File - Mrs. Franklin`s Classroom
advertisement

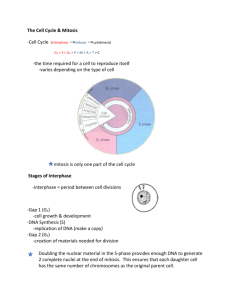
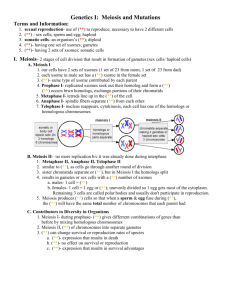
Exam Review Unit 1 & 2 UNIT 1: GENETICS Chapter 4: Meiosis and Mitosis What is the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete? How many chromosomes are found in each? Which undergo mitosis/meiosis? What are the three main stages of the cell cycle? Which stage takes the longest? List and describe the 4 main stages of mitosis. (Make sure you mention the sister chromatids, spindle fibers etc) What are the individual subunits of a nucleic acid? What are two examples of nucleic acids? What are the 4 nitrogenous bases? What is the complementary base pairing between them? What bonds are created to hold the strand of DNA together? Bonds that hold the backbone together? What is the difference between autosomal chromosomes and sex chromosomes? What are the three characteristics that enable the chromosomes to pair with one another? What information can be inferred by the karyotype? What is the difference between a haploid cell and diploid cell? List and describe all of the stages involved in meiosis? What is the purpose of meiosis? How many cells are created at the end of Meiosis I and at the end of meiosis II? How is genetic variation achieved through independent assortment, random fertilization and crossing over? Chapter 5: Mendelian Genetics What organism did Mendel use to study the patterns of inheritance? What is a true breeding organism? Know how to solve a monohybrid cross. Understand how to interpret the P and F1 generation. Know how to determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios. Know how to solve a dihybrid cross. Know how to determine the phenotypic ratios. Chapter 6: Beyond Mendelian Genetics Describe the following: codominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, epistasis, polygenic inheritance. Know how to solve genetic problems involving codominance, incomplete dominance and multiple alleles What are linked genes? How do you know if genes lie close together on a chromosome or far apart? How can the rate of crossing over enable scientists to map genes? What is sex-linked inheritance? Understand how to solve sex-linked inheritance problems. UNIT 2: EVOLUTION Chapter 7: Adaptation, Variation and Natural Selection How do mutations influence the process of evolution? How can mutations lead to variation and adaptations in a population? Do all mutations become adaptations? Explain. How to selective pressures play a role in the process of evolution? Define the following: mutation, adaptation, variation, selective advantage, selective pressure and natural selection. When is a variation considered to be a selective advantage? What is meant by the term ‘Survival of the Fittest’? How does artificial selection differ from natural selection? What is monoculture and how can it affect the variation and survival of individuals in a population? Chapter 8: Sources of Evidence for Evolution Describe how the following can be used as evidence for evolution: fossil record, transitional fossils, vestigial structures, biogeography, homologous structures, analogous structures, embryology and DNA Chapter 9: Mechanisms of Evolution What is allele frequency? Genotype frequency? How can the following factors influence the allele frequency in a population: mutations, gene flow, non-random mating, genetic drift, founders effect, bottleneck effect, natural selection (stabilizing, directional , disruptive) Explain the difference between founders effect and bottleneck effect. What are pre-zygotic and post-zygotic isolating mechanisms? Describe the following pre-zygotic isolating mechanisms: behavioural, habitat, temporal, mechanical, gametic. Describe the following post-zygotic isolating mechanisms: hybrid inviability, hybrid sterility, Hybrid breakdown. What is the difference between sympatric and allopatric speciation? Why are plants more likely to undergo sympatric speciation than animals? How did Adaptive radiation influence the finches from the Galapagos islands? Why do organisms evolve when they migrate to other areas and isolate themselves form their original population? Define the following: convergent and divergent evolution, gradualism and punctuated equilibrium.