The Cell Cycle & Mitosis
advertisement
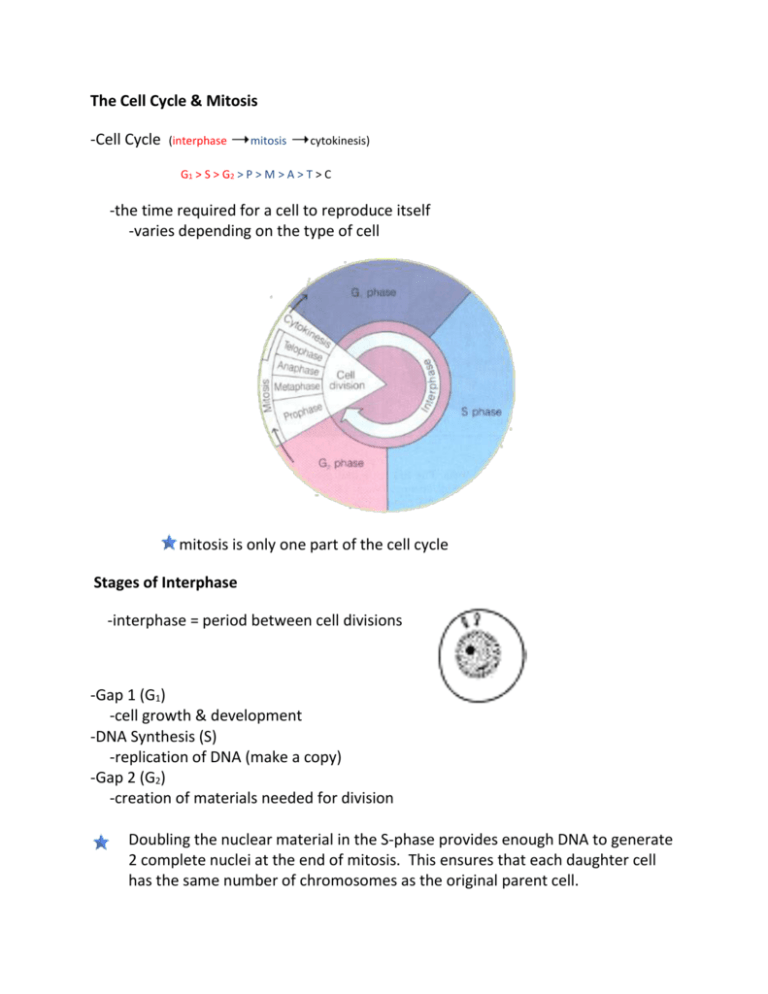
The Cell Cycle & Mitosis -Cell Cycle (interphase mitosis cytokinesis) G1 > S > G2 > P > M > A > T > C -the time required for a cell to reproduce itself -varies depending on the type of cell mitosis is only one part of the cell cycle Stages of Interphase -interphase = period between cell divisions -Gap 1 (G1) -cell growth & development -DNA Synthesis (S) -replication of DNA (make a copy) -Gap 2 (G2) -creation of materials needed for division Doubling the nuclear material in the S-phase provides enough DNA to generate 2 complete nuclei at the end of mitosis. This ensures that each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. Stages of Mitosis -mitosis = division of the nucleus -Prophase -chromosomes form -nuclear membrane breaks down -spindle forms; centrioles move REMEMBER: Mitosis makes somatic (body) cells that are diploid (46). 1 division > 2 identical daughter cells -Metaphase - chromosomes line up in the center of the cell - spindle attaches to chromosome (centromere) -Anaphase -centromeres split and chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell -Telophase -spindle breaks down -chromosomes unwind -nuclear membrane reforms telophase is essentially the opposite of prophase Methods of Splitting the Cell -cytokinesis = division of the cytoplasm Animal Cells -animal cells form a cleavage furrow -the cell membrane pinches inward a "figure-eight" shape indicates a cleavage furrow Plant Cells -plant cells form a cell plate Meiosis REMEMBER: Meiosis is a form of cell division that halves the number of chromosomes when forming specialized reproductive cells, such as gametes or spores. Meiosis makes gametes (egg/sperm) that are haploid (23). 2 divisions > 4 genetically different daughter cells = twice. Meiosis I and meiosis II is are basically the stages of mitosis Meiosis is an important process that allows for rapid generation of new genetic combinations. Two mechanisms help make these new genetic combinations: Crossing-over (Prophase I only) Random Fertilization (one egg + random sperm= zygote) .











