Dermatology Course Aim: to train the candidate so that he can
advertisement

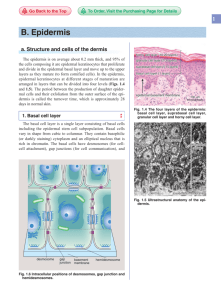
Dermatology Course Aim: to train the candidate so that he can diagnose and treat common skin affections STRUCURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN PROF. HAYDER AL-HAMAMY • Three Major Layers—Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis: – Epidermis: major permeability barrier, innate immune function, adhesion, ultraviolet protection. – Dermis: major structural element, three types of components—cellular, fibrous matrix, diffuse and filamentous matrix. Also site of vascular, lymphatic, and nerve networks. – Hypodermis (subcutis): insulation, mechanical integrity, containing the larger source vessels and nerves. • Permeability barrier Epidermis Atopic dermatitis Ectodermal dysplasias Ichthyoses Keratodermas Exfoliative dermatitis Bullous diseases Protection from pathogens Thermoregulation Sensation Epidermis Verruca vulgaris Dermis Ecthyma Cellulitis Leishmaniasis Human immunodeficiency virus Tinea pedis/corporis Epidermis Ectodermal dysplasias Dermis Raynaud HypodermisHyperthermia Epidermis Diabetic neuropathy Ultraviolet protection Wound repair/regeneration Physical appearance Dermis Leprosy HypodermisPruritus Postherpetic neuralgia Epidermis Xeroderma pigmentosum Oculocutaneous albinism Epidermis Keloid Dermis Venous stasis ulcer Pyoderma gangrenosum Epidermis Melasma Dermis Vitiligo HypodermisScleroderma Lipodystrophy Epidermis major cells: Keratinocytes other cells: melanocytes, Langerhans’ cells, Merkel’s cells Basal layer: columnar cells dividing cells for renewal of epidermis pushes cells into the upper 3 layers to end in stratum corneum “ the major barrier of the skin” Keratin: A protein cytoskeleton of keratinocytes Spinous layer: mid-epidermis spines between the cells on light microscopy polyhedral cells progressively flatten as they move upwards contain “lamellar granules” which are secretory organelles containing lipids with large bundles of keratin fillaments Spines are desmosomes which are adhesion structures between keratinocytes bind keratinocytes, resist mechanical stress, calcium dependent Granular layer cytoplasm contains basophilic kerato-hyaline granules cornified envelope of the cell is developed Stratum corneum complete differentiation of keratinocytes, loss of the nucleus, flattened cornified cells function: mechanical protection+ barrier to water loss & permeation of soluble substances from the environment. Barrier function = protein covered cells+ extracellular lipid matrix Melanocytes derived from the neural crest dendritic cells reside in the basal layer synthesize pigment “melanin” stored in “melanosomes” organelles then transferred to neighboring keratinocytes Merkel’s cells slow adapting mechanoreceptors located at sites of high-tactile sensitivity in between keratinocytes contain neuro-secretory granules Langerhans’ cells dendritic cells antigen processing & presenting cells mostly suprabasal in position convoluted nucleus pale staining cytoplasm containing charecterstic rod or racket-shaped structures called “ Birbeck granule” Dermo-epidermal junction 3 major parts 1- lamina lucida – hemidesmosomes ‘half desmosomes’+plasma membrane of the keratinocytes 2- lamina densa – basal lamina – type IV collagen 3- sublamina densa – anchoring fibrils type VII collagen Dermis connective tissue element of the skin 2 major regions 1- papillary dermis; upper, rete ridges, mechanical support & nutrition to the epidermis 2- reticular dermis deeper Fibrous matrix 1- collagen fibers major bulk of the dermis ‘75% of dry weight of dermis’ tensile strength & elasticity banded periodically 2- elastic fibers complex mesh assembelled into a contineuos network Cellular component fibroblasts: mesenchymally derived cells responsible for the synthesis & degredation of fibrous & diffuse matrix monocytes & macrophages defense system mast cells dermal dendritic cells Diffuse matrix glycosaminoglycans & proteoglycans form the ground substance in which fibers are embedded & holds water Nerves one million nerve fibers myelinated & non-myelinated freenreve endings- heat & pain mechanoreceptors pacinian& Meissners corpuscles itch receptors Sweat glands 1- eccrine sweat glands at the dermoepidermal junction with their ducts empty to the skin surface 2- apocrine sweat glands connected to the hair follicle Pilosebaceous follicle