Notes and Homework
advertisement

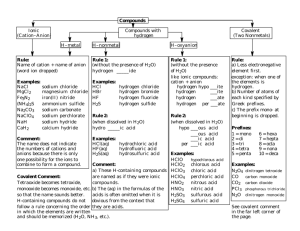
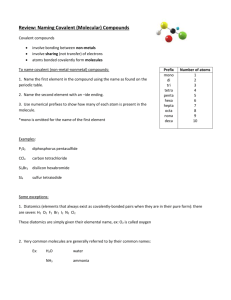
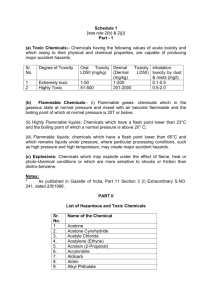
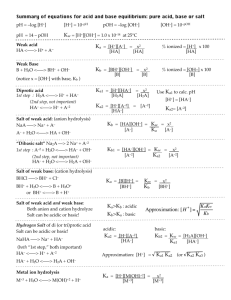
Review: Naming Covalent (Molecular) Compounds Covalent compounds involve bonding between non-metals involve sharing (not transfer) of electrons atoms bonded covalently form molecules To name covalent (non-metal-nonmetal) compounds: 1. Name the first element in the compound using the name as found on the periodic table. 2. Name the second element with an –ide ending. 3. Use numerical prefixes to show how many of each atom is present in the molecule. *mono is omitted for the name of the first element Prefix mono di tri tetra penta hexa hepta octa nona deca Number of atoms 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Examples: P2S5 diphosphorus pentasulfide CCl4 carbon tetrachloride Si2Br6 disilicon hexabromide SI4 sulfur tetraiodide Some exceptions: 1. Diatomics (elements that always exist as covalently-bonded pairs when they are in their pure form): there are seven: H2 O2 F2 Br2 I2 N2 Cl2 These diatomics are simply given their elemental name, ex: O2 is called oxygen 2. Very common molecules are generally referred to by their common names: Ex: H2O water NH3 ammonia Name the following compounds 1. SO2 ______________________________________________________ 2. CO ______________________________________________________ 3. ClO2 ______________________________________________________ 4. N2O ______________________________________________________ 5. P2O5 ______________________________________________________ 6. CBr4 ______________________________________________________ 7. N2S5 ______________________________________________________ 8. N2O5 ______________________________________________________ 9. BF3 ______________________________________________________ 10. SiCl4 ______________________________________________________ 11. IF7 ______________________________________________________ 12. P4O10 ______________________________________________________ 13. PO3 ______________________________________________________ 14. BrCl3 ______________________________________________________ 15. P2O4 ______________________________________________________ 16. NF4 ______________________________________________________ 17. S4N4 ______________________________________________________ 18. NF3 ______________________________________________________ 19. NO2 ______________________________________________________ 20. Cl2O7 ______________________________________________________ Write the formulas for the following compounds: 1. carbon dioxide ________________________ 2. nitrogen monoxide ________________________ 3. nitrogen dioxide ________________________ 4. sulfur trioxide ________________________ 5. tetraphosphorus decoxide ________________________ 6. tetraphosphorus hexoxide ________________________ 7. hydrogen monochloride ________________________ 8. dihydrogen monoxide ________________________ 9. nitrogen trichloride ________________________ 10. carbon disulfide ________________________ 11. disilicon hexabromide ________________________ 12. tetranitrogen tetrasulfide ________________________ 13. carbon monoxide ________________________ 14. dinitrogen pentoxide ________________________ 15. water ________________________ 16. ammonia ________________________ 17. phosphorus pentachloride ________________________ 18. carbon tetrachloride ________________________ 19. diselenium dichloride ________________________ 20. dinitrogen tetroxide ________________________ Naming Acids Acids are a special group of substances, they are compounds of non-metals but they form ions in solution. Acids can be recognized by the fact that their chemical formula generally begins with H Because acids are a unique group, they have different naming rules: Acid Example Anion Clchloride NO2nitrite NO3nitrate HCl HNO2 HNO3 Anion ending How To Name it Name -ide hydro(stem)ic acid hydrochloric acid -ite (stem)ous acid nitrous acid -ate (stem)ic acid nitric acid **Two stem ‘exceptions’: S sulfur – the stem is ‘sulfur’ ex. sulfuric acid P phosphorus – the stem is ‘phosphor’ ex. phosphoric acid Examples: Use the rules to name the following: 1. HBr 2. HClO4 3. H2S hydrobromic acid perchloric acid hydrosulfuric acid Complete the table with the missing acid names or formulas. Formula 1. HNO3 2. 3. H2SO3 4. H2C2H3O2 5. 6. H2S 7. 8. 9. 10. Name sulfuric acid phosphoric acid carbonic acid hypochlorous acid hydrosulfuric acid hydrofluoric acid So…let’s put this all together!! When naming or writing chemical formulas, first determine what type of compound you are dealing with: Ionic metal+non-metal/polyatomic Covalent: non-metal+non-metal Acid: formula begins with H Type of Chemical Bonds Classify the following compounds as ionic, covalent, or acids. 1. CaCl2 11. MgO 2. CO2 12. CuCl2 3. H2SO4 13. HCl 4. BaSO4 14. KI 5. K2O 15. NaOH 6. NaF 16. NO2 7. Na2CO3 17. AlPO4 8. CH4 18. FeCl3 9. SO3 19. P2O5 10. LiBr 20. N2O3 Naming Practice (all types of compounds) Name the following compounds: 1. CaCO3 2. SCl6 3. PCl5 4. CaS 5. Cu2SO3 6. K3N 7. NH4NO3 8. Al(OH)3 9. HNO3 (aq) 10. HBr (aq) 11. N2O4 12. O2 13. Mg3N2 14. NF3 15. NH3 16. H2CO3 (aq) 17. CS2 18. H2S (aq) 19. AuCl3 20. KMnO4 Write the formulas of the following compounds: 1. potassium nitrate 2. iron (III) chloride 3. acetic acid 4. nitrous acid 5. nitrogen monoxide 6. zinc phosphate 7. hydrochloric acid 8. tin (IV) chloride 9. magnesium hydride 10. nickel (II) chlorate 11. diphosphorus pentoxide 12. ferric hydroxide 13. phosphoric acid 14. strontium phosphide 15. sulfur dioxide 16. aluminum oxide 17. zinc fluoride 18. carbon dioxide 19. mercury (II) sulfate 20. sulphuric acid