Chapter 16 Common Exam Questions
advertisement
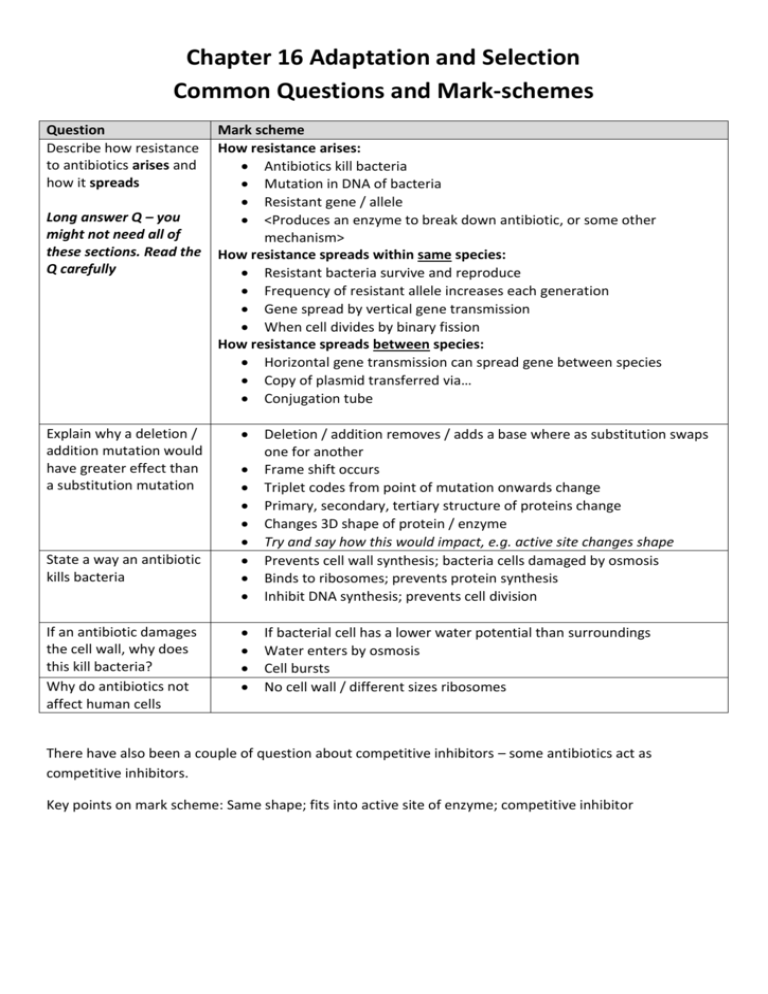
Chapter 16 Adaptation and Selection Common Questions and Mark-schemes Question Describe how resistance to antibiotics arises and how it spreads Long answer Q – you might not need all of these sections. Read the Q carefully Explain why a deletion / addition mutation would have greater effect than a substitution mutation State a way an antibiotic kills bacteria If an antibiotic damages the cell wall, why does this kill bacteria? Why do antibiotics not affect human cells Mark scheme How resistance arises: Antibiotics kill bacteria Mutation in DNA of bacteria Resistant gene / allele <Produces an enzyme to break down antibiotic, or some other mechanism> How resistance spreads within same species: Resistant bacteria survive and reproduce Frequency of resistant allele increases each generation Gene spread by vertical gene transmission When cell divides by binary fission How resistance spreads between species: Horizontal gene transmission can spread gene between species Copy of plasmid transferred via… Conjugation tube Deletion / addition removes / adds a base where as substitution swaps one for another Frame shift occurs Triplet codes from point of mutation onwards change Primary, secondary, tertiary structure of proteins change Changes 3D shape of protein / enzyme Try and say how this would impact, e.g. active site changes shape Prevents cell wall synthesis; bacteria cells damaged by osmosis Binds to ribosomes; prevents protein synthesis Inhibit DNA synthesis; prevents cell division If bacterial cell has a lower water potential than surroundings Water enters by osmosis Cell bursts No cell wall / different sizes ribosomes There have also been a couple of question about competitive inhibitors – some antibiotics act as competitive inhibitors. Key points on mark scheme: Same shape; fits into active site of enzyme; competitive inhibitor