nucleic * Stores genetic information- controls acid how body works and what you look like * Makes proteins Period 3, 6, 7 Function Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) in a 1:2:1 ratio * Provide energy * Make up hormones * Make up cell membrane * Many different functions depending on the number and type of amino acids * Structural support * Communication * Speed up chemical reaction Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) Phosphorus (P) Nitrogen (N) Examples * Sugar * Starch * Cellulose Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Little bit of Oxygen (O) Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) Sulfur (S) Nitrogen (N) * DNA * RNA Name Date Period 3, 6, 7 CARBON BASED MOLECULES SECTION 2.3 Carbon-based Molecule Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chemical Make-up Monomer/Polymer Function Examples Name Date Period 3, 6, 7 Carbon-based Molecules Section 2.3 • Are the foundation of life meaning ____________________________________________________________________ • Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. Carbon atoms form _________________________ with four other atoms (Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and/or Carbon), this makes it suited for the ___________________________________________________________________. • Chemically, this is due to carbon’s 4 ____________________________________ which make it able to form 4 bonds to achieve ____________________________. Valence electrons – ____________________________________________________________________; these are the electrons that are available to bond with other atoms • Many carbon-based molecules are made of many _________________________________________________ called monomers. – Monomers join together to form a ________________________________. • Assembling & Disassembling Polymers via Chemical Reactions – Hydrolysis- water interacts with a polymer _______________________________________________________ to each other. Break a _____________________ down into _____________________ – Dehydration synthesis- ___________________________________________________ together while losing water molecules. Build a _____________________ by bonded a bunch of _____________________