Heck: Chapter 5 tests: Ancient Greece
advertisement

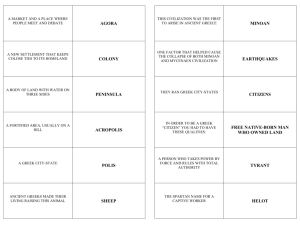
Heck: Chapter 5 tests: Ancient Greece Minoan Be able to locate on a map Minoan civilization was located on the island of Crete The Minoans did not need to build walls around their cities because of their strong navy discouraged invaders 1. The two Aegean civilizations that preceded the Greeks were the Minoans and the Mycenaean’s. Greece Olympics - The purpose of the Olympic games were to honor Zeus Map locations: Athens, Greece, Sparta, location of the Trojan War, Crete, Minoan civilization. Transportation and communications were difficult in Greece because of the rugged mountainous terrain Greek mythology: the Greek gods and goddesses all had human qualities and unique personalities 1. Sparta Sparta was founded by descendants of the Dorians Spartan society was noted for their emphasis on military and athletic ability Spartan boys were trained to be soldiers Helots : Member of the lowest class in Sparta constituting a body of serfs who were bound to the land and were owned by the state. Spartans used force to control the helots because they outnumbered the Spartans 20-1. Spartans paid a high price for their fantastic army Men were allowed to retire from military when they reached 60 years old Very little art, literature, philosophy, and science was created Spartan citizens gave up their individual freedoms Spartan women 1. Married much later than most Greek women 2. Greater personal and political rights than most Greek women 3. Trained in gymnastics, wrestling, and boxing Won the Peloponnesian War by joining forces with Persia 2. Homer Greek bard Wrote the Illiad and the Odyssey The Odyssey tells the story of the 10 year journey of a Mycenaean king to his homeland The Iliad tells the story of the Trojan War 3. City States: Agora: the public square where meetings took place Allowed male citizens to participate in politics Heck: Chapter 5 tests: Ancient Greece Pericles believes that the essence of a city’s survival is the participation of citizens in government. Polis: means city-state Tyrants are different from other leaders in that a tyrant seizes power illegally Phalanx is a type of military formation 4. Athens Established a direct democracy under the rule of Cleisthenes Believed in spending money on public buildings Older Athenian boys were taught by Sophists: (Sophists were teachers who specialized in using the tools of philosophy and rhetoric for the purpose of teaching arete—excellence, or virtue—predominantly to young statesmen and nobility) Golden Age Pericles (ruler from 461-429 BC) was the leader during this age Angered other members of the Delian League by using the league money to benefit Athens The greatest achievements in the arts and sciences are produced during the golden age Pericles believed that the essence of a city’s survival is to ensure a citizen’s participation in government. Elections Citizens preferred lotteries over elections because they believed that elections could be corrupted by the wealthy or powerful Draco introduced the first Athenian written law code. The Athenian ruler, Solon outlawed slavery due to debt WARS 1. Persian Wars A major factor in Greece’s victories was due to the cooperation of the independent Greek city states Spartan land powers and Athenian sea powers were equally important in turning back the Persians 1. The Persians in Salamis Straits were defeated by Athenian navy After the Persian wars, Greece was dominated by Athens. Peloponnesian War Conflict between Sparta and Athens After this war, Greece was in ruins During the war, more than 1/3 of the Athenians, including Pericles, died from a plague. Sparta won after they joined forces with Persia 2. The Battle of Thermopylae: Named after the narrow mountain pass where the battle occurred.