Lesson Plan + Worksheets
advertisement
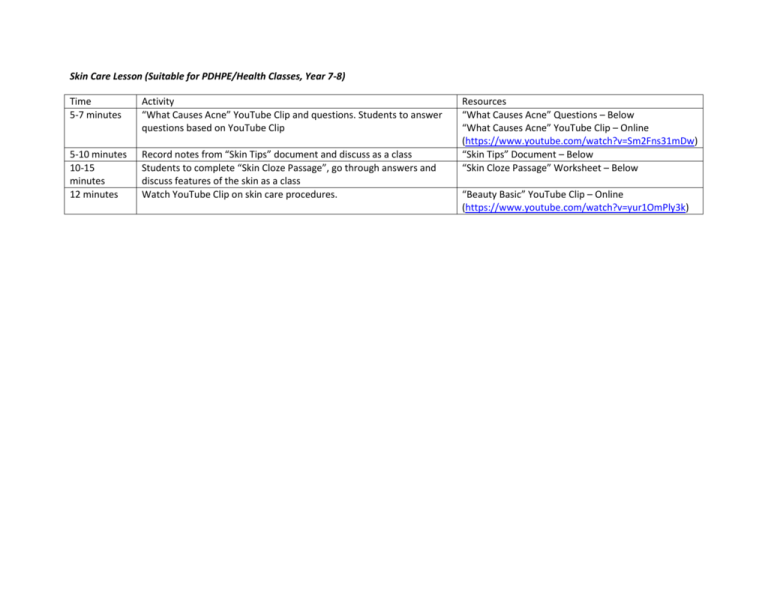
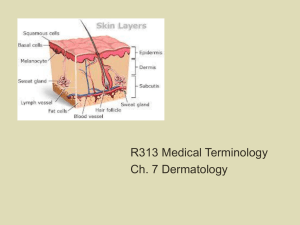
Skin Care Lesson (Suitable for PDHPE/Health Classes, Year 7-8) Time 5-7 minutes Activity “What Causes Acne” YouTube Clip and questions. Students to answer questions based on YouTube Clip 5-10 minutes 10-15 minutes 12 minutes Record notes from “Skin Tips” document and discuss as a class Students to complete “Skin Cloze Passage”, go through answers and discuss features of the skin as a class Watch YouTube Clip on skin care procedures. Resources “What Causes Acne” Questions – Below “What Causes Acne” YouTube Clip – Online (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sm2Fns31mDw) “Skin Tips” Document – Below “Skin Cloze Passage” Worksheet – Below “Beauty Basic” YouTube Clip – Online (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yur1OmPly3k) What Causes Acne Watch the video “What Causes Acne” and answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What two things does the PSU of the skin consist of? What does the sebaceous gland secrete? What is sebum’s purpose? Acne is cause by what; too much sebum or not enough sebum? What three things is the production of excess sebum caused by? What grows in the plugged follicles cause by excess sebum? What is the difference between a white head and black head pimple? What areas are commonly affected by acne? Skin Tips Skin care is important as having clear and healthy looking skin can help boost our confidence. Here are some common tips to improve or maintain the health of your skin (especially on your face): Wear sunscreen – even on a cloudy day sun can damage our skin. Wearing sunscreen protects us from the dangers of skin cancer and melanoma and also helps avoid wrinkly skin. For women a lot of make up can be purchased with a sunscreen built in e.g. tinted moisturising sunscreen. Don’t smoke! The skin is considered to be the body’s largest organ and needs a lot of blood circulating to keep it looking fresh, while non-smokers get the blood they need, smokers get toxins delivered to their skin meaning they have a dull and grey look. Get adequate rest and sleep and protect yourself from stress. Wash your face twice a day i.e. cleanse, tone, moisturise (you should also exfoliate but not as regularly, follow the instructions on your exfoliate). Don’t neglect certain areas of the skin e.g. moisturise your elbows, heels etc. Touch your face less and wash your hands more. Try to avoid squeezing pimples of touching your face too much and be sure to keep your hands clean as often you touch your face without realising. Allow your face products to do their job. For girls, keep your make up clean. If you use sponges or brushes to apply make up replace them regularly. Make up products only have a shelf life of about 6-12 months so if you haven’t used a product in that time you should throw it out. Use some products in moderation. Too much moisturising can suffocate the skin and exfoliating too much can irritate the skin and cause harm. Beware of counter girls. Salespeople at shops will try and sell you as many skin and make up products as they can. Try to keep your routine the same and if you do add a new product to your make up or skin care routine do it gradually so your skin can get used to it. BOYS! You need to take care of your skin too. Skin Cloze Passage Complete this passage by inserting the following words where you think they belong: cells, vessels, sense, pigment, top, dead, circulates, surface, epidermis, sebum, foreign, nutrients, cool, information, protection, glands, thicker, palms, temperature, looks, soles Epidermis: This layer is seen on the ................................ of the skin. It is made up of cells called keratinocytes, which are stacked on ................................ of each other, forming different sub-layers. The keratinocytes develop at the bottom and rise to the top, where they are shed from the surface as ................................ cells. Melanocytes and Langerhans ................................ are other important cells found in the epidermis, which have special functions Melanocytes are cells that produce a dark ................................ called melanin which contributes to skin colour and provides UV ................................. Dendritic “Langerhans” are cells that are involved in the epidermal immune system. They engulf ................................ material that invades the epidermis and migrate out of the skin to stimulate an immune response. Basal cells are small cells found at the bottom of the ................................. Dermis: The dermis consists mostly of connective tissue and is much ................................ than the epidermis. It is responsible for the skin's pliability and mechanical resistance and is also involved in the regulation of the body ................................. The dermis supplies the avascular epidermis with ................................ It contains ................................ organs for touch, pressure, pain and temperature. The dermis also contains blood ................................, nerve fibres, sebaceous and sweat ................................ and hair follicles. Blood Vessels are tiny pipes through which blood ................................. The blood vessels supply the skin with fresh blood, which contains nutrients and oxygen, and carry away waste products. Meissner's corpuscle are touch receptors are especially effective in detecting light touch and soft, fleeting movements. Pacinian corpuscles function as receptors for deep pressure and vibration. Free Nerve Endings are sensitive to pain, temperature changes and itchiness. Nerve Fibres forward ................................ Sebaceous Glands are small organs that secrete ................................. This oily substance is a natural moisturiser which conditions the hair and skin. Sebaceous glands are found all over the body, but they are more numerous in the scalp area and around the forehead, chin, cheeks and nose. Sweat Glands are sweat-producing structures. They are involved in thermoregulation, as they ................................ the skin by sweating. Hair Follicles are downward growths into the dermis of epidermal tissue and produce hair. They are found all over the body except on the ................................ of the hands and ................................ of the feet as well as on the lips. When the body gets cold, the hair stands upright with the help of the arrector pili muscle, closing up the skin's pores and keeping the warmth in. Arrector pili muscle is a small muscle is attached to the base of the follicle. When it is stimulated by cold or fright, it pulls the hair follicle up, causing it to stand upright. Subcutaneous layer: The subcutaneous layer below the dermis consists of loose connective tissue and much fat. It acts as a protective cushion and helps to insulate the body by monitoring heat gain and heat loss. Not all authors consider this layer a part of the skin, but it definitely has a strong impact on the way the skin ................................. Skin Cloze Passage (Teacher Version) Epidermis: This layer is seen on the surface of the skin. It is made up of cells called keratinocytes, which are stacked on top of each other, forming different sub-layers. The keratinocytes develop at the bottom and rise to the top, where they are shed from the surface as dead cells. Melanocytes and Langerhans Cells are other important cells found in the epidermis, which have special functions Melanocytes are cells that produce a dark pigment called melanin which contributes to skin colour and provides UV protection. Dendritic “Langerhans” are cells that are involved in the epidermal immune system. They engulf foreign material that invades the epidermis and migrate out of the skin to stimulate an immune response. Basal cells are small cells found at the bottom of the epidermis. Dermis: The dermis consists mostly of connective tissue and is much thicker than the epidermis. It is responsible for the skin's pliability and mechanical resistance and is also involved in the regulation of the body temperature. The dermis supplies the avascular epidermis with nutrients. It contains sense organs for touch, pressure, pain and temperature. The dermis also contains blood vessels, nerve fibres, sebaceous and sweat glands and hair follicles. Blood Vessels are tiny pipes through which blood circulates. The blood vessels supply the skin with fresh blood, which contains nutrients and oxygen, and carry away waste products. Meissner's corpuscle are touch receptors are especially effective in detecting light touch and soft, fleeting movements. Pacinian corpuscles function as receptors for deep pressure and vibration. Free Nerve Endings are sensitive to pain, temperature changes and itchiness. Nerve Fibres forward information. Sebaceous Glands are small organs that secrete sebum. This oily substance is a natural moisturiser which conditions the hair and skin. Sebaceous glands are found all over the body, but they are more numerous in the scalp area and around the forehead, chin, cheeks and nose. Sweat Glands are sweat-producing structures. They are involved in thermoregulation, as they cool the skin by sweating. Hair Follicles are downward growths into the dermis of epidermal tissue and produce hair. They are found all over the body except on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet as well as on the lips. When the body gets cold, the hair stands upright with the help of the arrector pili muscle, closing up the skin's pores and keeping the warmth in. Arrector pili muscle is a small muscle is attached to the base of the follicle. When it is stimulated by cold or fright, it pulls the hair follicle up, causing it to stand upright. Subcutaneous layer: The subcutaneous layer below the dermis consists of loose connective tissue and much fat. It acts as a protective cushion and helps to insulate the body by monitoring heat gain and heat loss. Not all authors consider this layer a part of the skin, but it definitely has a strong impact on the way the skin looks.